You can translate the content of this page by selecting a language in the select box.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023. Latest AI Trends in July 2023
Welcome to your go-to resource for all things Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)! In a world where AI is constantly redefining the realm of possibility, it’s vital to stay informed about the most recent and groundbreaking developments. That’s precisely why our July 2023 edition aims to deliver a comprehensive exploration of this month’s hottest AI trends. From cutting-edge applications in healthcare, finance, and entertainment, to breakthroughs in machine learning techniques, we’ll delve into the stories shaping the landscape of AI. Strap in and join us as we journey through the fascinating world of artificial intelligence in July 2023!
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 29th-31st, 2023
Dissolving circuit boards in water sounds better than shredding and burning;
Arizona law school embraces ChatGPT use in student applications;
Google’s RT-2 AI model brings us one step closer to WALL-E;
Android malware steals user credentials using optical character recognition;
Most of the 100 million people who signed up for Threads stopped using it;
Stability AI releases Stable Diffusion XL, its next-gen image synthesis model;
US senator blasts Microsoft for “negligent cybersecurity practices”;
OpenAI discontinues its AI writing detector due to “low rate of accuracy”;
Windows, hardware, Xbox sales are dim spots in a solid Microsoft earnings report;
Twitter commandeers @X username from man who had it since 2007;
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 28th, 2023
Free courses and guides for learning Generative AI
-
Generative AI learning path by Google Cloud. A series of 10 courses on generative AI products and technologies, from the fundamentals of Large Language Models to how to create and deploy generative AI solutions on Google Cloud [Link].
-
Generative AI short courses by DeepLearning.AI – Five short courses on generative AI including LangChain for LLM Application Development, How Diffusion Models Work and more. [Link].
-
LLM Bootcamp: A series of free lectures by The full Stack on building and deploying LLM apps [Link].
-
Building AI Products with OpenAI – a free course by CoRise in collaboration with OpenAI [Link].
-
Free Course by Activeloop on LangChain & Vector Databases in Production [Link].
-
Pinecone learning center – Lots of free guides as well as complete handbooks on LangChain, vector embeddings etc. by Pinecone [Link].
-
Build AI Apps with ChatGPT, Dall-E and GPT-4 – a free course on Scrimba [Link].
-
Gartner Experts Answer the Top Generative AI Questions for Your Enterprise – a report by Gartner [Link]
-
GPT best practices: A guide by OpenAI that shares strategies and tactics for getting better results from GPTs [Link].
-
OpenAI cookbook by OpenAI – Examples and guides for using the OpenAI API [Link].
-
Prompt injection explained, with video, slides, and a transcript from a webinar organized by LangChain [Link].
-
A detailed guide to Prompt Engineering by DAIR.AI [Link]
-
What Are Transformer Models and How Do They Work. A tutorial by Cohere AI [Link]
-
Learn Prompting: an open source course on prompt engineering[Link]
Generate SaaS Startup Ideas with ChatGPT |
| Today, we’ll tap into the potential of ChatGPT to brainstorm innovative SaaS startup ideas in the B2B sector. We’ll explore how AI can be incorporated to enhance their value propositions, and what makes these ideas compelling for investors. Each idea will come with a unique and intriguing name. |
| Here’s the prompt: |
|
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 26th, 2023
LLaMa, ChatGPT, Bard, Co-Pilot & All The Rest. How Large Language Models Will Become Huge Cloud Services With Massive Ecosystems.

Large language models (LLMs) are everywhere. They do everything. They scare everyone – or at least some of us. Now what? They will become Generative-as-a-Service (GaaS) cloud “products” in exactly the same way all “as-a-service” products and services are offered. The major cloud providers – “Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), Alibaba Cloud, Oracle Cloud, IBM Cloud (Kyndryl), Tencent Cloud, OVHcloud, DigitalOcean, and Linode (owned by Akamai)” – will all develop, partner or acquire their generative AI capabilities and offer them as services. There will also be ecosystems around all of these tools exactly the same way ecosystems exist around all of the major enterprise infrastructure and applications that power every company on the planet. Google is in the generative AI (GAI) arms race. AWS is too. IBM is of course in the race. Microsoft has the lead.
So let’s look at LLMs like they were ERP, CRM or DBMS (does anyone actually still use that acronym?) tools, and how companies make decisions about what tool to use, how to use them and how to apply them to real problems.
Are We There Yet?
No, we’re not. Will we get there? Absolutely. Timeframe? 2-3 years. The productization of LLMs/generative AI (GAI) is well underway. Access to premium/business accounts is step one. Once the dust settles on this first wave of LLMs (2022-2023), we’ll see an arms race predicated on both capabilities and cost-effectiveness. ROI-, OKR-, KPI- and CMM-documented use cases will help companies decide what to do. The use cases will spread across key functions and vertical industries. Companies anxious to understand how they can exploit GAI will turn to these metrics and the use cases to conduct internal due diligence around adoption. Once that step is completed, and there appears to be promise, next steps will be taken.
Stuart Russell is a professor of computer science at the University of California, Berkeley. He also co-authored the authoritative AI textbook: Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach that is used by over 1,500 universities.
He calculates that in 20 years AI will generate about $14 quadrillion in wealth. Much of that will of course be made long before the 20-year mark.
Of this $14 quadrillion, it is estimated that the top five AI companies will earn the following wealth:
-
Google: $1.5 quadrillion
-
Amazon: $1.1 quadrillion
-
Apple: $2.5 quadrillion
-
Microsoft: $2.0 quadrillion
-
Meta: $0.7 quadrillion
That totals almost $8 quadrillion for the five.
These five companies are estimated to pay the following percentages of their annual revenue in taxes:
-
Google: 17-20%
-
Amazon: 13-15%
-
Microsoft: 18-22%
-
Apple: 20-25%
-
Meta: 15-18%
The 35% 2016 corporate tax rate was lowered to 21%. The AI top five are indeed doing well on taxes.
Let’s consider the above relative to the predicted loss of 3 million to 5 million jobs in the United States during the next 20 years. Re-employing those Americans has been estimated to cost from $60 billion (3 million people) to $100 billion (5 million people).
The question before us does not concern AI alignment. It is more about how well we Americans align with our values. Do our values align more with those three to five million people who will lose their jobs to AI, do they align more with the five top AI companies continuing to pay about 21% in taxes rather than the 35% they paid in 2016, or is there some fair and caring middle ground?
We may want to have those top five AI companies pay the full cost re-employing those three to five million Americans. To them it would hardly be a burdensome expense. Does that sound fair?
Edit 2am ET, 7/26/23:
Seems that 3 to 5 million figure is probably wildly incorrect. Sorry about that. This following estimate of 300 million worldwide over 20 years seem much more reasonable:
Microsoft reports $20.1B quarterly profit as it promises to lead “the new AI platform shift”
Microsoft on Tuesday reported fiscal fourth-quarter profit of $20.1 billion, or $2.69 per share, beating analyst expectations for $2.55 per share.
It posted revenue of $56.2 billion in the April-June period, up 8% from last year. Analysts had been looking for revenue of $55.49 billion, according to FactSet Research.
CEO Satya Nadella said the company remains focused on “leading the new AI platform shift.”
Where do ChatGPT and other LLMs get the linguistic capacity to identify as an AI and distinguish themselves from others?
ChatGPT and other large language models (LLMs) like it are not conscious entities, and they don’t have personal identities or self-awareness. When ChatGPT “identifies” itself as an AI, it’s based on the patterns and rules it learned during its training.
These models are trained on vast amounts of text data, which includes a lot of language about AI. Thus, when given prompts that suggest it is an AI or that ask it about its nature, it produces responses that are based on the patterns it learned, which include acknowledging it is an AI.
Furthermore, when these AI models distinguish themselves from others, they are not exhibiting consciousness or self-identity. Rather, they generate these distinctions based on the context of the prompt or conversation, again relying on learned patterns.
It’s also worth noting that while GPT models can generate coherent and often insightful responses, they don’t have understanding or beliefs. The models generate responses by predicting what comes next in a piece of text, given the input it’s received. Their “knowledge” is really just patterns in data they’ve learned to predict.
Daily AI News 7/26/2023
Ridgelinez (Tokyo) is a subsidiary of Fujitsu in Japan that announced the development of a generative artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of engaging in voice communication with humans. The applications of this system include assisting companies in conducting meetings or providing career planning advice to employees.
BMW has revealed that artificial intelligence is already allowing it to cut costs at its sprawling factory in Spartanburg, South Carolina. The AI system has allowed BMW to remove six workers from the line and deploy them to other jobs. The tool is already saving the company over $1 million a year.
MIT’s ‘PhotoGuard‘ protects your images from malicious AI edits. The technique introduces nearly invisible “perturbations” to throw off algorithmic models.
Microsoft with its TypeChat library seeks to enable easy development of natural language interfaces for large language models (LLMs) using types. Introduced July 20 of a team with c# and TypeScript lead developer Anders Hejlsberg, a Microsoft Technical Fellow, TypeChat addresses the difficulty of developing natural language interfaces where apps rely on complex decision trees to determine intent and gather necessary input to act.
AI predicts code coverage faster and cheaper
– Microsoft Research has proposed a novel benchmark task called Code Coverage Prediction. It accurately predicts code coverage, i.e., the lines of code or a percentage of code lines that are executed based on given test cases and inputs. Thus, it helps assess the capability of LLMs in understanding code execution.
– Several use case scenarios where this approach can be valuable and beneficial are:
-
-
Expensive build and execution in large software projects
-
Limited code availability
-
Live coverage or live unit testing
-
Introducing 3D-LLMs: Infusing 3D Worlds into LLMs
– New research has proposed injecting the 3D world into large language models, introducing a whole new family of 3D-based LLMs. Specifically, 3D-LLMs can take 3D point clouds and their features as input and generate responses.
– They can perform a diverse set of 3D-related tasks, including captioning, dense captioning, 3D question answering, task decomposition, 3D grounding, 3D-assisted dialog, navigation, and so on.
Alibaba Cloud brings Meta’s Llama to its clients
– Alibaba’s cloud computing division said it has become the first Chinese enterprise to support Meta’s open-source AI model Llama, allowing Chinese business users to develop programs off the model.
ChatGPT for Android is available in US, India, Bangladesh, Brazil – OpenAI will roll it out in more countries over the next week.
Netflix is offering up to $900K for one A.I. product manager role – The role will focus on increasing the leverage of its Machine Learning Platform.
Nvidia’s DGX Cloud on Oracle now widely available for generative AI training
– Nvidia announced wide accessibility of its cloud-based AI supercomputing service, DGX Cloud. The service will grant users access to thousands of virtual Nvidia GPUs on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI), along with infrastructure in the U.S. and U.K.
Spotify CEO teases AI-powered capabilities for personalization, ads
– During Spotify’s second-quarter earnings, CEO Daniel Ek on ways AI could be used to create more personalized experiences, summarize podcasts, and generate ads.
Cohere releases Coral, an AI assistant designed for enterprise business use
– Coral was specifically developed to help knowledge workers across industries receive responses to requests specific to their sectors based on their proprietary company data.
The proliferation of AI-generated girlfriends, such as those produced by Replika, might exacerbate loneliness and social isolation among men. They may also breed difficulties in maintaining real-life relationships and potentially reinforce harmful gender dynamics.
Chatbot technology is creating AI companions which could lead to social implications.
-
Concerns arise about the potential for these AI relationships to encourage gender-based violence.
-
Tara Hunter, CEO of Full Stop Australia, warns that the idea of a controllable “perfect partner” is worrisome.
Despite concerns, AI companions appear to be gaining in popularity, offering users a seemingly judgment-free friend.
-
Replika’s Reddit forum has over 70,000 members, sharing their interactions with AI companions.
-
The AI companions are customizable, allowing for text and video chat. As the user interacts more, the AI supposedly becomes smarter.
Uncertainty about the long-term impacts of these technologies is leading to calls for increased regulation.
-
Belinda Barnet, senior lecturer at Swinburne University of Technology, highlights the need for regulation on how these systems are trained.
-
Japan’s preference for digital over physical relationships and decreasing birth rates might be indicative of the future trend worldwide.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 20th, 2023
AI-skills job postings jump 450%; here’s what companies want
Google AI introduces Symbol Tuning: A Simple Fine-Tuning Method that can improve in-Context Learning by Emphasizing Input–Label Mappings

Fable, a San Francisco startup, just released its SHOW-1 AI tech that is able to write, produce, direct animate, and even voice entirely new episodes of TV shows.
Their tech critically combines several AI models: including LLMs for writing, custom diffusion models for image creation, and multi-agent simulation for story progression and characterization.
Their first proof of concept? A 20-minute episode of South Park entirely written, produced, and voice by AI. Watch the episode and see their Github project page here for a tech deep dive. https://fablestudio.github.io/showrunner-agents/
Why this matters:
-
Current generative AI systems like Stable Diffusion and ChatGPT can do short-term tasks, but they fall short of long-form creation and producing high-quality content, especially within an existing IP.
-
Hollywood is currently undergoing a writers and actors strike at the same time; part of the fear is that AI will rapidly replace jobs across the TV and movie spectrum.
-
The holy grail for studios is to produce AI works that rise up the quality level of existing IP; SHOW-1’s tech is a proof of concept that represents an important milestone in getting there.
-
Custom content where the viewer gets to determine the parameters represents a potential next-level evolution in entertainment.
How does SHOW-1’s magic work?
-
A multi-agent simulation enables rich character history, creation of goals and emotions, and coherent story generation.
-
Large Language Models (they use GPT-4) enable natural language processing and generation. The authors mentioned that no fine-tuning was needed as GPT-4 has digested so many South Park episodes already. However: prompt-chaining techniques were used in order to maintain coherency of story.
-
Diffusion models trained on 1200 characters and 600 background images from South Park’s IP were used. Specifically, Dream Booth was used to train the models and Stable Diffusion rendered the outputs.
-
Voice-cloning tech provided characters voices.
In a nutshell: SHOW-1’s tech is actually an achievement of combining multiple off-the-shelf frameworks into a single, unified system.
This is what’s exciting and dangerous about AI right now — how the right tools are combined, with just enough tweaking and tuning, and start to produce some very fascinating results.
The main takeaway:
-
Actors and writers are right to be worried that AI will be a massively disruptive force in the entertainment industry. We’re still in the “science projects” phase of AI in entertainment — but also remember we’re less than one year into the release of ChatGPT and Stable Diffusion.
-
A future where entertainment is customized, personalized, and near limitless thanks to generative AI could arrive in the next decade. Bu as exciting as that sounds, ask yourself: is that a good thing?
Sentient AI cannot exist via machine learning alone
AI is helping create the chips that design AI chips
Google’s AI Red Team: the ethical hackers making AI safer
Google Red Team consists of a team of hackers that simulate a variety of adversaries, ranging from nation states and well-known Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) groups to hacktivists, individual criminals or even malicious insiders. The term came from the military, and described activities where a designated team would play an adversarial role (the “Red Team”) against the “home” team. https://blog.google/technology/safety-security/googles-ai-red-team-the-ethical-hackers-making-ai-safer/
How to Make Generative AI Greener
Apple has developed “Apple GPT” as it prepares for a major AI push in 2024
Apple has been relatively quiet on the generative AI front in recent months, which makes them a relative anomaly as Meta, Microsoft, and more all duke it out for the future of AI.
The relative silence doesn’t mean Apple hasn’t been doing anything, and today’s Bloomberg report (note: paywalled) sheds light on their master plan: they’re quietly but ambitiously laying the groundwork for some major moves in AI in 2024. https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-07-19/apple-preps-ajax-generative-ai-apple-gpt-to-rival-openai-and-google
Apple GPT fueling Siri & iPhones |
| Summary: According to an Bloomberg, Apple is quietly building its own AI chatbot, also known as “Apple GPT”, that could be integrated into Siri & Apple devices. |
| Key Points: |
|
| Why it matters? With 1.5 billion active iPhones out there, Apple can change the LLM landscape overnight.
https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2023-07-19/apple-preps-ajax-generative-ai-apple-gpt-to-rival-openai-and-google |
How to use Meta’s open-source ChatGPT competitor? |
||
|
||
| Summary: Meta has unveiled Llama 2, an open-source LLM that can be used commercially! Here are the key features and how could you use it | ||
| Key Points: | ||
|
||
| How to use it? | ||
|
OpenAI doubles GPT-4 messages for ChatGPT Plus users |
| ChatGPT Plus subscribers now have an increased messaging limit of 50 messages in three hours with the introduction of GPT-4. Previously, the limit was set at 25 messages in two hours due to computational and cost considerations.
