You can translate the content of this page by selecting a language in the select box.
The AWS Certified Machine Learning Specialty validates expertise in building, training, tuning, and deploying machine learning (ML) models on AWS.
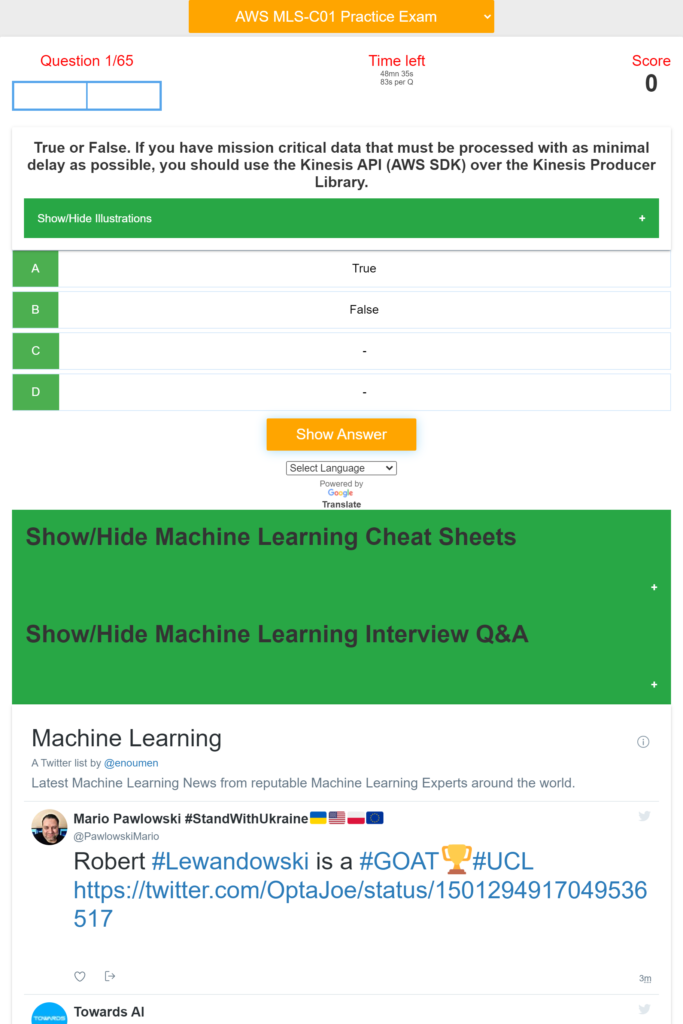
Use this App to learn about Machine Learning on AWS and prepare for the AWS Machine Learning Specialty Certification MLS-C01.
Download AWS machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on iOs
Download AWS Machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on Android/Web/Amazon
[appbox appstore 1611045854-iphone screenshots]
[appbox microsoftstore 9n8rl80hvm4t-mobile screenshots]

Download AWS machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on iOs
Download AWS Machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on Android/Web/Amazon
The App provides hundreds of quizzes and practice exam about:
– Machine Learning Operation on AWS
– Modelling
– Data Engineering
– Computer Vision,
– Exploratory Data Analysis,
– ML implementation & Operations
– Machine Learning Basics Questions and Answers
– Machine Learning Advanced Questions and Answers
– Scorecard
– Countdown timer
– Machine Learning Cheat Sheets
– Machine Learning Interview Questions and Answers
– Machine Learning Latest News
The App covers Machine Learning Basics and Advanced topics including: NLP, Computer Vision, Python, linear regression, logistic regression, Sampling, dataset, statistical interaction, selection bias, non-Gaussian distribution, bias-variance trade-off, Normal Distribution, correlation and covariance, Point Estimates and Confidence Interval, A/B Testing, p-value, statistical power of sensitivity, over-fitting and under-fitting, regularization, Law of Large Numbers, Confounding Variables, Survivorship Bias, univariate, bivariate and multivariate, Resampling, ROC curve, TF/IDF vectorization, Cluster Sampling, etc.
Domain 1: Data Engineering
Create data repositories for machine learning.
Identify data sources (e.g., content and location, primary sources such as user data)
Determine storage mediums (e.g., DB, Data Lake, S3, EFS, EBS)
Identify and implement a data ingestion solution.
Data job styles/types (batch load, streaming)
Data ingestion pipelines (Batch-based ML workloads and streaming-based ML workloads), etc.