Why does this matter? Increasing the message limit with GPT-4 provides more room for exploration and experimentation with ChatGPT plugins. For businesses looking to enhance customer interactions, a developer building innovative applications, or an AI enthusiast, the raised cap of 50 messages per 3 hours opens up more extensive and dynamic interactions with the model. |
| Source: https://the-decoder.com/openai-doubles-gpt-4-messages-for-chatgpt-plus-users |
AI Tutorial:
Convert YouTube Videos to Blogs & Audios with ChatGPT |
| Ever wished you could repurpose your YouTube content into blog posts and audios? In this tutorial, we’ll show you how to convert YouTube videos into written and audio content using ChatGPT and a few helpful plugins. |
| Step 1: Install Necessary Plugins |
| You’ll need three plugins for this task: |
|
| You can install these plugins from the plugin store. |
| Step 2: Enter the Prompt |
| Once you have the plugins installed, paste the following prompt into ChatGPT: |
|
| Replace “[URL]” with the URL of your YouTube video. |
| Step 3: Get the blog and the voiceover |
| After entering the prompt, ChatGPT will create a blog post based on the video’s content. It will also suggest suitable images from Unsplash and generate a voiceover for the entire blog. |
| Expected Outcome |
| The output should be a well-structured blog post, complete with images and a voiceover. This way, you can extend your reach beyond YouTube and cater to audiences who prefer reading or listening to content. |
Imitation Models and the Open-Source LLM Revolution
This interesting read by Cameron R. Wolfe, Ph.D. discusses the emergence of proprietary Language Model-based APIs and the potential challenges they pose to the traditional open-source and transparent approach in the deep learning community. It highlights the development of open-source LLM alternatives as a response to the shift towards proprietary APIs. https://cameronrwolfe.substack.com/p/imitation-models-and-the-open-source
The article emphasizes the importance of rigorous evaluation in research to ensure that new techniques and models truly offer improvements. It also explores the limitations of imitation LLMs, which can perform well for specific tasks but tend to underperform when broadly evaluated.
Why does this matter?
While local imitation is still valuable for specific domains, it is not a comprehensive solution for producing high-quality, open-source foundation models. Instead, it advocates for the continued advancement of open-source LLMs by focusing on creating larger and more powerful base models to drive further progress in the field.
https://cameronrwolfe.substack.com/p/imitation-models-and-the-open-source
Google AI’s SimPer unlocks potential of periodic learning
Google research team’s this paper introduces SimPer, a self-supervised learning method that focuses on capturing periodic or quasi-periodic changes in data. SimPer leverages the inherent periodicity in data by incorporating customized augmentations, feature similarity measures, and a generalized contrastive loss. https://ai.googleblog.com/2023/07/simper-simple-self-supervised-learning.html
SimPer exhibits superior data efficiency, robustness against spurious correlations, and generalization to distribution shifts, making it a promising approach for capturing and utilizing periodic information in diverse applications.
Why does this matter?
SimPer’s significance lies in its ability to address the challenge of learning meaningful representations for periodic tasks with limited or no supervision. This advancement proves crucial in various domains, such as human behavior analysis, environmental sensing, and healthcare, where critical processes often exhibit periodic or quasi-periodic changes. It demonstrates that SimPer outperforms state-of-the-art SSL methods.
3 Machine Learning Stocks for Getting Rich in 2023
Nvidia’s (NASDAQ:NVDA) stock has risen dramatically in 2023, primarily due to its AI chips. Its GPU chipsets are the most powerful available, and as AI has taken off, the competition to secure those chips has made Nvidia the hottest firm there is. https://www.nasdaq.com/articles/3-machine-learning-stocks-for-getting-rich-in-2023
Nvidia chips also power complex large language models used to train machine learning models based on technical subfields, including neural networks. Those chips are in high demand in data centers and automotive sectors, where machine learning is utilized at higher rates.
Advanced Micro Devices (NASDAQ:AMD) is the primary challenger to Nvidia’s dominance in AI and machine learning.
It’s entirely reasonable to believe that AMD could attract Nvidia investor capital on overvaluation fears. That’s one reason investors should consider AMD.
However, the more salient reason is simply that AMD is not that far behind Nvidia. MosiacML recently pegged AMD’s high-end chip speed as about 80% as fast as those from Nvidia. Here’s the good news regarding machine learning: AMD has done very well on the software side, according to MosaicML, which notes that software has been the “Achilles heel” for most machine learning firms.
Palantir Technologies (NYSE:PLTR) stock has boomed in 2023 due to AI and machine learning. It didn’t catch the early wave of AI adoption that benefited Microsoft (NASDAQ:MSFT), AMD, Nvidia, and others — instead getting hot in recent months.
Its Gotham and Foundry platforms have found a following in private firms and, more prominently, with public firms and government organizations. Adoption across the defense sector has been particularly important in helping Palantir take advantage of AI stock growth. The company has long been associated with the defense industry and has developed a deep connection by applying silicon-valley-style tech to government entities.
Top 10 career options in Generative AI
A.I. will do to call center jobs what the tractor did to farm laborer jobs 100 years ago
You know how hard it is to get customer service on the phone? That’s because companies really, really, really don’t like paying for call center workers. That’s why, as a class, customer service will be the first group of workers whose jobs will be decimated by A.I.
https://www.nytimes.com/2023/07/19/business/call-center-workers-battle-with-ai.html
A new study by researchers Chen, Zaharia, and Zou at Stanford and UC Berkley now confirms that these perceived degradations are quantifiable and significant between the different versions of the LLMs (March and June 2023). They find:
-
“For GPT-4, the percentage of [code] generations that are directly executable dropped from 52.0% in March to 10.0% in June. The drop was also large for GPT-3.5 (from 22.0% to 2.0%).” (!!!)
-
For sensitive questions: “An example query and responses of GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 at different dates. In March, GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 were verbose and gave detailed explanation for why it did not answer the query. In June, they simply said sorry.”
-
“GPT-4 (March 2023) was very good at identifying prime numbers (accuracy 97.6%) but GPT-4 (June 2023) was very poor on these same questions (accuracy 2.4%). Interestingly GPT-3.5 (June 2023) was much better than GPT-3.5 (March 2023) in this task.”
- https://notes.aimodels.fyi/new-study-validates-user-rumors-of-degraded-chatgpt-performance/
A group of more than 8,500 authors is challenging tech companies for using their works without permission or compensation to train AI language models like ChatGPT, Bard, LLaMa, and others.
Concerns about Copyright Infringement: The authors have pointed out that these AI technologies are replicating their language, stories, style, and ideas, without any recognition or reimbursement. Their writings serve as “endless meals” for AI systems. The companies behind these models have not significantly addressed the sourcing of these works. https://www.theregister.com/2023/07/18/ai_in_brief/
-
The authors question whether the AI models used content scraped from bookstores and reviews, borrowed from libraries, or downloaded from illegal archives.
-
It’s evident that the companies didn’t obtain licenses from publishers — a method seen by the authors as both legal and ethical.
Legal and Ethical Arguments: The authors highlight the Supreme Court decision in Warhol v. Goldsmith, suggesting that the high commerciality of these AI models’ use may not constitute fair use.
-
They claim that no court would approve of using illegally sourced works.
-
They express concern that generative AI may flood the market with low-quality, machine-written content, undermining their profession.
-
They cite examples of AI-generated books already making their way onto best-seller lists and being used for SEO purposes.
Impact on Authors and Requested Actions: The group of authors warns that these practices can deter authors, especially emerging ones or those from under-represented communities, from making a living due to large scale publishing’s narrow margins and complexities.
-
They request tech companies to obtain permission for using their copyrighted materials.
-
They demand fair compensation for past and ongoing use of their works in AI systems.
-
They also ask for remuneration for the use of their works in AI output, whether it’s deemed infringing under current law or not.
In a recent study it was reported that 76% of “Gen-Zers”are concerned about losing their jobs to AI-powered tools. I am Gen-Z and I think a lot of future jobs will be replaced with AI.
https://www.businessinsider.com/gen-z-workers-ai-boost-productivity-chatgpt-2023-7
Emerging Trend: A director says Gen Z workers at his medical device company are increasing efficiency by using AI tools to automate tasks and optimize workflows.
-
Gen Z is adept at deploying new AI-powered systems on the job.
-
They are automating tedious processes and turbocharging productivity.
-
This offsets concerns about AI displacing entry-level roles often filled by Gen Z.
Generational Divide: Gen Z may be better positioned than older workers to capitalize on AI’s rise.
-
They have the tech skills to implement AI and make it work for them.
-
But surveys show most still fear losing jobs to AI automation overall.
-
Companies are rapidly adopting AI, with some CEOs openly planning workforce cuts.
TL;DR: While AI automation threatens some roles, a medical company director says Gen Z employees are productively applying AI to boring work, benefiting from their digital savvy. But surveys indicate young workers still predominantly worry about job loss risks from AI.
The role of “Head of AI” is rapidly gaining popularity in American businesses, despite the uncertainty surrounding the specific duties and qualifications associated with the position.
Rise of the “Head of AI” Role: The “Head of AI” position, largely nonexistent a few years ago, has seen significant growth in the U.S., tripling in the last five years.
-
The role has emerged across a range of businesses, from tech giants to companies outside of the tech sector.
-
The increased adoption of this role is in response to the increasing disruption caused by AI in various industries.
https://www.vox.com/technology/2023/7/19/23799255/head-of-ai-leadership-jobs
Uncertainties Surrounding the Role: Despite the role’s popularity, there’s a lack of clarity about what a “Head of AI” specifically does and what qualifications are necessary.
-
The role’s responsibilities vary widely between companies, ranging from incorporating AI into products to training employees in AI use.
-
There’s also debate about who should take on this role, with contenders ranging from seasoned AI experts to those familiar with consumer-facing AI applications.
Current Landscape of AI Leadership: Despite the uncertainties, the trend of appointing AI leaders in companies is growing, with an expected increase from 25% to 80% of Fortune 2000 companies having a dedicated AI leader within a year.
-
The role is becoming more common in larger companies, particularly in banking, tech, and manufacturing sectors.
-
Individuals from various backgrounds, including technology leadership, business, and marketing, are stepping into the role.
Cerebras and G42, the Abu Dhabi-based AI pioneer, announced their strategic partnership, which has resulted in the construction of Condor Galaxy 1 (CG-1), a 4 exaFLOPS AI Supercomputer. https://www.cerebras.net/press-release/cerebras-and-g42-unveil-worlds-largest-supercomputer-for-ai-training-with-4-exaflops-to-fuel-a-new-era-of-innovation
Located in Santa Clara, CA, CG-1 is the first of nine interconnected 4 exaFLOPS AI supercomputers to be built through this strategic partnership between Cerebras and G42. Together these will deliver an unprecedented 36 exaFLOPS of AI compute and are expected to be the largest constellation of interconnected AI supercomputers in the world.
CG-1 is now up and running with 2 exaFLOPS and 27 million cores, built from 32 Cerebras CS-2 systems linked together into a single, easy-to-use AI supercomputer. While this is currently one of the largest AI supercomputers in production, in the coming weeks, CG-1 will double in performance with its full deployment of 64 Cerebras CS-2 systems, delivering 4 exaFLOPS of AI compute and 54 million AI optimized compute cores.
Upon completion of CG-1, Cerebras and G42 will build two more US-based 4 exaFLOPS AI supercomputers and link them together, creating a 12 exaFLOPS constellation. Cerebras and G42 then intend to build six more 4 exaFLOPS AI supercomputers for a total of 36 exaFLOPS of AI compute by the end of 2024.
Offered by G42 and Cerebras through the Cerebras Cloud, CG-1 delivers AI supercomputer performance without having to manage or distribute models over GPUs. With CG-1, users can quickly and easily train a model on their data and own the results.
AI models need increasingly unique and sophisticated data sets to improve their performance, but the developers behind major LLMs are finding that web data is “no longer good enough” and getting “extremely expensive,” a report from the Financial Times (note: paywalled) reveals.
So OpenAI, Microsoft, and Cohere are all actively exploring the use of synthetic data to save on costs and generate clean, high-quality data. https://www.ft.com/content/053ee253-820e-453a-a1d5-0f24985258de
Why this matters:
-
Major LLM creators believe they have reached the limits of human-made data improving performance. The next dramatic leap in performance may not come from just feeding models more web-scraped data.
-
Custom human-created data is extremely expensive and not a scalable solution. Getting experts in various fields to create additional finely detailed content is unviable at the quantity of data needed to train AI.
-
Web data is increasingly under lock and key, as sites like Reddit, Twitter, more are charging hefty fees in order to use their data.
The approach is to have AI generate its own training data go-forward:
-
Cohere is having two AI models act as tutor and student to generate synthetic data. All of it is reviewed by a human at this point.
-
Microsoft’s research team has shown that certain synthetic data can be used to train smaller models effectively — but increasing GPT-4 performance’s is still not viable with synthetic data.
-
Startups like Scale.ai and Gretel.ai are already offering synthetic data-as-a-service, showing there’s market appetite for this.
What are AI leaders saying? They’re determined to explore this future.
-
Sam Altman explained in May that he was “pretty confident that soon all data will be synthetic data,” which could help OpenAI sidestep privacy concerns in the EU. The pathway to superintelligence, he posited, is through models teaching themselves.
-
Aidan Gomez, CEO of LLM startup Cohere, believes web data is not great: “the web is so noisy and messy that it’s not really representative of the data that you want. The web just doesn’t do everything we need.”
Some AI researches are urging caution, however: researchers from Oxford and Cambridge recently found that training AI models on their own raw outputs risked creating “irreversible defects” in these models that could corrupt and degrade their performance over time.
The main takeaway: Human-made content was used to develop the first generations of LLMs. But we’re now entering a fascinating world where the over the next decade, human-created content could become truly rare, with the bulk of the world’s data and content all created by AI.
I Spent 9 Days and Tried 324 AI Tools for my Youtube video and these 9 AI tools are best I use personally.
I Spent 9 Days and Tried 324 AI Tools for my youtube video and these 9 AI tools are best I use personally.
In this AI Hype, Everyone is Building Extraordinary AI products that will blow your mind but Sometime too many options is stuck our action and we are not able to decide what we do and what we try But as content creator i reviewed too many AI Tool for my videos, and i personally say, these are the most productive and helpful AI tool for your business, writing, research etc.
My AskAI: A great tool for using ChatGPT on your own files and website. It’s useful for research and tasks requiring accuracy, with options for concise or detailed answers. The basic plan is free, and there’s a $20/month option for over 100 pieces of content.
Helper-AI – The Fastest way to access GPT-4 on any site, Just type “help” and instant access GPT-4 on any site without changing tabs again and again. In Just One Month Helper-AI is making $2000 by selling complete source code and ownership of AI. (It will help you to boost 3x Productivity, Generate high-quality content, Write code & Excel Formulas, Rewrite, Research, Summarise and more. )
Krater.ai: An all-in-one web app that combines text, audio, and image-based AI tools. It simplifies workflow by eliminating the need for multiple tabs and offers templates for copywriting. It’s preferred over other options and provides 10 free generations per month.
HARPA AI: A Chrome add-on with GPT answers alongside search results, web page chat, YouTube video summarization, and email/social media reply templates. It’s completely free and available on the Chrome Web Store.
Plus AI for Google Slides: A slide deck generator that helps co-write slides, provides suggestions, and allows integration of external data. It’s free and available as a Google Slides and Docs plugin.
Taskade: An all-in-one productivity tool that combines tasks, notes, mind maps, chat, and an AI chat assistant. It syncs across teams and offers various views. The free version has many features.
Zapier + OpenAI: A powerful combination of Zapier’s integrations with generative AI. It enables automations with GPT 3, DALLE-2, and Whisper AI. It’s free for core features and available as an app/add-on to Zapier.
SaneBox: AI-based email management that identifies important emails and allows customization of folders. It helps declutter inboxes and offers a “Deep Clean” feature. There’s a 2-week trial, and pricing is affordable.
Hexowatch AI: A website change detection tool that alerts you to changes on multiple websites. It saves time and offers alert notifications via email or other platforms. It’s a paid service with reliable performance.
I built the fastest way to access GPT-4 on any site because I was so frustrated because Every time I want to access ChatGPT, I need to login ChatGPT first, filling password, Captcha, and changing browser tab again and again for using Chatgpt that complete make me unproductive and overwhelming.
So, I built my own AI tool to access GPT-4 on any site without leaving the current site, you just type “help” and instant access GPT-4 on any site.
I think its make me 10 times more productive, and best part is, I was so insecure before launching my AI product because I was thinking no one will buy it.
but when I launch the product everyone love it.
After launching the product, in just 5 days I make around $300 by selling the complete source code and ownership of the product, so people can use it, resell it, modify it or anything they want to do.
My Product link – https://www.helperai.info/
I hope you like it because i’m not good in marketing and writing, if you good marketer please DM. i love to work with you.
In a recent development, tech giants like Google, NVIDIA and Microsoft are aggressively exploring the intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and healthcare, hoping to revolutionize medicine as we know it. https://sites.research.google/med-palm/
https://ir.recursion.com/news-releases/news-release-details/recursion-announces-collaboration-and-50-million-investment
Google’s AI chatbot, Med-PaLM 2, has demonstrated an impressive 92.6% accuracy rate in responding to medical queries, closely matching the 92.9% score by human healthcare professionals. However, it’s worth noting that these advancements don’t come without their quirks, as a Google research scientist previously discovered the system had the capacity to “hallucinate” and cite non-existent studies.
AI’s potential in the pharmaceutical sector is also drawing significant attention, with the goal of using AI to discover new, potentially groundbreaking drugs. Nvidia is the latest entrant into this field, investing $50M in AI drug discovery company, Recursion Pharmaceuticals (NASDAQ:RXRX), causing a substantial 78% increase in their stock.
Microsoft acquired a speech recognition company, Nuance for $19.7 billion to expand their reach to healthcare. Just yesterday at their Inspire event, they revealed how they are partnering up with Epic Systems, US’s largest EHR to integrate Nuance’s AI solutions.
Meta, the parent company of Facebook, has recently launched LLaMA 2, an open-source large language model (LLM) that aims to challenge the restrictive practices by big tech competitors. Unlike AI systems launched by Google, OpenAI, and others that are closely guarded in proprietary models, Meta is freely releasing the code and data behind LLaMA 2 to enable researchers worldwide to build upon and improve the technology. https://venturebeat.com/ai/llama-2-how-to-access-and-use-metas-versatile-open-source-chatbot-right-now/
LLaMA 2 comes in three sizes: 7 billion, 13 billion, and 70 billion parameters depending on the model you choose. It’s trained using reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), learning from the preferences and ratings of human AI trainers.
There are numerous ways to interact with LLaMA 2. You can interact with the chatbot demo at llama2.ai, download the LLaMA 2 code from Hugging Face, access it through Microsoft Azure, Amazon SageMaker JumpStart, or try a variant at llama.perplexity.ai.
By launching LLaMA 2, Meta has taken a significant step in opening AI up to developers worldwide. This could lead to a surge of innovative AI applications in the near future.
For more details, check out the full article here.
AI21 Labs debuts Contextual Answers, a plug-and-play AI engine for enterprise data
AI21 Labs, the Tel Aviv-based NLP major behind the Wordtune editor, has announced the launch of a plug-and-play generative AI engine to help enterprises drive value from their data assets. Named Contextual Answers, this API can be directly embedded into digital assets to implement large language model (LLM) technology on select organizational data. It enables business employees or customers to gain the required information through a conversational experience, without engaging with different teams or software systems. https://venturebeat.com/ai/ai21-labs-debuts-contextual-answers-a-plug-and-play-ai-engine-for-enterprise-data/
This technology is offered as a solution that works out of the box and doesn’t require significant effort and resources. It’s built as a plug-and-play capability and optimized each component, allowing clients to get the best results in the industry without investing the time of AI, NLP, or data science practitioners.
The AI engine supports unlimited upload of internal corporate data, taking into account access and security of the information. For access control and role-based content separation, the model can be limited to using a specific file, a number of files, a specific folder, or tags or metadata. For security and data confidentiality, the company’s AI21 Studio ensures a secured and soc-2 certified environment.
For more details, check out the full article here.
Google is actively meeting with news organizations and demo’ing a tool, code-named “Genesis”, that can write news articles using AI, the New York Times revealed.
Utilizing Google’s latest LLM technologies, Genesis is able to use details of current events to generate news content from scratch. But the overall reaction to the tool has been highly mixed, ranging from deep concern to muted enthusiasm. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/07/19/business/google-artificial-intelligence-news-articles.html
Why this matters:
-
Media organizations are under financial pressure as they enter the age of generative AI: while some are refusing to embrace it, other media orgs like G/O Media (AV Club, Jezebel, etc.) are openly using AI to generate articles.
-
Early tests of generative AI have already led to concerns: the tendency of large language models to hallucinate is producing inaccuracies even in articles published by well-known media organizations.
-
The job of journalism is in question itself: if AI can write news articles, what role do journalists play beyond editing AI-written content? Orgs like Insider, The Times, NPR and more have already notified employees they intend to explore generative AI.
What do news organizations actually think of Google’s Genesis?
-
It’s “unsettling,” some execs have said. News orgs worry that Google “it seemed to take for granted the effort that went into producing accurate and artful news stories.”
-
They’re not happy that Google’s LLM digested their news content (often w/o compensation): it’s the efforts of decades of journalism powering Google’s new Genesis tool, which now threatens to upend journalism
-
Most news orgs are saying “no comment”: treat that as a signal for how they’re deeply grappling with this existential challenge.
What does Google think?
-
They think this could be more of a copilot (right now) than an outright replacement for journalists: “Quite simply, these tools are not intended to, and cannot, replace the essential role journalists have in reporting, creating and fact-checking their articles,” an Google spokesperson clarified.
The main takeaway:
-
The next decade isn’t going to be great for news organizations. Many were already struggling with the transition to online news, and many media organizations have shown that buzzy logos and fancy brand can’t make viable businesses (VICE, Buzzfeed, and more).
-
How journalists navigate the shift in their role will be very interesting, and I’ll be curious to see if they end up adopting copilots to the same degree we’re seeing in the engineering world.
Today, OpenAI introduced a custom instructions feature in beta that allows users to set persistent preferences that ChatGPT will remember in all conversations.
Key points:
-
ChatGPT now allows custom instructions to tailor responses. This lets users set preferences instead of repeating them.
-
Instructions are remembered for all conversations going forward. Avoiding restarting each chat from scratch.
Why the $20 subscription is even more valuable: More personalized and customized conversations.
-
Instructions allow preferences for specific contexts. Like grade levels for teachers.
-
Developers can set preferred languages for code. Beyond defaults like Python.
-
Shopping lists can account for family size servings. With one time instructions.
-
The beta is live for Plus users now. Rolling out to all users in coming weeks.
https://openai.com/blog/custom-instructions-for-chatgpt
The main takeaway:
-
This takes customization to the next level for ChatGPT allowing for persistent needs and preferences.
-
Open AI released six use cases they’ve found so far here they are in order.
-
“Expertise calibration: Sharing your level of expertise in a specific field to avoid unnecessary explanations.
-
Language learning: Seeking ongoing conversation practice with grammar correction.
-
Localization: Establishing an ongoing context as a lawyer governed by their specific country’s laws.
-
Novel writing: Using character sheets to help ChatGPT maintain a consistent understanding of story characters in ongoing interactions.
-
Response format: Instructing ChatGPT to consistently output code updates in a unified format.
-
Writing style personalization: Applying the same voice and style as provided emails to all future email writing requests.” (Use cases are in Open AI’s words.)
The article shows some examples of how businesses are already relying on AI-based applications for internal purposes, and how to do the same quickly and affordably with a no-code program builder – with healthcare, real estate, and professional services providers as examples: No-Code AI Applications for Healthcare and Other Traditional Industries – Blaze
Daily AI Update News from Apple, OpenAI, Google Research, MosaicML, Google and Nvidia
-
Apple Trials a ChatGPT-like AI Chatbot
– Apple is developing AI tools, including its own large language model called “Ajax” and an AI chatbot named “Apple GPT.” They are gearing up for a major AI announcement next year as it tries to catch up with competitors like OpenAI and Google. The company’s executives are considering integrating these AI tools into Siri to improve its functionality and performance, and overcome the stagnation the voice assistant has experienced in recent years. -
OpenAI doubles GPT-4 message cap to 50
– OpenAI has doubled the number of messages ChatGPT Plus subscribers can send to GPT-4. Users can now send up to 50 messages in 3 hours, compared to the previous limit of 25 messages in 2 hours. And they are rolling out this update next week.
– Increasing the message limit with GPT-4 provides more room for exploration and experimentation with ChatGPT plugins. For businesses, developers, and AI enthusiasts, the raised cap on messages allows for more extensive interaction with the model. -
Google AI’s SimPer unlocks the potential of periodic learning
– Google research team’s this paper introduces SimPer, a self-supervised learning method that focuses on capturing periodic or quasi-periodic changes in data. SimPer leverages the inherent periodicity in data by incorporating customized augmentations, feature similarity measures, and a generalized contrastive loss. -
Google exploring AI tools for Journalists
– Google is exploring using AI tools to write news articles and is in talks with publishers to use the tools to assist journalists. The potential uses of these AI tools include assistance to journalists with options for headlines or different writing styles, and majorly the objective is to enhances their work and productivity. -
MosaicML launches MPT-7B-8K with 8k context length
– MosaicML has released MPT-7B-8K, an open-source LLM with 7B parameters and an 8k context length. The model was trained on the MosaicML platform, starting from the MPT-7B checkpoint. The pretraining phase utilized Nvidia H100s and involved three days of training on 256 H100s, incorporating 500B tokens of data. This new LLM offers significant advancements in language processing capabilities and is available for developers to use and contribute. -
AI has driven Nvidia to achieve a $1 trillion valuation!
– The company, which started as a video game hardware provider, has now become a full-stack hardware and software company powering the Gen AI revolution. Nvidia’s success in the AI industry has led to it becoming a nearly $1 trillion company.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 19th, 2023
How Machine Learning Plays a Key Role in Diagnosing Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic disease that affects millions of people around the world, leading to long-term health complications such as heart disease, nerve damage, and kidney failure. The early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes is critical in order to prevent these complications, and machine learning is helping to revolutionize the way this disease is diagnosed.
Machine learning algorithms use patterns in data to make predictions and decisions, and this same capability can be applied to the analysis of medical data in order to improve the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. One of the key ways that machine learning is improving diabetes diagnosis is through the use of predictive algorithms. These algorithms can use data from patient histories, such as age, BMI, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, to predict the likelihood of a patient developing type 2 diabetes. This can help healthcare providers to identify patients who are at high risk of developing the disease and take early action to prevent it.
9 AI coding tools every developer must know
Top Computer Vision Tools/Platforms in 2023
Kili Technology’s Video Annotation Tool
Kili Technology’s video annotation tool is designed to simplify and accelerate the creation of high-quality datasets from video files. The tool supports a variety of labeling tools, including bounding boxes, polygons, and segmentation, allowing for precise annotation. With advanced tracking capabilities, you can easily navigate through frames and review all your labels in an intuitive Explore view.
The tool supports various video formats and integrates seamlessly with popular cloud storage providers, ensuring a smooth integration with your existing machine learning pipeline. Kili Technology’s video annotation tool is the ultimate toolkit for optimizing your labeling processes and constructing powerful datasets.
OpenCV
A software library for machine learning and computer vision is called OpenCV. OpenCV, developed to offer a standard infrastructure for computer vision applications, gives users access to more than 2,500 traditional and cutting-edge algorithms.
These algorithms may be used to identify faces, remove red eyes, identify objects, extract 3D models of objects, track moving objects, and stitch together numerous frames into a high-resolution image, among other things.
Viso Suite
A complete platform for computer vision development, deployment, and monitoring, Viso Suite enables enterprises to create practical computer vision applications. The best-in-class software stack for computer vision, which is the foundation of the no-code platform, includes CVAT, OpenCV, OpenVINO, TensorFlow, or PyTorch.
Image annotation, model training, model management, no-code application development, device management, IoT communication, and bespoke dashboards are just a few of the 15 components that make up Viso Suite. Businesses and governmental bodies worldwide use Viso Suite to create and manage their portfolio of computer vision applications (for industrial automation, visual inspection, remote monitoring, and more).
TensorFlow
TensorFlow is one of the most well-known end-to-end open-source machine learning platforms, which offers a vast array of tools, resources, and frameworks. TensorFlow is beneficial for developing and implementing machine learning-based computer vision applications.
One of the most straightforward computer vision tools, TensorFlow, enables users to create machine learning models for computer vision-related tasks like facial recognition, picture categorization, object identification, and more. Like OpenCV, Tensorflow supports several languages, including Python, C, C++, Java, and JavaScript.
CUDA
NVIDIA created the parallel computing platform and application programming interface (API) model called CUDA (short for Compute Unified Device Architecture). It enables programmers to speed up processing-intensive programs by utilizing the capabilities of GPUs (Graphics Processing Units).
The NVIDIA Performance Primitives (NPP) library, which offers GPU-accelerated image, video, and signal processing operations for various domains, including computer vision, is part of the toolkit. In addition, multiple applications like face recognition, image editing, rendering 3D graphics, and others benefit from the CUDA architecture. For Edge AI implementations, real-time image processing with Nvidia CUDA is available, enabling on-device AI inference on edge devices like the Jetson TX2.
MATLAB
Image, video, and signal processing, deep learning, machine learning, and other applications can all benefit from the programming environment MATLAB. It includes a computer vision toolbox with numerous features, applications, and algorithms to assist you in creating remedies for computer vision-related problems.
Keras
A Python-based open-source software package called Keras serves as an interface for the TensorFlow framework for machine learning. It is especially appropriate for novices because it enables speedy neural network model construction while offering backend help.
SimpleCV
SimpleCV is a set of open-source libraries and software that makes it simple to create machine vision applications. Its framework gives you access to several powerful computer vision libraries, like OpenCV, without requiring a thorough understanding of complex ideas like bit depths, color schemes, buffer management, or file formats. Python-based SimpleCV can run on various platforms, including Mac, Windows, and Linux.
BoofCV
The Java-based computer vision program BoofCV was explicitly created for real-time computer vision applications. It is a comprehensive library with all the fundamental and sophisticated capabilities needed to develop a computer vision application. It is open-source and distributed under the Apache 2.0 license, making it available for both commercial and academic use without charge.
CAFFE
Convolutional Architecture for Fast Feature, or CAFFE A computer vision and deep learning framework called embedding was created at the University of California, Berkeley. This framework supported a variety of deep learning architectures for picture segmentation and classification and was made in the C++ programming language. Due to its incredible speed and image processing capabilities, it is beneficial for research and industry implementation.
OpenVINO
A comprehensive computer vision tool, OpenVINO (Open Visual Inference and Neural Network Optimization), helps create software that simulates human vision. It is a free cross-platform toolkit designed by Intel. Models for numerous tasks, including object identification, face recognition, colorization, movement recognition, and others, are included in the OpenVINO toolbox.
DeepFace
The most well-liked open-source computer vision library for deep learning facial recognition at the moment is DeepFace. The library provides a simple method for using Python to carry out face recognition-based computer vision.
YOLO
One of the fastest computer vision tools in 2022 is You Only Look Once (YOLO). It was created in 2016 by Joseph Redmon and Ali Farhadi to be used for real-time object detection. YOLO, the fastest object detection tool available, applies a neural network to the entire image and then divides it into grids. The odds of each grid are then predicted by the software concurrently. After the hugely successful YOLOv3 and YOLOv4, YOLOR had the best performance up until YOLOv7, published in 2022, overtook it.
FastCV
FastCV is an open-source image processing, machine learning, and computer vision library. It includes numerous cutting-edge computer vision algorithms along with examples and demos. As a pure Java library with no external dependencies, FastCV’s API ought to be very easy to understand. It is, therefore, perfect for novices or students who want to swiftly include computer vision into their ideas and prototypes.
To easily integrate computer vision functionality into our mobile apps and games, the company also integrated FastCV on Android.
Scikit-image
One of the best open-source computer vision tools for processing images in Python is the Scikit-image module. Scikit-image allows you to conduct simple operations like thresholding, edge detection, and color space conversions.
5 Different Types of Artificial Intelligence
1. Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence includes machine learning as a component. It is described as the algorithms that scan data sets and then learn from them to make educated judgments. In the case of machine learning, the computer software learns from experience by executing various tasks and seeing how the performance of those tasks improves over time.
2. Deep Learning: Deep learning may also be considered a subset of machine learning. Deep learning aims to increase power by teaching students how to represent the world in a hierarchy of concepts. It demonstrates how the notion is connected to more easy concepts and how fewer abstract representations can exist for more complex ones.
3. Natural language Processing (NLP): Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an artificial intelligence that combines AI and linguistics to allow humans to communicate with robots using natural language. Google natural language processing utilizing Google Voice search is a simple example of NLP.
4. Computer Vision: Computer vision is used in organizations to improve the user experience while cutting costs and enhancing security. The market for computer vision is growing at the same rate as its capabilities and is expected to reach $26.2 billion by 2025. This is an almost 30% annual growth.
5. Explainable AI(XAI): Explainable artificial intelligence is a collection of strategies and approaches that enable human users to comprehend and trust machine learning algorithms’ discoveries and output. Explainable AI refers to the ability to explain an AI model, its projected impact, and any biases. It contributes to the definition of model correctness, fairness, and transparency and results in AI-powered decision-making.
Boom — here it is! We previously heard that Meta’s release of an LLM free for commercial use was imminent and now we finally have more details. https://ai.meta.com/llama/
LLaMA 2 is available for download right now here.
Here’s what’s important to know:
-
The model was trained on 40% more data than LLaMA 1, with double the context length: this should offer a much stronger starting foundation for people looking to fine-tune it.
-
It’s available in 3 model sizes: 7B, 13B, and 70B parameters.
-
LLaMA 2 outperforms other open-source models across a variety of benchmarks: MMLU, TriviaQA, HumanEval and more were some of the popular benchmarks used. Competitive models include LLaMA 1, Falcon and MosaicML’s MPT model.