Domain 2: Exploratory Data Analysis
Sanitize and prepare data for modeling.
Perform feature engineering.
Analyze and visualize data for machine learning.
Domain 3: Modeling
Frame business problems as machine learning problems.
Select the appropriate model(s) for a given machine learning problem.
Train machine learning models.
Perform hyperparameter optimization.
Evaluate machine learning models.
Domain 4: Machine Learning Implementation and Operations
Build machine learning solutions for performance, availability, scalability, resiliency, and fault
tolerance.
Recommend and implement the appropriate machine learning services and features for a given
problem.
Apply basic AWS security practices to machine learning solutions.
Deploy and operationalize machine learning solutions.
Machine Learning Services covered:
Amazon Comprehend
AWS Deep Learning AMIs (DLAMI)
AWS DeepLens
Amazon Forecast
Amazon Fraud Detector
Amazon Lex
Amazon Polly
Amazon Rekognition
Amazon SageMaker
Amazon Textract
Amazon Transcribe
Amazon Translate
Other Services and topics covered are:
Ingestion/Collection
Processing/ETL
Data analysis/visualization
Model training
Model deployment/inference
Operational
AWS ML application services
Language relevant to ML (for example, Python, Java, Scala, R, SQL)
Notebooks and integrated development environments (IDEs),
S3, SageMaker, Kinesis, Lake Formation, Athena, Kibana, Redshift, Textract, EMR, Glue, SageMaker, CSV, JSON, IMG, parquet or databases, Amazon Athena
Amazon EC2, Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR), Amazon Elastic Container Service, Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service , Amazon Redshift
Important: To succeed with the real exam, do not memorize the answers in this app. It is very important that you understand why a question is right or wrong and the concepts behind it by carefully reading the reference documents in the answers.
Note and disclaimer: We are not affiliated with Microsoft or Azure or Google or Amazon. The questions are put together based on the certification study guide and materials available online. The questions in this app should help you pass the exam but it is not guaranteed. We are not responsible for any exam you did not pass.
Download AWS machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on iOs
Download AWS Machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on Android/Web/Amazon
- [D] Does it make sense to talk about the probabilities of models?by /u/bouncyprojector (Machine Learning) on April 27, 2024 at 1:06 am
https://lunaverus.com/programLikelihoods There is a neat way to frame unsupervised learning as likelihood maximization, but not in the usual way where you just compute the likelihood of the data using a model and ignore the likelihood of the model itself. Rather, this is the combined likelihood of model and data... Does it make sense to talk about the probabilities of ML models? submitted by /u/bouncyprojector [link] [comments]
- [D] How can healthcare management improve?by /u/Acceptable_Smoke_235 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 9:06 pm
I have been thinking about this question lately: How can healthcare management enhance the implementation and research of machine learning in healthcare? I am really interested in the perspective of people in the field of machine learning. I have seen many threads on this sub about health being the hardest sector for starting a machine learning carreer. I really want to know why this is the case, and where it could improve. submitted by /u/Acceptable_Smoke_235 [link] [comments]
- Databricks DBRX is now available in Amazon SageMaker JumpStartby Shikhar Kwatra (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 26, 2024 at 7:52 pm
Today, we are excited to announce that the DBRX model, an open, general-purpose large language model (LLM) developed by Databricks, is available for customers through Amazon SageMaker JumpStart to deploy with one click for running inference. The DBRX LLM employs a fine-grained mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture, pre-trained on 12 trillion tokens of carefully curated data and
- [P] Source code for EURISKO and Automated Mathematician (AM) found in public archivesby /u/SeawaterFlows (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 7:43 pm
Blog post: https://white-flame.com/am-eurisko.html EURISKO: https://github.com/white-flame/eurisko Running EURISKO in Medley Interlisp: https://github.com/seveno4/EURISKO Automated Mathematician (AM): https://github.com/white-flame/am submitted by /u/SeawaterFlows [link] [comments]
- Knowledge Bases in Amazon Bedrock now simplifies asking questions on a single documentby Suman Debnath (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 26, 2024 at 7:12 pm
At AWS re:Invent 2023, we announced the general availability of Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock. With Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock, you can securely connect foundation models (FMs) in Amazon Bedrock to your company data for fully managed Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). In previous posts, we covered new capabilities like hybrid search support, metadata filtering
- Open-Sourced: Automated Data Sorting Tools [P]by /u/Kilroy_GreyFox (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 5:29 pm