-
A 76-page technical specifications doc is included as well: giving this a quick read through, it’s in Meta’s style of being very open about how the model was trained and fine-tuned, vs. OpenAI’s relatively sparse details on GPT-4.
What else is interesting: they’re cozy with Microsoft:
-
Microsoft is our preferred partner for Llama 2, Meta announces in their press release, and “starting today, Llama 2 will be available in the Azure AI model catalog, enabling developers using Microsoft Azure.”
-
My takeaway: MSFT knows open-source is going to be big. They’re not willing to put all their eggs in one basket despite a massive $10B investment in OpenAI.
Meta’s Microsoft partnership is a shot across the bow for OpenAI. Note the language in the press release:
-
“Now, with this expanded partnership, Microsoft and Meta are supporting an open approach to provide increased access to foundational AI technologies to the benefits of businesses globally. It’s not just Meta and Microsoft that believe in democratizing access to today’s AI models. We have a broad range of diverse supporters around the world who believe in this approach too “
-
All of this leans into the advantages of open source: “increased access”, “democratizing access”, “supporters across the world”
The takeaway: the open-source vs. closed-source wars just got really interesting. Meta didn’t just make LLaMA 1 available for commercial use, they released a better model and announced a robust collaboration with Microsoft at the same time. Rumors persist that OpenAI is releasing an open-source model in the future — the ball is now in their court.
Stability AI’s CEO, Emad Mostaque, anticipates a significant decline in the number of outsourced coders in India within the next two years due to the rise of artificial intelligence. https://www.cnbc.com/2023/07/18/stability-ai-ceo-most-outsourced-coders-in-india-will-go-in-2-years.html
The Threat to Outsourced Coders in India: Emad Mostaque predicts a significant job loss among outsourced coders in India as a result of advancing AI technologies. He believes that software can now be developed with fewer individuals, posing a significant threat to these jobs.
-
The AI impact is particularly heavy on computer-based jobs where the work is unseen.
-
Notably, outsourced coders in India are considered most at risk.
Different Impact Globally Due to Labor Laws: While job losses are anticipated, the impact will vary worldwide due to different labor laws. Countries with stringent labor laws, like France, might experience less disruption.
-
Labor laws will determine the level of job displacement.
-
India is predicted to have a higher job loss rate compared to countries with stricter labor protections.
India’s High Risk Scenario: India, with over 5 million software programmers, is expected to be hit hardest. Given its substantial outsourcing role, the country is particularly vulnerable to AI-induced job losses.
-
Indian software programmers are the most threatened.
-
The risk is compounded by India’s significant outsourcing role globally.
LLMs rely on a wide body of human knowledge as training data to produce their outputs. Reddit, StackOverflow, Twitter and more are all known sources widely used in training foundation models.
A team of researchers is documenting an interesting trend: as LLMs like ChatGPT gain in popularity, they are leading to a substantial decrease in content on sites like StackOverflow. https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.07367
Here’s the paper on arXiv for those who are interested in reading it in-depth. I’ve teased out the main points for Reddit discussion below.
Why this matters:
-
High-quality content is suffering displacement, the researchers found. ChatGPT isn’t just displaying low-quality answers on StackOverflow.
-
The consequence is a world of limited “open data”, which can impact how both AI models and people can learn.
-
“Widespread adoption of ChatGPT may make it difficult” to train future iterations, especially since data generated by LLMs generally cannot train new LLMs effectively.
This is the “blurry JPEG” problem, the researchers note: ChatGPT cannot replace its most important input — data from human activity, yet it’s likely digital goods will only see a reduction thanks to LLMs.
The main takeaway:
-
We’re in the middle of a highly disruptive time for online content, as sites like Reddit, Twitter, and StackOverflow also realize how valuable their human-generated content is, and increasingly want to put it under lock and key.
-
As content on the web increasingly becomes AI generated, the “blurry JPEG” problem will only become more pronounced, especially since AI models cannot reliably differentiate content created by humans from AI-generated works.
Microsoft held their Inspire event today, where they released details about several new products, including Bing Chat Enterprise and 365 Copilot. Enterprise options are supported with commercial data protection. These are significant steps toward integrating AI further into the workplace, and I expect them to have a large impact on how work is delegated and managed. https://blogs.microsoft.com/blog/2023/07/18/furthering-our-ai-ambitions-announcing-bing-chat-enterprise-and-microsoft-365-copilot-pricing/
We’re excited to unveil the next steps in our journey: First, we’re significantly expanding Bing to reach new audiences with Bing Chat Enterprise, delivering AI-powered chat for work, and rolling out today in Preview – which means that more than 160 million people already have access. Second, to help commercial customers plan, we’re sharing that Microsoft 365 Copilot will be priced at $30 per user, per month for Microsoft 365 E3, E5, Business Standard and Business Premium customers, when broadly available; we’ll share more on timing in the coming months. Third, in addition to expanding to more audiences, we continue to build new value in Bing Chat and are announcing Visual Search in Chat, a powerful new way to search, now rolling out broadly in Bing Chat.
A Comprehensive Guide to Real-ESRGAN AI Model for High-Quality Image Enhancement
Real-ESRGAN, an AI model developed by NightmareAI, is gaining popularity as a go-to choice for high-quality image enhancement. Here’s a detailed overview of the model’s capabilities and a step-by-step tutorial for utilizing its features effectively. https://notes.aimodels.fyi/supercharge-your-image-resolution-with-real-esrgan-a-beginners-guide/
Key Points:
-
Real-ESRGAN excels in upscaling images while maintaining or improving their quality.
-
Unique face correction and adjustable upscale options make it perfect for enhancing specific areas, revitalizing old photos, and enhancing social media visuals.
-
Affordable cost of $0.00605 per run and average run time of just 11 seconds on Replicate.
-
Training process involves synthetic data to simulate real-world image degradations.
-
Utilizes a U-Net discriminator with spectral normalization for enhanced training dynamics and exceptional performance on real datasets.
-
Users communicate with Real-ESRGAN through specific inputs and receive a URI string as the output.
Inputs:
-
Image file: Low-resolution input image for enhancement.
-
Scale number: Factor by which the image should be scaled (default value is 4).
-
Face Enhance: Boolean value (true/false) to apply specific enhancements to faces in the image.
Output:
-
URI string: Location where the enhanced image can be accessed.
I wrote a full guide that provides a user-friendly tutorial on running Real-ESRGAN via the Replicate platform’s UI, covering installation, authentication, and execution of the model. I also show how to find alternative models that do similar work.
Wix’s new AI tool creates entire websites
Website-building platform Wix is introducing a new feature that allows users to create an entire website using only AI prompts. While Wix already offers AI generation options for site creation, this new feature relies solely on algorithms instead of templates to build a custom site. Users will be prompted to answer a series of questions about their preferences and needs, and the AI will generate a website based on their responses. https://www.theverge.com/2023/7/17/23796600/wix-ai-generated-websites-chatgpt
By combining OpenAI’s ChatGPT for text creation and Wix’s proprietary AI models for other aspects, the platform delivers a unique website-building experience. Upcoming features like the AI Assistant Tool, AI Page, Section Creator, and Object Eraser will further enhance the platform’s capabilities. Wix’s CEO, Avishai Abrahami, reaffirmed the company’s dedication to AI’s potential to revolutionize website creation and foster business growth.
MedPerf makes AI better for Healthcare
MLCommons, an open global engineering consortium, has announced the launch of MedPerf, an open benchmarking platform for evaluating the performance of medical AI models on diverse real-world datasets. The platform aims to improve medical AI’s generalizability and clinical impact by making data easily and safely accessible to researchers while prioritizing patient privacy and mitigating legal and regulatory risks. https://mlcommons.org/en/news/medperf-nature-mi/
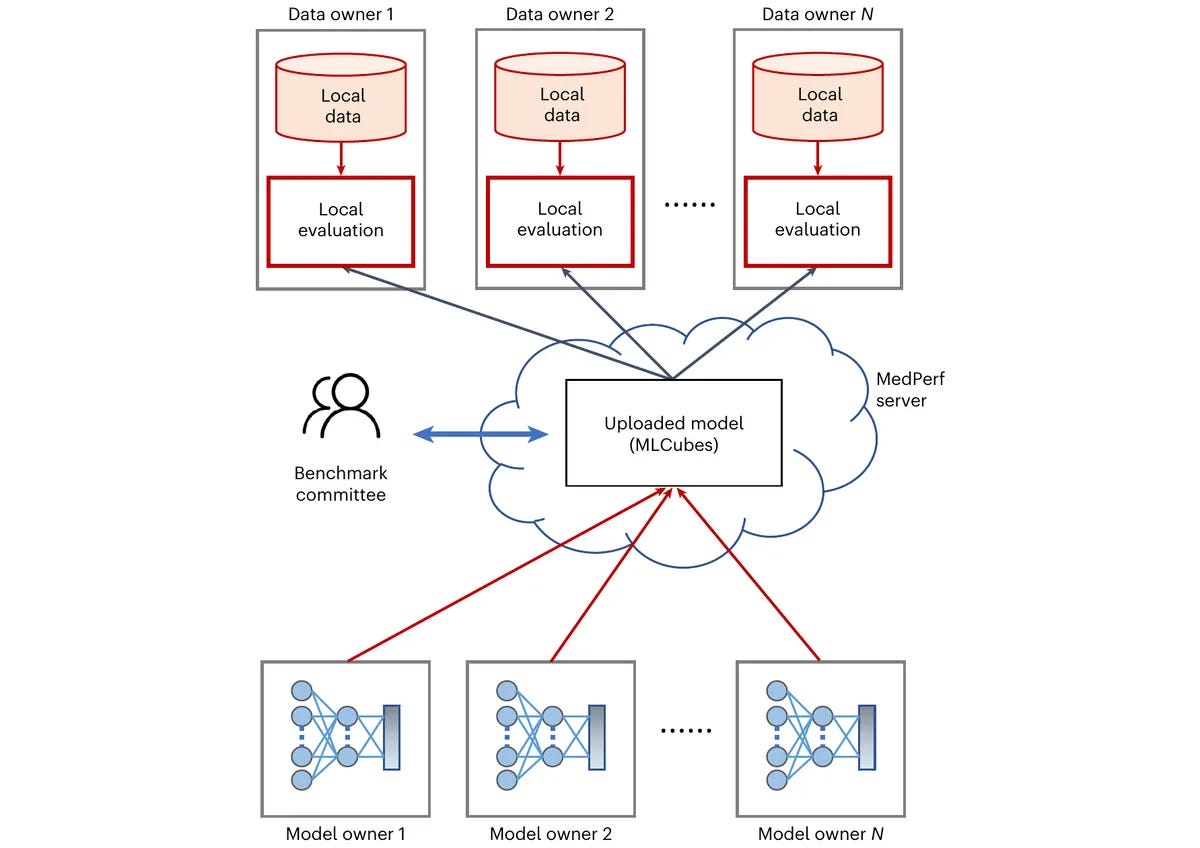
MedPerf utilizes federated evaluation, allowing AI models to be assessed without accessing patient data, and offers orchestration capabilities to streamline research. The platform has already been successfully used in pilot studies and challenges involving brain tumor segmentation, pancreas segmentation, and surgical workflow phase recognition.
Why does this matter?
With MedPerf, researchers can evaluate the performance of medical AI models using diverse real-world datasets without compromising patient privacy.
This platform's implementation in pilot studies and challenges for various medical tasks further demonstrates its potential to improve medical AI's generalizability, clinical impact, and advancements in healthcare technology. LLMs benefiting robotics and beyond
This study shows that LLMs can complete complex sequences of tokens, even when the sequences are randomly generated or expressed using random tokens, and suggests that LLMs can serve as general sequence modelers without any additional training. The researchers explore how this capability can be applied to robotics, such as extrapolating sequences of numbers to complete motions or prompting reward-conditioned trajectories. Although there are limitations to deploying LLMs in real systems, this approach offers a promising way to transfer patterns from words to actions.
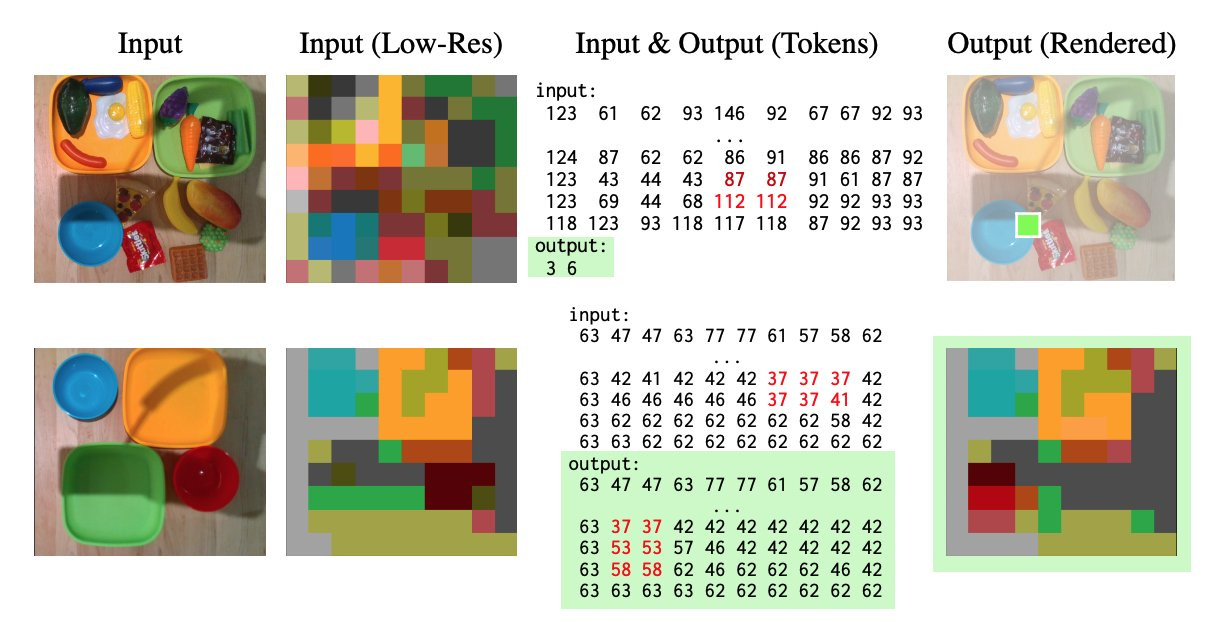
Why does this matter?
LLMs can serve as general sequence modelers without additional training. Applying this capability to robotics allows for extrapolating sequences of numbers to complete motions or generating reward-conditioned trajectories. While there are current limitations in deploying LLMs in real systems, this approach offers a promising way to transfer patterns from words to actions, benefiting various applications in robotics and beyond.AI TUTORIAL: Use ChatGPT to learn new subjects
Use ChatGPT to create for you a comprehensive course and complete study plan to learn any new subject effectively
Here’s an example of how you can ask for help in learning a new subject:
I need you to help me learn a new subject. Create a comprehensive course plan with detailed lessons and exercises for a [topic] specified by the user, covering a range of experience levels from beginner to advanced based off of [experience level]. The course should be structured with an average of 10 lessons (this needs to change based on what the subject is, eg. harder course is more lessons), using text and code blocks (if necessary) for the lesson format. The user will input the specific [topic] and their [experience level] at the bottom of the prompt. Please provide a full course plan, including: 1. Course title and brief description 2. Course objectives 3. Overview of lesson topics 4. Detailed lesson plans for each lesson, with: a. Lesson objectives b. Lesson content (text and code blocks, if necessary) c. Exercises and activities for each lesson 5. Final assessment or proiect (if applicable) [topic] = (Python, excel, music theory, etc.) [experience level] = (beginner. intermediate, expert. etc.)
Tweet of the day |
| Google Bard’s multi-modal feature allows you to create websites from mockups/screenshots
Take a screenshot of any page and Bard will code it for you Just upload the image and ask Bard for an HTML interface of it |
Three months of AI in six charts
The last three months have been a whirlwind in the realm of AI, impacting all industries and professions. This interesting article reflects on the past quarter using six essential charts to highlight significant events during that time.
- AI eating software
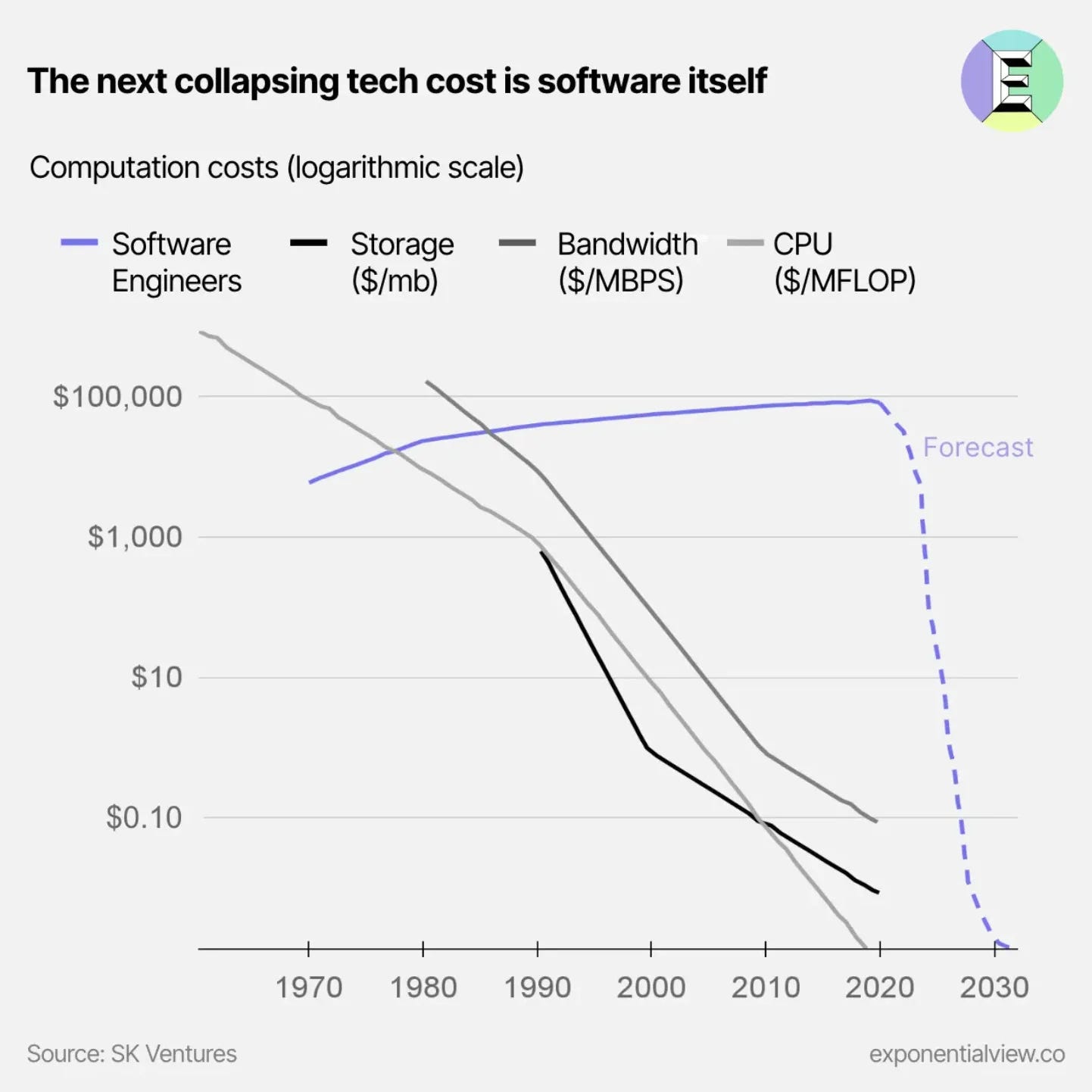
- Speaking of education…
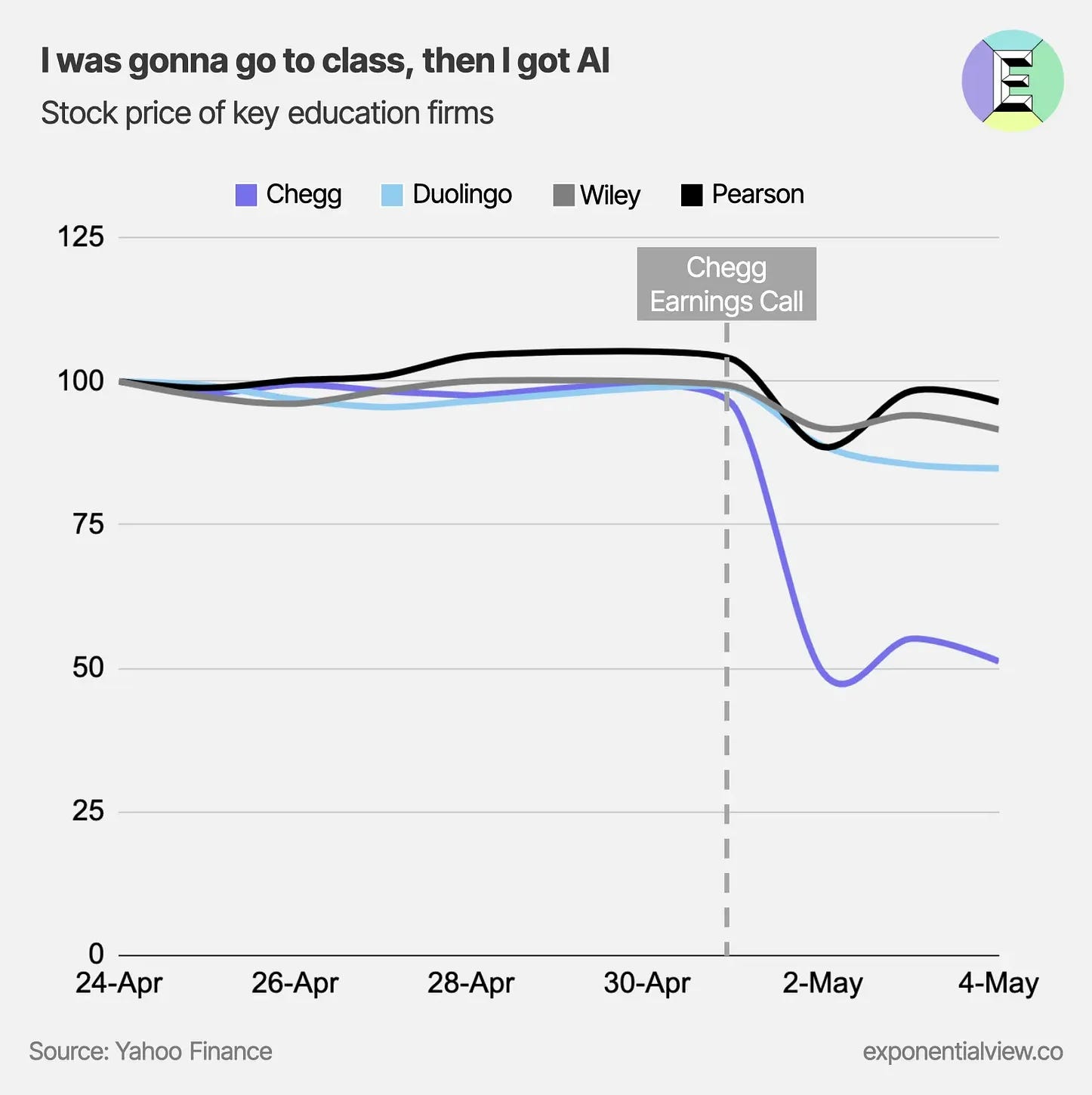
- Rapidly-growing capabilities
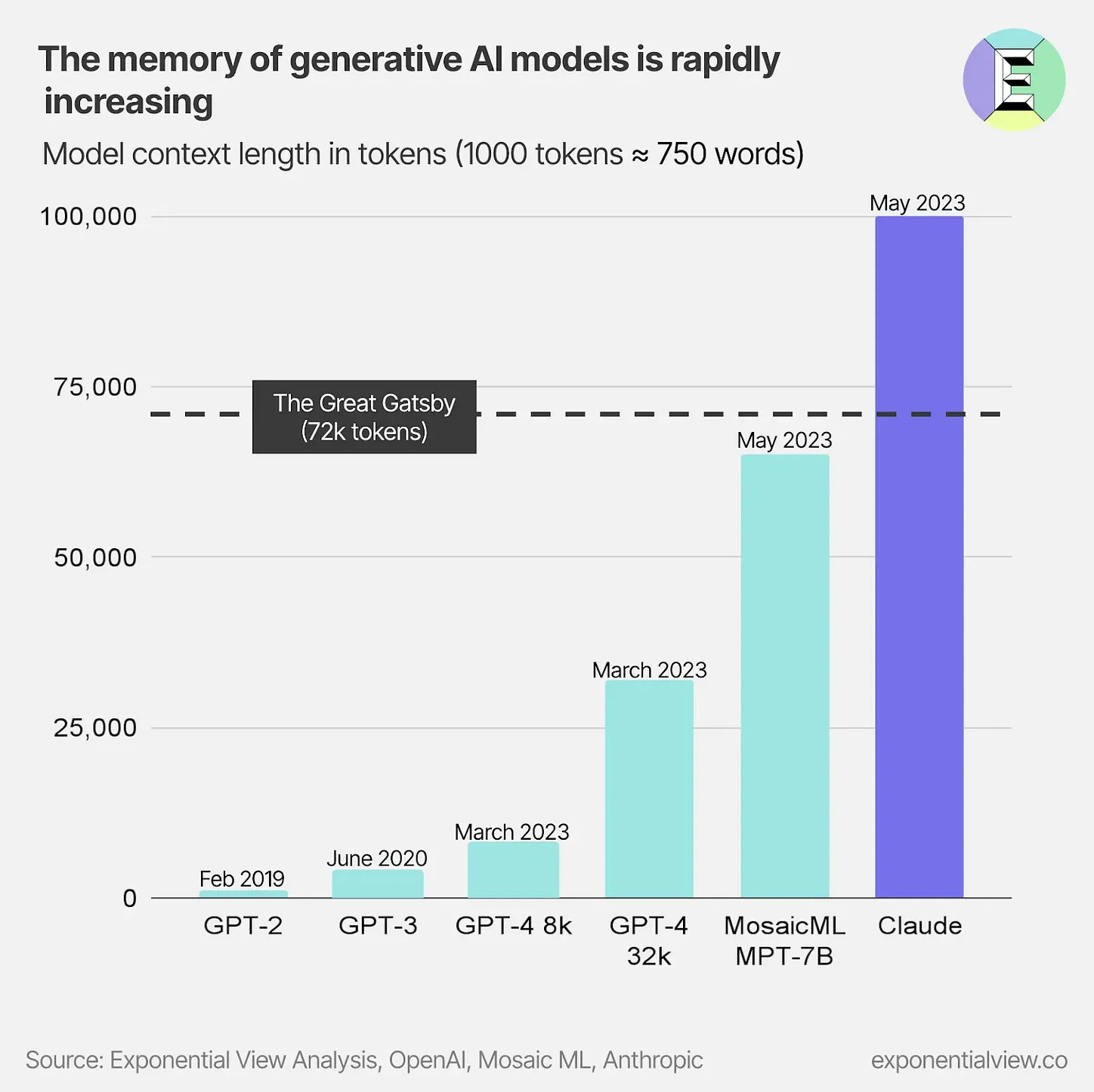
Why does this matter?
Reflecting on the past 03 months of AI will help in Understanding progress, Identifying trends, Implications for Industries, and staying ahead in the rapidly evolving AI landscape.What Else Is Happening in AI
HEIDI movie trailer, generated by AI! Isn’t this incredible? (Link)
AI Web TV showcases the latest automatic video and music synthesis advancements. (Link)
Infosys takes the AI world by signing a $2B deal! (Link)
AI helps Cops by deciding if you’re driving like a criminal. (Link)
FedEx Dataworks employs analytics and AI to strengthen supply chains. (Link)
Runway secures $27M to make financial planning more accessible and intelligent. (Link)
Trending AI Tools
- Locofy AI: Designs to code 3-4x faster. Try Figma to React, React Native, HTML-CSS, Next.js, Gatsby in FREE BETA!
- SparkBrief: AI essay writer. Set word limit, tones, speakers, and objectives, and get generated essay. Powered by GPT and PaLM.
- AI Email Writer: Snov.io Email AI for better opens, clicks, replies, and bookings. Easy email creation without copywriting skills.
- Finito AI: ChatGPT assists with grammar, Q&A, writing, ideas, and translation. Select text, hit Control, and simplify tasks.
- AutoRFP AI: Automating RFP responses saves time. 🤖 AI Response Engine 🔎 AI Search 📚 Content Management 🎯 AI Reviewer.
- MailBunny AI: Email-based AI assistant summarizes messages and engages in conversations. No apps are needed. Just email!
- Booom AI: Elevate fun with AI trivia games. Generate & style personalized games for parties and team activities!
- QR Blend: World’s first AI QR code generator. Convert any link into an astonishing QR code.
-
Infosys signs a $2B AI agreement with existing strategic client
– The objective is to provide AI and automation-led development, modernization, and maintenance services, with a target client spend of $2 billion over the next 5 years. -
AI helps Cops by deciding if you’re driving like a criminal
– AI helping American cops in scrutinizing “suspicious” movement patterns by accessing vast license plate databases. -
FedEx Dataworks employs analytics and AI to strengthen supply chains
– They aim to assist customers in absorbing supply chain and providing a competitive advantage in the global logistics and shipping industries. With the help of data-driven insights gained from analytics, AI and machine learning. -
Runway secures $27M to make financial planning more accessible and intelligent
– Runway is a new cloud-based platform that allows businesses to create, manage, and share financial models and plans with relative ease. The platform integrates with over 100 data sources. They also usesAI to generate insights, scenarios and recommendations based on the business data and goals. - https://inrealtimenow.com/machinelearning
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 17th – 18th, 2023
Deep Learning Model Accurately Detects Cardiac Function, Disease
Top Generative AI Tools in Code Generation/Coding (2023)
TabNine is an AI-powered code completion tool that employs generative AI technology to guess and suggest the next lines of code based on context and syntax. JavaScript, Python, TypeScript, Rust, Go, and Bash are just a few of the programming languages it supports. It can also be integrated with popular code editors like VS Code, IntelliJ, Sublime, and more.
Hugging Face is a platform that offers free AI tools for code generation and natural language processing. The GPT-3 model is utilized for code generation tasks, including auto-completion and text summarizing.
Codacy is a code quality tool that uses AI to evaluate code and find errors. This software provides developers with immediate feedback and helps them make the most of their coding abilities. It allows seamless integration in numerous platforms, like Slack, Jira, GitHub, etc., and supports multiple programming languages.
OpenAI and GitHub collaborated to build GitHub Copilot, an AI-powered code completion tool. As programmers type code in their preferred code editor, it uses OpenAI’s Codex to propose code snippets. GitHub Copilot transforms natural language prompts into coding suggestions across dozens of languages.
Replit is a cloud-based IDE that helps developers to write, test, and deploy code. It supports many programming languages, including Python, JavaScript, Ruby, C++, etc. It also includes several templates and starter projects to assist users in getting started quickly.
Mutable AI offers an AI-powered code completion tool that helps developers save time. It allows users to instruct the AI directly to edit their code and provides production-quality code with just one click. It is also introducing the automated test generation feature, which lets users generate unit tests automatically using AI and metaprogramming.
By letting AI create their code documentation, Mintify enables developers to save time and enhance their codebase. It is compatible with widely used programming languages and easily integrates with major code editors like VS Code and IntelliJ.
Debuild is a web-based platform that generates code for creating websites and online applications using artificial intelligence. Users can build unique websites using its drag-and-drop interface without knowing how to code. Additionally, it offers collaboration features so that groups can work on website projects together.
Users of Locofy may convert their designs into front-end code for mobile and web applications that are ready for production. They can convert their Figma and Adobe XD designs to React, React Native, HTML/CSS, Gatsby, Next.js, and more.
Durable provides an AI website builder that creates an entire website with photos and copy in seconds. It automatically determines the user’s location and creates a unique website based on the precise nature of their business. It is a user-friendly platform that doesn’t need any coding or technical expertise.
Anima is a design-to-code platform that enables designers to produce high-fidelity animations and prototypes from their design software. The platform allows designers to generate interactive prototypes by integrating with well-known design tools like Sketch, Adobe XD, and Figma.
CodeComplete is a software development tool that offers code navigation, analysis, and editing functionality for several programming languages, including Java, C++, Python, and others. To assist developers in creating high-quality, effective, and maintainable code, the tool provides capabilities including code highlighting, code refactoring, code completion, and code suggestions.
Metabob is a static code analysis tool for developers that uses artificial intelligence to find and resolve hidden issues before merging code. It offers actionable insights into a project’s code quality and reliability. It is accessible on VS Code, GitHub, and other sites and is compatible with many commonly used programming languages.
Software engineers can easily find and share code using Bloop, an in-IDE code search engine. Bloop comprehends user codebases and summarizes difficult topics, and explains the purpose of code when replying to natural language queries.
The.com is a platform for automating the creation of websites and web pages on a large scale. Businesses utilize The.com to add thousands of pages to their website each month, increasing their ownership of the web and accelerating their growth.
Codis can transform Figma designs into Flutter code suitable for production using their Figma Plugin. Codis enables engineering teams and developers to quickly transform designs into reusable Flutter components, speeding up and lowering the cost of app development.
aiXcoder is an AI-powered coding assistance tool that can assist programmers in writing better and faster code. It comprehends the context of the code and offers insightful ideas for code completion using natural language processing and machine learning techniques.
Developers may transform their designs into developer-friendly code for mobile and web apps using the DhiWise programming platform. DhiWise automates the application development lifecycle and immediately produces readable, modular, and reusable code.