Hello r/MachineLearning, I'm excited to share a project that was initially intended to integrate automated AI maintenance features for Windows into an application I was building to sell commercially, but has now been open-sourced for community use and development. The project focuses on automated data sorting and could serve as a base for more advanced machine learning applications. You can explore the project here: [NazTech Automated Data Sorting Tools](https://github.com/nazpins/naztech-automated-data-sorting-tools) These tools are designed to quickly automate sorting large data dumps, employing python algorithms suitable for handling large datasets. While the project is no longer in active development from my end, the python scripts are functional and open for any adaptations or enhancements you might find interesting for your own ML projects. I started building the framework for the actual application but due to time constraints and a lot going on irl, I haven't had time to continue working on it. I am happy however to share these tools with the community and hopefully they can be beneficial to someone else down the road. Cheers! submitted by /u/Kilroy_GreyFox [link] [comments]
- [D]What Nomenclature do you follow for naming ML Models?by /u/BravoZero6 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 4:42 pm
Hi All, I am brainstorming some kind of a nomenclature for our team so that theres a standard way of naming ML models like their pickle files . Any inputs will be appreciated. thanks submitted by /u/BravoZero6 [link] [comments]
- [D] Advice Needed: Enhancing NER for ADE Detection in Clinical Texts (Thesis Work)by /u/Popsuga (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 4:29 pm
Hi r/MachineLearning community, I'm currently working on the second part of my thesis focused on Named Entity Recognition (NER) for detecting Adverse Drug Events (ADE) in clinical texts. In my first thesis project, I tried to replicate a paper but had to pivot to the n2c2 dataset, which led to challenges in model performance. I've fine-tuned a DeBERTa model with standard practices, but I'm struggling with achieving high accuracy, particularly with precision and recall. This is my first deep dive into a thesis and the world of NLP, and any guidance would be immensely appreciated. Also, any common pitfalls for thesis work or useful resources on this topic would be extremely helpful. I'm eager to learn from the community and improve my research. Thank you so much for your time! submitted by /u/Popsuga [link] [comments]
- [R]Large language models may not be able to sample behavioral probability distributionsby /u/GYX-001 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 4:11 pm
Through our experiments, we found that LLM agents have a certain ability to understand probability distributions, the LLM agent's sampling ability for probability distributions is lacking and it is difficult to give a behavior sequence that conforms to a certain probability distribution through LLMs alone. We are looking forward to your thoughts, critiques, and discussions on this topic. Full Paper & Citation: You can access the full paper https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.09043. Please cite our work if it contributes to your research. https://preview.redd.it/ai7uks7nluwc1.png?width=935&format=png&auto=webp&s=891dd57ef50d1ee99b1a8b2372b9a460397754d6 submitted by /u/GYX-001 [link] [comments]
- [D] GAN/Adversary Autoencoder/Cycle GANby /u/investmentwholesome (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 4:09 pm
Main aim: Style transfer between two discrete timeseries signals. Here are the details: Dataset: Discrete time series. 1700 rows, with 97 percent of it with zeroes. Cannot remove these zeroes as it means something. Values ranging from 0-32 for one of the features in Domain A needs to translated to another feature with same range in domain B. Another feature from 0-5000 from domain A, translated to a different domain B with same range. I can recreate the same dataset multiple times with small variations, so we can have larger datasets. I would create sequences of size 20 or 30 and batch: 32 or 64 initially. Generator Network: A simple encoder with linear layer first hidden size:16 , relu, 2nd linear layer :8 and relu again . A symmetric Decoder . Discriminator: 2 linear layers with hidden size 8 and leaky Relu between them. And sigmoid as final layer. Loss function : BCEloss . Also experimented BCE + MSE loss for generator. Training: I'm using pytorch. Only trained with one feature/signal and tried to generate this feature from noise. Didn't move to cycle consistency yet. With the small dataset training, the discriminator becomes too strong, I even tried to set reduce the learning rate for discriminator as 0.0001 and generator as 0.01 , it didn't work. Tried to add/complicate the layer of generator, still didn't work. Tried to train discriminator every 10th epoch, while the generator trained more. Didn't work. Also tried to normalize the data. I want to explore Adversarial autoencoder /cycle Gan , but the generator is unable to learn anything with vanilla GAN as well. Can someone help or give me some ideas on what I can do ? Thanks submitted by /u/investmentwholesome [link] [comments]
- GPU out of memory error message on Colab with Llama 3 [D]by /u/ReputationMindless32 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 3:43 pm
Hi guys, I just tried to run Llama 3 on my Colab(free version) and seems that I ran out of the memory: OutOfMemoryError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 32.00 MiB. GPU 0 has a total capacity of 14.75 GiB of which 9.06 MiB is free. Process 8863 has 14.74 GiB memory in use. Of the allocated memory 14.60 GiB is allocated by PyTorch, and 22.06 MiB is reserved by PyTorch but unallocated. If reserved but unallocated memory is large try setting PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF=expandable_segments:True to avoid fragmentation. See documentation for Memory Management (https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/cuda.html#environment-variables) Anyone have the same experience? Has anyone managed to run Llama 3 on free version of Colab (or similar platform)? Thanks! submitted by /u/ReputationMindless32 [link] [comments]
- [D] Overwhelming LLM release rate: Seeking suggestions for building a test set to evaluate LLMsby /u/Distinct-Target7503 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 2:43 pm
Hi everyone, I'm trying to build my own test set in order to make an initial fast evaluation of the huge number of models that pop up on huggingface.co every week, and I'm searching for a starting point or suggestions. If someone would share some questions that they use to test LLM abilities, even as high-level concepts, or simply give me some tips or suggestions, I would really appreciate that! Thanks in advance to everyone for any kind of reply." submitted by /u/Distinct-Target7503 [link] [comments]
- [R] Reinforcement Learning via Regressing Relative Rewardsby /u/athens117 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 1:10 pm
https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.16767 New deep RL algorithm that works with both language models and diffusion models. submitted by /u/athens117 [link] [comments]
- [D] Clean caption datasetby /u/themathstudent (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 11:09 am
I am attempting to train CLIP from scratch. However, there is a lack of available datasets. The one dataset that seemed quite diverse and clean seems to be taken down (laion-400m). Looking at HF datasets, these are the two datasets that are promising, but wondering if there has been anything better/ cleaner. - conceptual captions: uses alt-text. - red_caps: reddit threads, but these are mostly the first comment on the image than an actual caption. TIA submitted by /u/themathstudent [link] [comments]
- [D] LLMs: Why does in-context learning work? What exactly is happening from a technical perspective?by /u/synthphreak (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 11:01 am
Everywhere I look for the answer to this question, the responses do little more than anthropomorphize the model. They invariably make claims like: Without examples, the model must infer context and rely on its knowledge to deduce what is expected. This could lead to misunderstandings. One-shot prompting reduces this cognitive load by offering a specific example, helping to anchor the model's interpretation and focus on a narrower task with clearer expectations. The example serves as a reference or hint for the model, helping it understand the type of response you are seeking and triggering memories of similar instances during training. Providing an example allows the model to identify a pattern or structure to replicate. It establishes a cue for the model to align with, reducing the guesswork inherent in zero-shot scenarios. These are real excerpts, btw. But these models don’t “understand” anything. They don’t “deduce”, or “interpret”, or “focus”, or “remember training”, or “make guesses”, or have literal “cognitive load”. They are just statistical token generators. Therefore pop-sci explanations like these are kind of meaningless when seeking a concrete understanding of the exact mechanism by which in-context learning improves accuracy. Can someone offer an explanation that explains things in terms of the actual model architecture/mechanisms and how the provision of additional context leads to better output? I can “talk the talk”, so spare no technical detail please. I could make an educated guess - Including examples in the input which use tokens that approximate the kind of output you want leads the attention mechanism and final dense layer to weight more highly tokens which are similar in some way to these examples, increasing the odds that these desired tokens will be sampled at the end of each forward pass; like fundamentally I’d guess it’s a similarity/distance thing, where explicitly exemplifying the output I want increases the odds that the output get will be similar to it - but I’d prefer to hear it from someone else with deep knowledge of these models and mechanisms. submitted by /u/synthphreak [link] [comments]
- [D] Critical batch size and LLMsby /u/kiockete (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 9:21 am