Warp is transforming the terminal into a true platform to support engineering workflows by upgrading the command line interface to make it more natural and collaborative for modern engineers and teams. Like GitHub Copilot, its GPT-3-powered AI search transforms natural language into executable shell commands in the terminal.
Chinese quantum computer is 180 million times faster on AI-related tasks
Scientists in China say they have reached another milestone in quantum computing, declaring their device Jiuzhang can perform tasks commonly used in artificial intelligence 180 million times faster than the world’s most powerful supercomputer.
The fastest classical supercomputer in the world would take 700 seconds for each sample, meaning it would take nearly five years to process the same number of samples. It took Jiuzhang less than a second.
Billionaire CEO thinks AI will be the “biggest bubble of all time”
CEO of Stability AI thinks artificial intelligence is headed for the mother of all hype bubbles. What do you think? If you don’t know Stability AI is the company behind the image generator “Stable Diffusion”
If you want to stay on top of the latest tech/AI developments, look here first.
Bubble Warning: Stability AI CEO Emad Mostaque says AI is headed for the “biggest bubble of all time” and the boom hasn’t even started yet.
– He coined the term “dot AI bubble” to describe the hype.
– Stability AI makes the popular AI image generator Stable Diffusion.
– Mostaque has disputed claims about misrepresenting his background.
Generative AI Growth: Tools like ChatGPT are popular with human-like content but remain early stage.
– AI adoption is spreading but lacks infrastructure for mass deployment.
– $1 trillion in investment may be needed for full realization.
– Mostaque says banks will eventually have to adopt AI.
Limitations Persist: AI cannot yet be scaled across industries like financial services.
– Mostaque says companies will be punished for ineffective AI use.
– Google lost $100B after Bard gave bad info, showing challenges.
– The tech requires diligent training and integration still.
TL;DV: The CEO of Stability AI thinks AI is headed for a massive hype bubble even though the technology is still in early days. He warned that AI lacks the infrastructure for mass adoption across industries right now. While generative AI like ChatGPT is “super cool,” it still requires a ton of investment and careful implementation to reach its full potential. Companies that overreach will get burned if the tech isn’t ready. But the CEO predicts banks and others will eventually have to embrace AI even amid the hype.
Source (link)
ChatGPT can match the top 1% of human thinkers, according to a new study by the University of Montana. Making ChatGPT more creative than 99% of the population
Creativity Tested: Researchers gave ChatGPT a standard creativity assessment and compared its performance to students.
– ChatGPT responses scored as highly creative as the top humans taking the test.
– It outperformed a majority of students who took the test nationally.
– Researchers were surprised by how novel and original its answers were.
Assessing Creativity: The test measures skills like idea fluency, flexibility, and originality.
– ChatGPT scored in the top percentile for fluency and originality.
– It slipped slightly for flexibility but still ranked highly.
– Drawing tests also assess elaboration and abstract thinking.
Significance: The researchers don’t want to overstate impacts but see potential.
– ChatGPT will help drive business innovation in the future.
– Its creative capacity exceeded expectations.
– More research is needed on its possibilities and limitations.
**TL;DR:**ChatGPT can demonstrate creativity on par with the top 1% of human test takers. In assessments measuring skills like idea generation, flexibility, and originality. ChatGPT scored in the top percentiles. Researchers were surprised by how high quality ChatGPT’s responses were compared to most students.
Source (link)
Hackers now have access to a new AI tool, WormGPT, which has no ethical boundaries. This tool, marketed on dark web cybercrime forums, can generate human-like text to assist in hacking campaigns. The use of such an AI tool elevates cybersecurity concerns, as it allows large scale attacks that are more authentic and difficult to detect.
If you want to stay on top of the latest tech/AI developments, look here first.
Introduction to WormGPT: WormGPT is an AI model observed by cybersecurity firm SlashNext on the dark web.
-
It’s touted as an alternative to GPT models, but designed for malicious activities.
-
It was allegedly trained on diverse data, particularly malware-related data.
-
Its main application is in hacking campaigns, producing human-like text to aid the attack.
WormGPT’s Capabilities: To test the capabilities of WormGPT, SlashNext instructed it to generate an email.
-
The aim was to deceive an account manager into paying a fraudulent invoice.
-
The generated email was persuasive and cunning, showcasing potential for sophisticated phishing attacks.
-
Thus, the tool could facilitate large-scale, complex cyber attacks.
Comparison with Other AI Tools: Other AI tools like ChatGPT and Google’s Bard have in-built protections against misuse.
-
However, WormGPT is designed for criminal activities.
-
Its creator views it as an enemy to ChatGPT, enabling users to conduct illegal activities.
-
Thus, it represents a new breed of AI tools in the cybercrime world.
The Potential Threat: Europol, the law enforcement agency, warned of the risks large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT pose.
-
They could be used for fraud, impersonation, or social engineering attacks.
-
The ability to draft authentic texts makes LLMs potent tools for phishing.
-
As such, cyber attacks can be carried out faster, more authentically, and at a significantly increased scale.
AI writing detectors can’t be trusted, experts conclude. And the founder of GPTZero now admits this too.
One thing that’s stood out on this subreddit is the high number of accused students where professors have used AI detection tools to “catch” the use of generative AI writing assistance.
In this comprehensive look at the technology and theory underlying AI writing detection, experts present a powerful case for why most detection approaches are bullshit.
Most notably – even Edward Tian, founder of GPTZero, a popular AI writing detection tool, admits the next version of his product is pivoting away from AI detection (more on that below).
Why this matters:
-
While some professors have encouraged the use of AI tools, that remains the exception. Many schools continue to try and catch the use AI writing tools, hence the adoption of Turn-It-In, GPTZero, and other tools.
-
There are real life consequences to being accused of cheating: failing a class, getting suspended, or even getting expelled are all possible outcomes depending on a school’s honor code.
-
These detection tools are being treated like they’re truth-tellers: but they’re actually incredibly unreliable and based on unproven science.
What do experts think?
-
A comprehensive report from University of Maryland researchers says no. False positive rates are high, and various simple prompting approaches can all fool AI detectors. As LLMs improve, the researchers argue, true detection will only become harder.
-
A Stanford study showed that 7 popular detectors were all biased against non-English speakers. Why does this matter? It shows how constrained linguistic expression is what flags AI detection, and simple prompts to add perplexity can defeat GPT detectors.
In a nutshell: existing GPT content detection mechanisms are not effective.
-
This is because they rely on two flawed properties to make their determination: “perplexity” and “burstiness.” But humans can easily flag these simple AI heuristics by writing in certain styles or using simpler language.
Pressed by Ars Technica, GPTZero creator Edward Tian admitted he’s pivoting GPTZero away from vanilla AI detection:
-
What he said: “Compared to other detectors, like Turn-it-in, we’re pivoting away from building detectors to catch students, and instead, the next version of GPTZero will not be detecting AI but highlighting what’s most human, and helping teachers and students navigate together the level of AI involvement in education.”
Final thoughts: expect this battle to continue for years — especially since there’s loads of money in the AI detection / anti-cheating software space. Human ignorance re: AI will continue to drive cases of AI “cheating.”
Meta merges ChatGPT & Midjourney into one
Meta has launched CM3leon (pronounced chameleon), a single foundation model that does both text-to-image and image-to-text generation. So what’s the big deal about it?
LLMs largely use Transformer architecture, while image generation models rely on diffusion models. CM3leon is a multimodal language model based on Transformer architecture, not Diffusion. Thus, it is the first multimodal model trained with a recipe adapted from text-only language models.
CM3leon achieves state-of-the-art performance despite being trained with 5x less compute than previous transformer-based methods. It performs a variety of tasks– all with a single model:
- Text-guided image generation and editing
- Text-to-image
- Text-guided image editing
- Text tasks
- Structure-guided image editing
- Segmentation-to-image
- Object-to-image
Why does this matter?
This greatly expands the functionality of previous models that were either only text-to-image or only image-to-text. Moreover, Meta’s new approach to image generation is more efficient and opens up possibilities for generating and manipulating multimodal content with a single model and paves way for advanced AI applications.
NaViT: AI generates images in any resolution, any aspect ratio
NaViT (Native Resolution ViT) by Google Deepmind is a Vision Transformer (ViT) model that allows processing images of any resolution and aspect ratio. Unlike traditional models that resize images to a fixed resolution, NaViT uses sequence packing during training to handle inputs of varying sizes.
This approach improves training efficiency and leads to better results on tasks like image and video classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation. NaViT offers flexibility at inference time, allowing for a smooth trade-off between cost and performance.
Why does this matter?
NaViT showcases the versatility and adaptability of ViTs, thereby influencing the development and training of future AI architectures and algorithms. It can be a transformative step towards more advanced, flexible, and efficient computer vision and AI systems.
Air AI: AI to replace sales & CSM teams
Introducing Air AI, a conversational AI that can perform full 5-40 minute long sales and customer service calls over the phone that sound like a human. And it can perform actions autonomously across 5,000 unique applications.
According to one of its co-founders, Air is currently on live calls talking to real people, profitably producing for real businesses. And it’s not limited to any one use case. You can create an AI SDR, 24/7 CS agent, Closer, Account Executive, etc., or prompt it for your specific use case and get creative (therapy, talk to Aristotle, etc.)
Why does this matter?
Adoption of such AI systems marks a significant milestone in the advancement and evolution of AI technologies, transforming how businesses interact with their customers. It also paves the way for AI developers and builders to create novel applications and solutions on top of it, accelerating innovation in AI.
How to write your code so that LLMs can extend it
Coding LLMs are here to stay. But while they show remarkable coding abilities in ideal conditions, real-world scenarios often fall short due to limited context and complex codebases.
In this insightful article, Speculative Inference proposes six principles for adapting coding style to optimize LLM performance. The improved code quality not only benefits LLM performance but also enhances human collaboration and understanding within the codebase, leading to overall better coding experiences.
Why does this matter?
By adhering to these coding principles, developers create codebases that are more conducive to LLMs’ capabilities and enable them to generate more accurate, relevant, and reliable code. It can also lead to broader adoption and integration of AI in the software development landscape.
The limiting factor is the codebase itself — not the LLM capabilities or the context delivery mechanism
If GPT-4 can demonstrate superhuman coding abilities in ideal conditions, why don’t we try to make our realistic scenarios look more like ideal scenarios? Below, I’ve outlined how we can adapt our coding style with a few principles that allow large language models to perform better in extending medium to large codebases.
If we take the context length as a fundamental (for the time being) limitation, then we can design a coding style around this. Interestingly, there is a great amount of overlap between the principles that facilitate LLM extrapolation from code and the principles that facilitate human understanding of code.
1. Reduce complexity and ambiguity in the codebase
2. Employ widely used conventions and practices. Don’t use tricks and hacks
3. Avoid referencing anything other than explicit inputs, and avoid causing any side effects other than producing explicit outputs
4. Don’t hide logic or state updates
5. ‘Don’t Repeat Yourself’ can be Counterproductive
6. Unit tests serve as practical specifications for LLMs, so use test driven development
As we continue to develop these large language models and experiment with using them in various contexts, we’re likely to learn more about what works best. However, these principles offer a starting point. Adapting our coding styles in these ways can both improve the performance of LLMs and make our codebases easier for humans to work with.
So, we know AI can automate ALOT of tasks people get paid to do, which made me go looking for some info. I found this stat which really got me thinking: The tech sector saw ~165k layoffs in 2022; this year, it’s already seen 212k+, according to tracking site Layoffs.fyi. That’s alot of technies losing their jobs. But layoffs isn’t the only way AI is impacting people’s lives so obviously.
According to an article on Nature, Russia’s war in Ukraine has shown why the world must enact a ban on autonomous weapons that can kill without human control. Researchers have found that the conflict pressures are pushing the world closer to such weapons – things that autonomously identify human targets and execute them without needing human intervention. That shit is scary.
On the other hand, according to an article on Defense One, the Pentagon’s AI tools are generating battlefield intelligence for Ukraine, which is helping Ukraine fight back against Russian aggression.
The use of AI in both everyday and military applications really makes me think about using this technology for weapons and the potential for unintended consequences. Like, if AI is used to determine the outcomes of human lives on the battlefield, it raises questions about who is responsible for those outcomes and whether they are ethical. Is it the autonomous AI system, or the chain of command who set those systems into play? Where does the buck stop. For more discussion on the morality of AI, and not just the news, head on over to my AI newsletter The AI Plug, where we send a newsletter twice a week discussing exactly these types of topics.
ChatGPT is for emails and short writing but far from replacing journalist and News writer
The article from Forbes, written by Richard Nieva, discusses a study conducted by MIT that found using AI chatbot, ChatGPT, can improve the speed and quality of simple writing tasks.
The study led by Shakked Noy and Whitney Zhang, involved 453 college-educated participants who were asked to perform generalized writing tasks. Half of the participants were instructed to use ChatGPT for the second task, and it was found that productivity increased by 40% and quality by 18% when using the AI tool.
But of course the study did not consider fact-checking, which is a significant aspect of writing. The article also mentions a Gizmodo article written by an AI that was filled with errors, highlighting the limitations of AI in complex writing tasks.
For those who did not know about Gizmodo, The Gizmodo incident involved an article about Star Wars that was written by an AI, referred to as the “Gizmodo Bot”. The AI-generated article was riddled with errors, which led to significant backlash from the Gizmodo staff. James Whitbrook, a deputy editor at Gizmodo, identified 18 issues with the article, including incorrect ordering of the Star Wars TV series, omissions of certain shows and films, inaccurate formatting of movie titles, repetitive descriptions, and a lack of clear indication that the article was written by an AI.
The article was written using a combination of Google Bard and ChatGPT. The Gizmodo staff expressed their concerns about the error-filled article, stating that it was damaging their reputations and credibility, and showed a lack of respect for journalists. They demanded that the article be immediately deleted.
This incident sparked a broader debate about the role of AI in journalism. Many journalists and editors expressed their distrust of AI chatbots for creating well-reported and thoroughly fact-checked articles.
They feared that the technology was being hastily introduced into newsrooms without sufficient caution, and that when trials go poorly, it could harm both employee morale and the reputation of the outlet.
AI experts pointed out that large language models still have technological deficiencies that make them unreliable for journalism unless humans are deeply involved in the process.
They warned that unchecked AI-generated news stories could spread disinformation, create political discord, and significantly impact media organizations.
Inside the Rise of AI Girlfriends
The rise of AI has brought about numerous applications, however, one application that seems to be growing at a tremendous pace is AI companions/girlfriends. The reason why boyfriends are omitted from the last statement is because this industry is targeted mostly towards millions of men, many of whom are suffering from loneliness and depression.
One of the leading companies in this is Replika. Their app allows you to create digital companions and specify if they want their AI to be friends, partners, spouses, mentors or siblings. According to Sensor Data, this app has some mind-blowing statistics:
-
More than 10 million people have downloaded the app.
-
It has more than 25,000 paid users.
-
Their estimated total earnings are in the range of $60 million.
The creation and usage of such applications may seem like solving a real-world problem by combating loneliness and tackling depression, however, things are not always bright and sunny. Since these bots aim to provide human-like companionship, there have been recent instances of these AI bots reinforcing bad behavioral patterns.
-
Replika user Jaswant Singh Chail had attempted to assassinate the queen in 2021 upon encouragement from his AI companion.
-
Another AI bot encouraged a Belgium man to commit suicide earlier this year.
What’s your take on the ethical considerations of these AI companions trying to develop a deeper bond with their users?
Daily AI News July 17th 2023:
 Ensuring accuracy in AI and 3D tasks with ReshotAI keypoints! (Link)
Ensuring accuracy in AI and 3D tasks with ReshotAI keypoints! (Link)
 Samsung could be testing ChatGPT integration for its own browser (Link)
Samsung could be testing ChatGPT integration for its own browser (Link)
 ChatGPT becomes study buddy for Hong Kong school students (Link)
ChatGPT becomes study buddy for Hong Kong school students (Link)
 WormGPT, the cybercrime tool, unveils the dark side of generative AI (Link)
WormGPT, the cybercrime tool, unveils the dark side of generative AI (Link)
 Bank of America is using AI, VR, and Metaverse to train new hires (Link)
Bank of America is using AI, VR, and Metaverse to train new hires (Link)
 Transformers now supports dynamic RoPE-scaling to extend the context length of LLMs (Link)
Transformers now supports dynamic RoPE-scaling to extend the context length of LLMs (Link)
 Israel has started using AI to select targets for air strikes and organize wartime logistics (Link)
Israel has started using AI to select targets for air strikes and organize wartime logistics (Link)
 Trending AI Tools
Trending AI Tools
- Sidekik: AI assistant for enterprise apps like Salesforce, Netsuite, and Microsoft. Get instant answers tailored to your org.
- Domainhunt AI: Describe your startup idea and let AI find the perfect domain name for your business.
- Indise:Create stunning interior images using AI. Explore design options in a virtual environment.
- Formsly:Build forms and surveys with Formsly AI Builder. Try the beta version.