In a video about "A little guide to building Large Language Models in 2024" at 41:38 the author starts to talk about the limits of how big the batch size can be. Well, if you start to have a very large batch size, the model for each optimization step makes less efficient use of each token, because the batch size is so big that each token is kind of washed out in the optimization step. And roughly, it's a little bit hard to measure this limit, which we call the critical batch size. I thought that the bigger batch size is always better for training LLMs, because: It better approximates the true gradient. We go through the dataset faster. To my knowledge the limits are only infrastructure, hardware, communication overhead etc. I found a paper that introduces the "critical batch size" concept - An Empirical Model of Large-Batch Training. It mostly talks about the speed/efficiency tradeoff for data parallelism of large batch sizes. Also another highly cited paper Scaling Laws for Neural Language Models: Training at the critical batch size provides a roughly optimal compromise between time and compute efficiency So I don't really understand what author of the video meant by saying: each token is kind of washed out in the optimization step Are there any other issues with large batch sizes other than infrastructure, hardware or implementation limits? submitted by /u/kiockete [link] [comments]
- [Discussion] Time series regression problem?by /u/seboz12345 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 9:21 am
Hi guys,I have a problem for which I am not sure what would be the best approach (and I cannot really find any relevant literature).I have a small dataset (~100 measurements like the one attached) of a sensor value, for which I want to predict a certain relevant event. Here t_0 is the relevant moment in time which I want to predict. The problem is, that I need to trigger something when the event is reached. If I need too long to trigger after it was reached, it will not be a positive outcome.My initial idea was to basically chunk the time series before the event, and try to predict the remaining time from that segment until the event is reached. When it is below a threshold, I can trigger my action. I wanted to have a look at e.g. XGBoost and feed it small chunks of the timeseries and run this process continuously. I am not really sure if that is the correct approach there.Is that a known problem? What would be a good name for this problem to search for literature? Do you have suggestions how to solve it? Thanks. https://preview.redd.it/l59gsmswkswc1.png?width=1303&format=png&auto=webp&s=f9e83d7b87ce5227378de6a0805a916fd4f93314 submitted by /u/seboz12345 [link] [comments]
- [D] What is the State of Art for text to speech synthesis?by /u/Zelun (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 4:24 am
I'm starting to do some research for my graduation and I'm looking for some papers on text to speech synthesis. I'm doing some reproductions on a paper I found to be interesting called Natural TTS Synthesis by Conditioning WaveNet on Mel Spectrogram Prediction. Basically it's a model that receives text, turns it into a spectogram and the spectogram is used to build the audio file. Since I'm still at the start of reproduction, are there papers that you guys would recommend looking into? Did you work with speech synthesis (TTS)? What are good refferences I should look into? I saw this post over here https://www.reddit.com/r/MachineLearning/comments/nxkuvn/d_what_is_actually_the_state_of_the_art_in_text/ But it already has 3 years. Maybe there is something newer than FastSpeech2? submitted by /u/Zelun [link] [comments]
- [D] Meta-learning vs Federated Learning?by /u/Tight_Confusion_1695 (Machine Learning) on April 26, 2024 at 3:53 am
[D] Hey everyone, do you have any suggestions on what's the better option and the most effective way to dive into a hot topic these days? I stumbled upon a repository for Federated Learning at: https://github.com/muditbhargava66/dropgrad https://github.com/adap/flower But can't seem to find anything similar for Meta Learning. Any advice on how to pick my PhD topic would be greatly appreciated! submitted by /u/Tight_Confusion_1695 [link] [comments]
- [P] Multihead Mixture of Experts - Implementation of dense subtoken routing suggested in https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.15045by /u/Prudent_Student2839 (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 10:00 pm
My friend implemented the method of Multihead Mixture of Experts in this arxiv paper https://arxiv.org/pdf/2404.15045 and he wanted me to share it with you! https://github.com/lhallee/Multi_Head_Mixture_of_Experts__MH-MOE Try it out. Let me know what you think and I will pass it on to him. submitted by /u/Prudent_Student2839 [link] [comments]
- [D] HyenaDNA and Mamba are not good at sequential labelling ?by /u/blooming17 (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 8:02 pm
Hello guys, I've been working on a sequential labelling using DNA sequences as inputs. Lately there have been 2 foundation models released HyenaDNA (Based on Hyena operator) and Caduceus (based on mamba), I used both pretrained and from scratch models and performances are terrible even with pretrained ones. Does anyone have experience with this type of models, and what are the potential causes for performance drop ? I am literally getting zero performance for the minority class ? Does mamba deal poorly with class imbalance ? submitted by /u/blooming17 [link] [comments]
- [P] Drug toxicity prediction model with graph-based neural networksby /u/Soroush_ra (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 7:10 pm
This is a small drug toxicity prediction GNN model I wrote/trained repo: https://github.com/Null-byte-00/toxicity-prediction-gnn submitted by /u/Soroush_ra [link] [comments]
- [D] What are your horror stories from being tasked impossible ML problemsby /u/LanchestersLaw (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 6:45 pm
ML is very good at solving a niche set of problems, but most of the technical nuances are lost on tech bros and managers. What are some problems you have been told to solve which would be impossible (no data, useless data, unrealistic expectations) or a misapplication of ML (can you have this LLM do all of out accounting). submitted by /u/LanchestersLaw [link] [comments]
- [P] Dreamboothing MusicGenby /u/Sufficient-Tennis189 (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 5:43 pm
Dreambooth the MusicGen model suite on small consumer GPUs, in a matter of minutes, using this repository: https://github.com/ylacombe/musicgen-dreamboothing The aim of this project is to provide tools to easily fine-tune and dreambooth the MusicGen model suite, with little data and to leverage a series of optimizations and tricks to reduce resource consumption, thanks to LoRA adaptors. For example, the model can be fine-tuned on a particular music genre or artist to give a checkpoint that generates in that given style. The aim is also to easily share and build on these trained checkpoints, Specifically, this involves: using as few data and resources as possible. We're talking fine-tuning with as little as 15mn on an A100 and as little as 10GB to 16GB of GPU utilization. easily share and build models thanks to the Hugging Face Hub. optionally, generate automatic music descriptions optionally, training MusicGen in a Dreambooth-like fashion, where one key-word triggers generation in a particular style Wandb example of what the training run looks like here. submitted by /u/Sufficient-Tennis189 [link] [comments]
- Deploy a Hugging Face (PyAnnote) speaker diarization model on Amazon SageMaker as an asynchronous endpointby Sanjay Tiwary (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 25, 2024 at 5:03 pm
Speaker diarization, an essential process in audio analysis, segments an audio file based on speaker identity. This post delves into integrating Hugging Face’s PyAnnote for speaker diarization with Amazon SageMaker asynchronous endpoints. We provide a comprehensive guide on how to deploy speaker segmentation and clustering solutions using SageMaker on the AWS Cloud.
- Evaluate the text summarization capabilities of LLMs for enhanced decision-making on AWSby Dinesh Subramani (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 25, 2024 at 4:25 pm
Organizations across industries are using automatic text summarization to more efficiently handle vast amounts of information and make better decisions. In the financial sector, investment banks condense earnings reports down to key takeaways to rapidly analyze quarterly performance. Media companies use summarization to monitor news and social media so journalists can quickly write stories on
- [D] Old Paper - Troubling Trends in Machine Learning Scholarshipby /u/pyepyepie (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 3:50 pm
I just wanted to remind or introduce newcomers to this paper. I think this discussion should be re-opened since many people here actually do influence the trends of the field. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.03341 On a personal note (feel free to skip): Specifically, I want to point out the issue of "Mathiness", as it seems like this problem got way out of hand and most best papers of conferences suffer from it (one of the most important ML papers tried to be mathy and introduced a big mistake, I believe other papers have bigger issues but no one bothers to check it). So here are my personal points to academics and researchers: We (I think most will relate), practitioners, do not need equations to know what recall is and clearly don't want to read difficult-to-understand versions of what linear regression is, it just makes your paper unuseful. If you don't want to waste our time, please put it in the appendix or completely remove it. Reviewers, please don't get impressed by unnecessary math, if it's complicated and does nothing useful, who cares? Also, it might be flawed anyway and you will probably not catch it. submitted by /u/pyepyepie [link] [comments]
- [D] UAI-2024 results waiting areaby /u/PaganPasta (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 3:38 pm
Following the review phase(old post), creating a thread for others like me waiting for the decision. All the best! submitted by /u/PaganPasta [link] [comments]
- [D] Why transformers are not trained layer-wise?by /u/kiockete (Machine Learning) on April 25, 2024 at 2:16 pm
It seems to me that thanks to the residual path the gradient that flows to each layer is the same regardless of the transformer layer/block. Example: ProjectionAndCost(X + L1(X) + L2(X + L1(X)) + L3(X + L1(X) + L2(X + L1(X))) ...) Since the input to ProjectionAndCost is just sum of outputs from all layers and initial embeddings then the gradient that comes to the layer L1 is the same as the gradient that comes to L2 or L3. So we could: first train only L1: ProjectionAndCost(X + L1(X)) freeze L1, include L2 and train: ProjectionAndCost(X + L1(X) + L2(X + L1(X))) freeze L1 and L2, include L3 and train: ProjectionAndCost(X + L1(X) + L2(X + L1(X)) + L3(X + L1(X) + L2(X + L1(X)))) .. and so on We can't train first L2 then L1, because the input to L2 depends on L1, but we could train lower layers first then gradually add and train deeper layers. Is there any problem with that approach? submitted by /u/kiockete [link] [comments]