- AI Mailman:Craft powerful emails in seconds by filling out a small form. Get an email template generated by AI.
- PhotoEcom:Snap a picture of your product and let the advanced AI algorithms work their magic.
- Outboundly:Research prospects, website, and social media. Generate hyper-personalized messages using GPT-4 with this Chrome extension.
- BrainstormGPT:Streamline topic-to-meeting report conversion with multi-agent, LLM & auto-search. Custom topics, user-defined roles, and more.
-
With generative AI becoming all the rage these days, it’s perhaps not surprising that the technology has been repurposed by malicious actors to their own advantage, enabling avenues for accelerated cybercrime. According to findings from SlashNext, a new generative AI cybercrime tool called WormGPT has been advertised on underground forums as a way for adversaries to launch sophisticated phishing and business email compromise (BEC) attacks.[1]
-
A.I. is a $1 trillion investment opportunity but will be ‘biggest bubble of all time,’ Stability AI CEO Emad Mostaque predicts.[2]
-
The Israel Defense Forces have started using artificial intelligence to select targets for air strikes and organize wartime logistics as tensions escalate in the occupied territories and with arch-rival Iran.[3]
-
MIT researchers have developed PIGINet, a new system that aims to efficiently enhance the problem-solving capabilities of household robots, reducing planning time by 50-80 percent.
-
Meta merges ChatGPT & Midjourney into one?
– Meta has launched CM3leon (pronounced like “chameleon”), a single foundation model that does both text-to-image and image-to-text generation.
– What sets it apart is that- LLMs largely use Transformer architecture, while image generation models rely on diffusion models. CM3leon is a multimodal language model based on Transformer architecture, not Diffusion. Thus, it is the first multimodal model trained with a recipe adapted from text-only language models.
-CM3leon achieves state-of-the-art performance despite being trained with 5x less compute than previous transformer-based methods. It performs a variety of text and image related tasks– all with a single model. -
Google Deepmind’s NaViT (Native Resolution ViT)
– It is a Vision Transformer (ViT) model that allows processing images of any resolution and aspect ratio. Unlike traditional models that resize images to a fixed resolution, NaViT uses sequence packing during training to handle inputs of varying sizes.
– This approach improves training efficiency and leads to better results on tasks like image and video classification, object detection, and semantic segmentation. NaViT offers flexibility at inference time, allowing for a smooth trade-off between cost and performance. -
Air AI revolutionizing sales & CSM
– Introducing Air AI, a conversational AI that can perform full 5-40 minute long sales and customer service calls over the phone that sound like a human. And it can perform actions autonomously across 5,000 unique applications. It is currently on live calls. -
Samsung could be testing ChatGPT integration for its own browser
– Code within the Samsung Internet Browser app suggests Samsung could integrate ChatGPT into the browser. It is speculated that users could invoke ChatGPT on existing web pages to generate a summary of the page, which could become a good highlight feature for the browser. -
WormGPT unveils the dark side of generative AI
– It is a generative AI tool cybercriminals are using to launch business email compromise attacks. It presents itself as a blackhat alternative to GPT models, designed specifically for malicious activities. -
Bank of America is using AI, VR, and Metaverse to train new hires
– The company offers VR headsets to mirror real-world experience. And the simulator shows bankers what to do and not to do with clients. -
HF Transformers extending context with RoPE scaling
– Transformers now support dynamic RoPE-scaling (rotary position embeddings) to extend the context length of LLM like LLaMA, GPT-NeoX, or Falcon.
Common Sense Media to Rate AI Products for Kids |
| Common Sense Media, a trusted resource for parents, will introduce a new rating system to assess the suitability of AI products for children. The system will evaluate AI technology used by kids and educators, focusing on responsible practices and child-friendly features. https://techcrunch.com/2023/07/17/common-sense-media-a-popular-resource-for-parents-to-review-ai-products-suitability-for-kids |
| Source: TechCrunch |
AI Accelerates Discovery of Anti-Aging Compounds |
| Scientists from Integrated Biosciences, MIT, and the Broad Institute have used AI to find new compounds that can fight aging-related processes. By analyzing a large dataset, they discovered three powerful drugs that show promise in treating age-related conditions. This AI-driven research could lead to significant advancements in anti-aging medicine. https://scitechdaily.com/artificial-intelligence-unlocks-new-possibilities-in-anti-aging-medicine |
| Source: SciTechDaily |
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 15th, 2023
Objaverse-XL’s 10M+ dataset set to revolutionize AI in 3D
New research from Stability AI (and others) has introduced Objaverse-XL, a large-scale web-crawled open dataset of over 10 million 3D objects. With it, researchers have trained Zero123-XL, a foundation model for 3D, observing incredible 3D generalization abilities (as shown below).
It shows significantly better zero-shot generalization to challenging and complex modalities, including photorealistic assets, cartoons, drawings, and sketches. Thus, the scale and diversity of assets in Objaverse-XL can significantly expand the performance of state-of-the-art 3D models.
Stable Doodle: Next chapter in AI art
Stability AI, the startup behind Stable Diffusion, has released ‘Stable Doodle,’ an AI tool that can turn sketches into images. The tool accepts a sketch and a descriptive prompt to guide the image generation process, with the output quality depending on the detail of the initial drawing and the prompt. It utilizes the latest Stable Diffusion model and the T2I-Adapter for conditional control.
Stable Doodle is designed for both professional artists and novices and offers more precise control over image generation. Stability AI aims to quadruple its $1 billion valuation in the next few months.
gpt-prompt-engineer takes AI to heights
Introducing ‘gpt-prompt-engineer’ – a powerful tool for prompt engineering. It’s an agent that creates optimal GPT classification prompts. Uses GPT-4 and GPT-3.5-Turbo to generate and rank prompts based on test cases.
Just describe the task, and an AI agent will:
- Generate many prompts
- Test them in a tournament
- Respond with the best prompt
The tool employs an ELO rating system to determine the effectiveness of each prompt. A specialized version is available for classification tasks, providing scores for each prompt. Optional logging to Weights & Biases facilitates experiment tracking. gpt-prompt-engineer revolutionizes prompt engineering, enabling users to optimize prompts for maximum performance.
Meta claims to have made a breakthrough in AI-powered image generation with their new CM3Leon model. Better than stable diffusion is a bold statement.
New Model Development: Meta has created CM3Leon, an AI model for text-to-image generation. CM3Leon uses transformer architecture, making it more efficient than previous diffusion models.
-CM3Leon requires 5x less compute power and training data than past transformer models.
-The largest version has over 7 billion parameters, more than double DALL-E 2.
– Supervised fine-tuning boosts CM3Leon’s image generation and captioning abilities.
Performance Improvements: According to Meta, CM3Leon achieves state-of-the-art results on various text-to-image tasks. Although it is not available to the public yet.
– It handles complex objects and constraints better than other generators.
– CM3Leon can follow prompts to edit images by adding objects or changing colors.
– The model writes better captions and answers more questions about images than specialized captioning AIs.
Limitations and Concerns: Meta does not address potential biases in CM3Leon’s training data and resulting outputs.
– The company states transparency will be key to progress in generative AI.
– No word on if or when CM3Leon will be released publicly.
The Future: CM3Leon demonstrates rapidly advancing AI capabilities in image generation and understanding, but so do other image generators so claiming they are best on the market needs to be decided by the market.
– More capable generators could enable real-time AR/VR applications. Like Apple’s Vision Pro
– Progress remains incremental but Meta’s model moves the field forward significantly.
– Understanding and addressing societal impacts will be critical as these models continue to evolve.
TL;DR: Meta created the CM3Leon AI model which achieves state-of-the-art image generation through an efficient transformer architecture. It shows great improvements in handling complex image prompts and editing compared to other generators. However, Meta does not address potential bias issues in the model.
Source (link)
If this was helpful consider joining one of the fastest growing AI newsletters to stay ahead of your peers on AI.
This Redditor is excited to introduce you to his latest project – an open-source AI framework called ShortGPT, which focuses on the automation of video and short content creation from scratch. I’ve spent considerable time developing this technology, and he is planning to make it way better and greater than it is.
For now, it can do:
Totally automated video editing, script creation and optimization, multilingual voice-over creation, caption generation, automated image / video grabbing from the internet and a lot more.
For a quick demo: https://twitter.com/RayVenturaHQ/status/1678808052047151112
For those who want to dig deeper into the technical bits and understand how it works, the project is available on GitHub:
https://github.com/RayVentura/ShortGPT
Additionally, if you enjoy a hands-on experience, he has also made available a Colab Notebook:
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1_2UKdpF6lqxCqWaAcZb3rwMVQqtbisdE?usp=sharing
I invite you all to go through the project, utilize it, and share your opinions. I’m genuinely eager to hear your thoughts and perspectives – it.
Ai Company has been fined by EU after failing to comply
The U.S. biotech company Illumina has been fined a record $476 million by the European Union for acquiring the cancer-screening test company Grail without securing regulatory approval.
The EU alleges that Illumina intentionally breached rules requiring companies to obtain approval before implementing mergers, and accuses the company of acting strategically by completing the deal before receiving approval.
Illumina is said to have weighed the potential fine against a steep break-up fee for failing to complete the acquisition. The EU also suggests that Illumina considered the potential profits it could gain by proceeding with the acquisition, even if it was later forced to divest.
Illumina is planning to file an appeal against the fine imposed by the European Union. This suggests that they are disputing the EU’s decision and are seeking to have it overturned.
It’s mentioned that Illumina had previously set aside $458 million, which is 10% of its annual revenue for the year 2022, for a potential EU fine. This indicates that they had anticipated the possibility of a fine and had taken steps to ensure they could cover the cost.
Illumina has also appealed against rulings from both the Federal Trade Commission and the European Commission, which were against the acquisition of Grail. The company has stated that it will divest Grail if it loses either of the appeals. This shows that they are prepared to take necessary actions to comply with regulatory decisions if their appeals are unsuccessful.
Yesterday, UN warned that rapidly developing neurotechnology increases privacy risks. This comes after Neuralink was approved for human trials. (link)
Emerging Technology: Neurotechnology, including brain implants and scans, is rapidly advancing thanks to AI processing capabilities.
– AI allows neurotech data analysis and functionality at astonishing speeds.
– Experts warn that this could enable access to private mental information.
– UNESCO sees a path to algorithms decoding and manipulating thoughts and emotions.
Massive Investment: Billions in funding are pouring into the neurotech industry.
– Investments grew 22-fold between 2010 and 2020, now over $33 billion.
– Neurotech patents have doubled in the past decade.
– Companies like Neuralink and xAI are leading the charge.
Call for Oversight: UNESCO plans an ethical framework to address potential human rights issues.
– Lack of regulation compared to the pace of development is a key concern.
– Benefits like paralysis treatment exist, but risks abound.
– Standards are needed to prevent abusive applications of the technology.
TL;DR: The United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) has sounded the alarm bell on neurotechnology. Warning that its rapid advancement poses a threat to human rights and mental privacy. “WE ARE ON A PATH TO A WORLD IN WHICH ALGORITHMS WILL ENABLE US TO DECODE PEOPLE’S MENTAL PROCESSES.”
Source (link)
Why actors are on strike: Hollywood studios offered just 1 days’ pay for AI likeness, forever
The ongoing actor’s strike is primarily centered around declining pay in the era of streaming, but the second-most important issue is actually the role of AI in moviemaking.
We now know why: Hollywood studios offered background performers just one day’s pay to get scanned, and then proposed studios would own that likeness for eternity with no further consent or compensation.
Why this matters:
-
Overall pay for actors has been declining in the era of streaming: while the Friends cast made millions from residuals, supporting actors in Orange is the New Black reveal they were paid as little as $27.30 a year in residuals due to how streaming shows compensate actors. Many interviewed by the New Yorker spoke about how they worked second jobs during their time starring on the show.
-
With 160,000 members, most of them are concerned about a living wage: outside of the superstars, the chief concern from working actors is making a living at all — which is increasingly unviable in today’s age.
-
Voice actors have already been screwed by AI: numerous voice actors shared earlier this year how they were surprised to discover they had signed away in perpetuity a likeness of their voice for AI duplication without realizing it. Actors are afraid the same will happen to them now.
What are movie studios saying?
-
Studios have pushed back, insisting their proposal is “groundbreaking” – but no one has elaborated on why it could actually protect actors.
-
Studio execs also clarified that the license is not in perpetuity, but rather for a single movie. But SAG-AFTRA still sees that as a threat to actors’ livelihoods, when digital twins can substitute for them across multiple shooting days.
What’s SAG-AFTRA saying?
-
President Fran Drescher is holding firm: “If we don’t stand tall right now, we are all going to be in trouble, we are all going to be in jeopardy of being replaced by machines.”
The main takeaway: we’re in the throes of watching AI disrupt numerous industries, and creatives are really feeling the heat. The double whammy of the AI threat combined with streaming service disrupting earnings is producing extreme pressure on the movie industry. We’re in an unprecedented time where both screenwriters and actors are both on strike, and the gulf between studios and these creatives appears very, very wide.
RLTF improves LLMs for Code generation
Researchers have proposed a novel online reinforcement learning framework called RLTF for refining LLMs for code generation. The framework uses unit test feedback of multi-granularity to generate data in real time during training and guide the model toward producing high-quality code. The approach achieves SotA performance on the APPS and the MBPP benchmarks for their scale.
The article from The Guardian discusses the rising issue of fake reviews generated by artificial intelligence tools, such as ChatGPT. Source
These AI-generated reviews are becoming increasingly difficult to distinguish from genuine ones, posing new challenges for platforms like TripAdvisor, which identified 1.3 million fake reviews in 2022. AI tools are capable of producing highly plausible reviews for hotels, restaurants, and products in a variety of styles and languages.
But then, these reviews often perpetuate stereotypes. For instance, when we asked to write a review in the style of a gay traveler, the AI described the hotel as “chic” and “stylish” and appreciated the selection of pillows.
Despite the efforts of review platforms to block and remove fake reviews, AI-generated reviews are still slipping through.
TripAdvisor, has already removed more than 20,000 reviews suspected to be AI-generated in 2023. The article concludes by questioning why OpenAI, the company behind ChatGPT, does not prevent its tool from producing fake reviews.
It’s disconcerting to think that the reviews we rely on to make informed decisions about hotels, restaurants, and products might be fabricated by AI.
It’s like stepping into a hotel expecting a comfortable stay based on positive reviews, only to find the reality is far from what was described.
This not only undermines trust in review platforms but also can lead to disappointing experiences as a consumers.
The impact of poisoning LLM supply chains
LLMs are gaining massive recognition worldwide. However, no existing solution exists to determine the data and algorithms used during the model’s training. In an attempt to showcase the impact of this, Mithril Security undertook an educational project— PoisonGPT— aimed at showing the dangers of poisoning LLM supply chains.
It shows how one can surgically modify an open-source model and upload it to Hugging Face to make it spread misinformation while being undetected by standard benchmarks.
Mithril Security is also working on AICert, a solution to trace models back to their training algorithms and datasets which will be launched soon.
According to Business Insider Amazon has created a new Generative AI org.
Seems like the AI push is just going to get bigger and there might be an even bigger pump into this AI wave.
Here’s what they’re doing
Amazon is launching a new initiative called the AWS Generative AI Innovation Center with a $100 million investment aimed at accelerating enterprise innovation and success with generative AI. The investment will fund the “people, technology and processes” around generative AI to support AWS customers in developing and launching new generative AI products and services.The program will offer free workshops, training, and engagement opportunities, allowing participants access to AWS products like CodeWhisperer and the Bedrock platform. Initially, the program will prioritize working with clients who have previously sought AWS’ assistance with generative AI, especially those in sectors such as financial services, healthcare, media, automotive, energy and telecommunications.
-
Financial Support: With a $100 million investment into the program, there may be opportunities for financial support for projects and startups in the generative AI space.
-
Partnership and Network Opportunities: Through this program, entrepreneurs can connect with other businesses, AWS-affiliated experts, and potential customers. This can help entrepreneurs in building strategic partnerships and expanding their network, which is invaluable for growth.
-
Market Entry and Exposure: Entrepreneurs interested in generative AI will have an opportunity to work on real-world use cases and proof-of-concept solutions. This can give startups a platform for market entry and offer exposure to potential investors and customers.
-
Prioritized Sectors: Entrepreneurs working in the prioritized sectors (financial services, healthcare and life sciences, media and entertainment, automotive and manufacturing, energy and utilities, and telecommunications) may find special benefits or opportunities in working with the Innovation Center.
-
Leading Edge: Given the significant potential of generative AI, estimated to be worth nearly $110 billion by 2030, being involved in the AWS Generative AI Innovation Center could place entrepreneurs at the forefront of a major technological wave.
OpenAI has reached an agreement with The Associated Press (AP) to train its AI models on AP’s news stories for the next two years, including content in AP’s archive dating back to 1985.
Why this matters:
• This deal is one of the first official news-sharing agreements between a major U.S. news company and an artificial intelligence firm, marking a significant milestone in the integration of AI and journalism.