- Enhance conversational AI with advanced routing techniques with Amazon Bedrockby Ameer Hakme (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 24, 2024 at 4:30 pm
Conversational artificial intelligence (AI) assistants are engineered to provide precise, real-time responses through intelligent routing of queries to the most suitable AI functions. With AWS generative AI services like Amazon Bedrock, developers can create systems that expertly manage and respond to user requests. Amazon Bedrock is a fully managed service that offers a choice of
- Improve LLM performance with human and AI feedback on Amazon SageMaker for Amazon Engineeringby Yunfei Bai (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 24, 2024 at 4:27 pm
The Amazon EU Design and Construction (Amazon D&C) team is the engineering team designing and constructing Amazon warehouses. The team navigates a large volume of documents and locates the right information to make sure the warehouse design meets the highest standards. In the post A generative AI-powered solution on Amazon SageMaker to help Amazon EU
- Improve accuracy of Amazon Rekognition Face Search with user vectorsby Arik Porat (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 24, 2024 at 4:13 pm
In various industries, such as financial services, telecommunications, and healthcare, customers use a digital identity process, which usually involves several steps to verify end-users during online onboarding or step-up authentication. An example of one step that can be used is face search, which can help determine whether a new end-user’s face matches those associated with
- Accelerate ML workflows with Amazon SageMaker Studio Local Mode and Docker supportby Shweta Singh (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 23, 2024 at 7:20 pm
We are excited to announce two new capabilities in Amazon SageMaker Studio that will accelerate iterative development for machine learning (ML) practitioners: Local Mode and Docker support. ML model development often involves slow iteration cycles as developers switch between coding, training, and deployment. Each step requires waiting for remote compute resources to start up, which
- Significant new capabilities make it easier to use Amazon Bedrock to build and scale generative AI applications – and achieve impressive resultsby Swami Sivasubramanian (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 23, 2024 at 11:50 am
We introduced Amazon Bedrock to the world a little over a year ago, delivering an entirely new way to build generative artificial intelligence (AI) applications. With the broadest selection of first- and third-party foundation models (FMs) as well as user-friendly capabilities, Amazon Bedrock is the fastest and easiest way to build and scale secure generative
- Building scalable, secure, and reliable RAG applications using Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrockby Mani Khanuja (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 23, 2024 at 11:40 am
This post explores the new enterprise-grade features for Knowledge Bases on Amazon Bedrock and how they align with the AWS Well-Architected Framework. With Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrock, you can quickly build applications using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) for use cases like question answering, contextual chatbots, and personalized search.
- Integrate HyperPod clusters with Active Directory for seamless multi-user loginby Tomonori Shimomura (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 22, 2024 at 5:50 pm
Amazon SageMaker HyperPod is purpose-built to accelerate foundation model (FM) training, removing the undifferentiated heavy lifting involved in managing and optimizing a large training compute cluster. With SageMaker HyperPod, you can train FMs for weeks and months without disruption. Typically, HyperPod clusters are used by multiple users: machine learning (ML) researchers, software engineers, data scientists,
- The executive’s guide to generative AI for sustainabilityby Wafae Bakkali (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 22, 2024 at 5:40 pm
Organizations are facing ever-increasing requirements for sustainability goals alongside environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices. A Gartner, Inc. survey revealed that 87 percent of business leaders expect to increase their organization’s investment in sustainability over the next years. This post serves as a starting point for any executive seeking to navigate the intersection of generative
- [D] Simple Questions Threadby /u/AutoModerator (Machine Learning) on April 21, 2024 at 3:00 pm
Please post your questions here instead of creating a new thread. Encourage others who create new posts for questions to post here instead! Thread will stay alive until next one so keep posting after the date in the title. Thanks to everyone for answering questions in the previous thread! submitted by /u/AutoModerator [link] [comments]
- Introducing automatic training for solutions in Amazon Personalizeby Ba'Carri Johnson (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 20, 2024 at 12:38 am
Amazon Personalize is excited to announce automatic training for solutions. Solution training is fundamental to maintain the effectiveness of a model and make sure recommendations align with users’ evolving behaviors and preferences. As data patterns and trends change over time, retraining the solution with the latest relevant data enables the model to learn and adapt,
- Use Kubernetes Operators for new inference capabilities in Amazon SageMaker that reduce LLM deployment costs by 50% on averageby Rajesh Ramchander (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 19, 2024 at 4:55 pm
We are excited to announce a new version of the Amazon SageMaker Operators for Kubernetes using the AWS Controllers for Kubernetes (ACK). ACK is a framework for building Kubernetes custom controllers, where each controller communicates with an AWS service API. These controllers allow Kubernetes users to provision AWS resources like buckets, databases, or message queues
- Talk to your slide deck using multimodal foundation models hosted on Amazon Bedrock – Part 2by Archana Inapudi (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 19, 2024 at 3:15 pm
In Part 1 of this series, we presented a solution that used the Amazon Titan Multimodal Embeddings model to convert individual slides from a slide deck into embeddings. We stored the embeddings in a vector database and then used the Large Language-and-Vision Assistant (LLaVA 1.5-7b) model to generate text responses to user questions based on
- Scale AI training and inference for drug discovery through Amazon EKS and Karpenterby Matthew Welborn (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 19, 2024 at 3:07 pm
This is a guest post co-written with the leadership team of Iambic Therapeutics. Iambic Therapeutics is a drug discovery startup with a mission to create innovative AI-driven technologies to bring better medicines to cancer patients, faster. Our advanced generative and predictive artificial intelligence (AI) tools enable us to search the vast space of possible drug
- Generate customized, compliant application IaC scripts for AWS Landing Zone using Amazon Bedrockby Ebbey Thomas (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 18, 2024 at 5:57 pm
As you navigate the complexities of cloud migration, the need for a structured, secure, and compliant environment is paramount. AWS Landing Zone addresses this need by offering a standardized approach to deploying AWS resources. This makes sure your cloud foundation is built according to AWS best practices from the start. With AWS Landing Zone, you eliminate the guesswork in security configurations, resource provisioning, and account management. It’s particularly beneficial for organizations looking to scale without compromising on governance or control, providing a clear path to a robust and efficient cloud setup. In this post, we show you how to generate customized, compliant IaC scripts for AWS Landing Zone using Amazon Bedrock.
- Live Meeting Assistant with Amazon Transcribe, Amazon Bedrock, and Knowledge Bases for Amazon Bedrockby Bob Strahan (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 18, 2024 at 5:08 pm
You’ve likely experienced the challenge of taking notes during a meeting while trying to pay attention to the conversation. You’ve probably also experienced the need to quickly fact-check something that’s been said, or look up information to answer a question that’s just been asked in the call. Or maybe you have a team member that always joins meetings late, and expects you to send them a quick summary over chat to catch them up. Then there are the times that others are talking in a language that’s not your first language, and you’d love to have a live translation of what people are saying to make sure you understand correctly. And after the call is over, you usually want to capture a summary for your records, or to send to the participants, with a list of all the action items, owners, and due dates. All of this, and more, is now possible with our newest sample solution, Live Meeting Assistant (LMA).
- Meta Llama 3 models are now available in Amazon SageMaker JumpStartby Kyle Ulrich (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 18, 2024 at 4:31 pm
Today, we are excited to announce that Meta Llama 3 foundation models are available through Amazon SageMaker JumpStart to deploy and run inference. The Llama 3 models are a collection of pre-trained and fine-tuned generative text models. In this post, we walk through how to discover and deploy Llama 3 models via SageMaker JumpStart. What is
- Slack delivers native and secure generative AI powered by Amazon SageMaker JumpStartby Jackie Rocca (AWS Machine Learning Blog) on April 18, 2024 at 12:00 pm
We are excited to announce that Slack, a Salesforce company, has collaborated with Amazon SageMaker JumpStart to power Slack AI’s initial search and summarization features and provide safeguards for Slack to use large language models (LLMs) more securely. Slack worked with SageMaker JumpStart to host industry-leading third-party LLMs so that data is not shared with the infrastructure owned by third party model providers. This keeps customer data in Slack at all times and upholds the same security practices and compliance standards that customers expect from Slack itself.
Download AWS machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on iOs

Download AWS Machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on Android/Web/Amazon
A Twitter List by enoumenDownload AWS machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on iOs
Download AWS Machine Learning Specialty Exam Prep App on Android/Web/Amazon