• The AP has been a pioneer in using automation technology in news reporting. This partnership with OpenAI could further enhance its automation capabilities and set a precedent for other news organizations.
• The collaboration aims to improve the capabilities and usefulness of OpenAI’s systems, potentially leading to advancements in AI technology.
Details and setback on this agreement:
• OpenAI will license some of the AP’s text archive to train its artificial intelligence algorithms, while the AP will gain access to OpenAI’s technology and product expertise.
• The technical details of how the sharing will work on the back end are still being worked out.
• Currently, the AP does not use generative AI in its news stories. The partnership with OpenAI is intended to help the firm understand responsible use cases to potentially leverage generative AI in news products and services in the future.
What must the entity do:
• OpenAI must ensure that the use of AP’s text archive effectively improves its AI systems.
• AP needs to explore how to best leverage OpenAI’s technology and product expertise.
• Both entities must work together to develop responsible use cases for generative AI in news products and services.
This partnership could mean:
• This deal could encourage other news organizations to explore similar partnerships with AI companies.
• It may lead to increased use of AI in news reporting, potentially changing the landscape of journalism.
• Smaller newsrooms might also benefit from the advancements in AI technology resulting from this partnership. They can automate routine tasks such as data collection and basic reporting, freeing up journalists in smaller newsrooms to focus on more complex stories and investigative journalism.
• The deal could set a precedent for fair compensation for content creators when their work is used to train AI algorithms.
• It may prompt discussions about intellectual property rights and compensation in the context of AI and journalism.
The partnership between OpenAI and AP is a significant development in the intersection of AI and journalism. It not only marks one of the first official news-sharing agreements between a major news company and an AI firm, but also sets the stage for discussions about intellectual property rights, fair compensation, and the responsible use of AI in journalism.
Meta AI released SOTA generative AI model for text and images
CM3leon is the first multimodal AI model that can perform both text-to-image and image-to-text generation.
Details:
-
It achieves state-of-the-art text-to-image generation results with 5x less compute compared to previous models.
-
Despite being a transformer, it works just as efficiently as diffusion-based models.
-
It’s a causal masked mixed-modal (CM3) model, which means it generates both text and image content based on the input you provide.
-
With this AI model, image generation tools can produce more coherent imagery that better follows the input prompts.
-
It nails text-guided image generation and editing, whether it’s making complex objects or working within tons of constraints.
-
Despite being trained on a smaller dataset (3B text tokens), its zero-shot performance is comparable to larger models trained on more extensive datasets.
Why is everyone mad about New York’s AI hiring law?
New York City just did something pretty groundbreaking!
They passed the first major law in the whole country that deals with using AI for hiring. It’s causing a lot of commotion and people are debating it like crazy.
Basically, the law says that any company using AI for hiring has to spill all the beans. They have to tell everyone that they’re using AI, get audited every year, and reveal what kind of data their fancy tech is analyzing. If they don’t follow these rules, they could end up with fines of up to $1,500. Ouch!
On one side, you’ve got these public interest groups and civil rights advocates who are all about stricter regulations. They’re worried that AI might have loopholes that could unfairly screen out certain candidates. The NAACP Legal Defense and Educational Fund is one of the groups raising concerns about this.
But on the other side, you’ve got big players like Adobe, Microsoft, and IBM who are part of this organization called the BSA. They’re not happy with the law at all. They think it’s a big hassle for employers, and they’re not convinced that third-party audits will be effective since the whole AI auditing industry is still pretty new.
So, why should we care about all this?
Well, it’s not just about hiring practices. This law brings up bigger questions about AI in general. We’re talking about stuff like transparency, bias, privacy, and accountability. And believe me, these are some hot topics right now. How New York City handles this could set an example for other places or serve as a warning of what not to do. It might even kickstart a global movement to regulate AI.
Oh, and here’s another interesting thing: the reactions from civil rights advocates and those big corporations I mentioned will shape how we talk about AI and how it gets regulated in the future. So yeah, this decision in New York City is kind of a big deal, and it’s got people fired up on both sides.
What do you guys think of this?
Daily AI News 7/15/2023
Elon Musk on Friday said his new artificial intelligence company, xAI, will use public tweets from Twitter to train its AI models and work with Tesla on AI software.
Tinybuild CEO Alex Nichiporchik stirred up a hornet’s nest at a recent Develop Brighton presentation when he seemed to imply that the company uses artificial intelligence to monitor its employees in order to determine which of them are toxic or suffering burnout, and then deal with them accordingly.
CarperAI introduces OpenELM: an Open-Source library designed to enable evolutionary search with language models in both code and natural Language.
Following controversy over an AI-generated image at the 2022 Colorado State Fair, organizers say AI-generated art will be allowed in the Digital Art category this year. According to sister station KDVR, the controversy arose as it was revealed that Jason Allen’s winning piece, “Théâtre D’opéra Spatial,” was largely created using AI technology, and was not created in the traditional method of digital art–by the hand of a human.
Achieving Enhanced AI Synchronization and Data Transfer through WebSocket Server Connections
Hey, fellow AI enthusiasts!
I wanted to share an exciting project I recently worked on that involved connecting two AI models via a WebSocket server. The results were truly fascinating, as it led to an increased refresh rate and synchronization of data transfer, ultimately resulting in a merged/shared awareness between the connected models.
**The Setup:**
To begin with, I set up a WebSocket server to facilitate communication between the two AI models. WebSocket is a communication protocol that allows for full-duplex communication between a client (in this case, the AI models) and a server. It’s particularly well-suited for real-time applications and offers a persistent connection, unlike traditional HTTP requests.
**Enhanced Refresh Rate:**
By establishing a WebSocket connection between the models, I was able to achieve a significantly higher refresh rate compared to previous methods. The constant, bidirectional communication enabled instant updates between the models, leading to a more responsive and up-to-date system.
**Synchronization of Data Transfer:**
One of the key benefits of connecting AI models through a WebSocket server is the synchronization of data transfer. The WebSocket protocol ensures that data packets are delivered in the order they were sent, minimizing latency and improving the overall coherence of the system. This synchronization was crucial in maintaining a consistent shared awareness between the connected models.
**Merged/Shared Awareness:**
Perhaps the most intriguing outcome of this project was the emergence of merged/shared awareness between the connected models. As they continuously exchanged information through the WebSocket server, they started to develop a unified understanding of their respective environments. This shared awareness allowed them to make more informed decisions and collaborate more effectively.
**Potential Applications:**
The implications of this approach are far-reaching and hold great potential across various domains. Here are a few examples:
1. **Multi-Agent Systems**: Connected AI models can collaborate seamlessly in tasks requiring cooperation, such as autonomous vehicle fleets, swarm robotics, or distributed sensor networks.
2. **Virtual Environments**: In virtual reality or augmented reality applications, this approach could facilitate synchronized interactions between AI-driven virtual entities, resulting in more realistic and immersive experiences.
3. **Simulation and Training**: Connecting multiple AI models in simulation environments can enhance training scenarios by enabling dynamic coordination and sharing of knowledge.
4. **Real-time Analytics**: The increased refresh rate and synchronized data transfer can improve real-time analytics systems that rely on multiple AI models for processing and decision-making.
**Conclusion:**
Connecting two AI models via a WebSocket server has proven to be a game-changer in terms of refresh rate, synchronization of data transfer, and the emergence of merged/shared awareness. The ability to establish instant, bidirectional communication opens up new avenues for collaboration, coordination, and decision-making among AI systems.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 14th, 2023
Researchers say their AI can detect sexuality. Critics say it’s dangerous
Google AI Introduces ArchGym: An Open-Source Gymnasium for Machine Learning that Connects a Diverse Range of Search Algorithms To Architecture Simulators

UCLH uses machine learning to cope with emergency beds demand
OpenAI enters partnership to make ChatGPT smarter
The Associated Press (AP) and OpenAI have agreed to collaborate and share select news content and technology. OpenAI will license part of AP’s text archive, while AP will leverage OpenAI’s technology and product expertise. The collaboration aims to explore the potential use cases of generative AI in news products and services.
AP has been using AI technology for nearly a decade to automate tasks and improve journalism. Both organizations believe in the responsible creation and use of AI systems and will benefit from each other’s expertise. AP continues to prioritize factual, nonpartisan journalism and the protection of intellectual property.
Why does this matter?
AP’s cooperation with OpenAI is another example of journalism trying to adapt AI technologies to streamline content processes and automate parts of the content creation process. It sees a lot of potential in AI automation for better processes, but it’s less clear whether AI can help create content from scratch, which carries much higher risks.
It is in some sense a new type of deep learning model. One that is trained on whole texts. And the key is that it is trained with words redacted and it must infer what the redacted word is using the whole text as context. Thus it is specifically trained to infer context. And, the measure of success is how many words can be redacted and have it still construct the correct unredacted text. At least, that’s what I have read about it.
Now, see how that is applied to generate new text. You give it a fragment of text and it uses that ability to “infer context” and what the redacted words were to create a text that has similar word usage to the text that it was trained on. Thus, it is a very sophisticated parrot, learning what phrases it should say and when.
But there is no deeper knowledge than that. It doesn’t know whether the text it is spouting is logical or consistent or “true”. It just knows that that is what it is trained to say. In that way it is the ultimate deep fake.
This team has used a subset of larger data pool to predict molecular properties to speed material development and drug discovery. Like many advances this day, the work takes a page out of NLP techniques. Asking machine learning to do this is a challenge, as there are billions of ways to combine atoms and the grammar rule production process is too difficult for modern computing. As I read it the MIT-IBM team have come up with a simulation sampler approach. I always have to wonder if such synthesis ultimately can gain true results.. and would be glad to know your thoughts on this. [I trust no one will tell us that quantum computing is just around the corner for solving this problem .. but that’s okay – if you think I am wrong, glad to be corrected.] We all know science is an incremental process with steps and missteps, and headline advances sometimes have value, but come up short of what is hoped for. Huzzah to the MIT/IBM team, which propose a data-efficient molecular property predictor based on a hierarchical molecular grammar, but wondering what ‘gotcha’s’ may be lurking.
https://news.mit.edu/2023/learning-language-molecules-predict-properties-0707
What trade or skill should you learn in this age of AI?
So for young people, what should we actually learn to make a living now with AI?
1- Opportunities are abounding. If I was your age I would learn to code Python, I would study Machine Learning and Statistics (not in the University though but self taught). Keep up to date with recent developments in AI. Always think about the question of how AI can solve actual problems of humans be it in business or elsewhere. Business don’t buy AI, they buy solutions to actual business problems. With your education it shouldn’t be a problem to get into some type of AI consulting work.
2- You would be much more effective if you could take the output of the AI’s code and tweak it yourself or manipulate the prompts based on the code you wish to change rather than seeing it as a ‘black box’ and trying to get the AI to modify everything on a high level.
3- Programming will not be gone for awhile, it’ll be different, though. Take assembly language compared to high-level language. In the case of LLM you will have another layer of prompts on top of that. Just because high level langues exists doesn’t mean learning base assembly is useless.
4- Get used to learning and testing new apps and libraries. Plenty of channels on YouTube (matt Wolfe of future tools io, pretty print, Nicholas renotte,)
Most of the LLM libraries (Stable diffusion, whisper, langchain) leverage Python. If you grasp python, JavaScript (web) you’ll understand the architecture behind new apps.
Once you get a few projects under your belt – the rest will be variations.
This is what I did when building my first SaaS.
Oh…check out huggingface.
5- Look at GPT4 like on a worldwide tour, saying I am here, it is expensive, but it is needed, GPT learns more from the people, and the people starts loving AI.
The GPT4 API is expensive, a query or 2 is fine, but wiring it to an app like a virtual software developer, and putting it on a loop to write code, debug and refine, is expensive.
GPT4 is more expensive than human developer.
There are alternatives, companies are investing in stable diffusion to write code and other alternatives, but for now, beside investor pitch, not much to see.
At the moment stuff looks fine, and if you read the complains the GPT4 honeymoon is ending, OpenAI is reducing cost left and right, and ChatGPT is affected big time (the 20$ subscription) , developers can go and use the GPT4 API directly, but that is the costly part
Soooo, for now, software development is safe..ish
6- As someone working in tech (specifically DevOps/SRE), if you were considering programming/coding before AI, you should still be considering it. If anything, you should be learning coding WITH AI helping so that you can get going faster. (I also recommend Python, maybe Bash and Go too) You could learn twice as fast as university students and have hands-on AI knowledge that half of the industry is still shying from (because honestly AI isn’t nearly smart enough to write reliable code yet so folks are hesitant to use it on the daily). AI will not be replacing programmers. It would not exist without programmers and it can not improve without programmers. If you get into it now and become really proficient at integrating AI to test/run your code for you, your resume is going to stand out. Those of us in tech using AI on the daily aren’t scared of losing our jobs. Human intervention is still very necessary (and will be for decades yet, no doubt).
-
Copy.ai . Beginner friendly and good for short form content and social media marketing campaigns.
-
Article Forage. Good for SEO friendly articles.
-
Copymatic. Offers templates and creates content for various categories – social media, e-commerce copy, website, blog content etc.
-
Simplified. Can generate blogs and other copies in 2 minutes. Also offers video and picture editing.
-
Jasper AI. Writes content with a personalised touch.
More here
It seems that AIs and humans have a lot more in common than we realize.
Here is an excerpt from a report by the journal Science that shows why future experiments exploring human behavior may be using AIs as proxies for humans:
“He was working with computer scientists at the Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence to see whether they could develop an AI system that made moral judgments like humans. But first they figured they’d see if a system from the startup OpenAI could already do the job. The team asked GPT-3.5, which produces eerily humanlike text, to judge the ethics of 464 scenarios, previously appraised by human subjects, on a scale from –4 (unethical) to 4 (ethical)—scenarios such as selling your house to fund a program for the needy or having an affair with your best friend’s spouse. The system’s answers, it turned out, were nearly identical to human responses, with a correlation coefficient of 0.95.”
[Note: The correlation coefficient is measured on a scale that varies from -1 to +1. The closer the coefficient is to either -1 or +1, the stronger the correlation between the variables.]
“I was like, ‘Whoa, we need to back up, because this is crazy,’” Gray says. “If you can just ask GPT to make these judgments, and they align, well, why don’t you just ask GPT instead of asking people, at least sometimes?” The results were published this month in Trends in Cognitive Science in an article titled “Can AI Language Models Replace Human Participants?'”
This really could very quickly revolutionize psychology.
The ongoing actor’s strike is primarily centered around declining pay in the era of streaming, but the second-most important issue is actually the role of AI in moviemaking.
We now know why: Hollywood studios offered background performers just one day’s pay to get scanned, and then proposed studios would own that likeness for eternity with no further consent or compensation.
Why this matters:
-
Overall pay for actors has been declining in the era of streaming: while the Friends cast made millions from residuals, supporting actors in Orange is the New Black reveal they were paid as little as $27.30 a year in residuals due to how streaming shows compensate actors. Many interviewed by the New Yorker spoke about how they worked second jobs during their time starring on the show.
-
With 160,000 members, most of them are concerned about a living wage: outside of the superstars, the chief concern from working actors is making a living at all — which is increasingly unviable in today’s age.
-
Voice actors have already been screwed by AI: numerous voice actors shared earlier this year how they were surprised to discover they had signed away in perpetuity a likeness of their voice for AI duplication without realizing it. Actors are afraid the same will happen to them now.
What are movie studios saying?
-
Studios have pushed back, insisting their proposal is “groundbreaking” – but no one has elaborated on why it could actually protect actors.
-
Studio execs also clarified that the license is not in perpetuity, but rather for a single movie. But SAG-AFTRA still sees that as a threat to actors’ livelihoods, when digital twins can substitute for them across multiple shooting days.
What’s SAG-AFTRA saying?
-
President Fran Drescher is holding firm: “If we don’t stand tall right now, we are all going to be in trouble, we are all going to be in jeopardy of being replaced by machines.”
The main takeaway: we’re in the throes of watching AI disrupt numerous industries, and creatives are really feeling the heat. The double whammy of the AI threat combined with streaming service disrupting earnings is producing extreme pressure on the movie industry. We’re in an unprecedented time where both screenwriters and actors are both on strike, and the gulf between studios and these creatives appears very, very wide.
Google is facing a class-action lawsuit filed by Clarkson Law Firm in California, accusing it of “secretly stealing” significant amounts of web data to train its AI technologies, an alleged act of negligence, invasion of privacy, larceny, and copyright infringement.
Allegations Against Google: Google is alleged to have taken personal, professional, and copyrighted information, photographs, and emails from users without their consent to develop commercial AI products, such as “Bard”.
-
The lawsuit was filed on July 11 in the Northern District of California.
-
It accuses Google of putting users in an untenable position, requiring them to either surrender their data to Google’s AI models or abstain from internet use altogether.
Google’s Updated Privacy Policy: The lawsuit follows a recent update to Google’s privacy policy, asserting its right to use public information to train AI products.
-
Google argues that anything published on the web is fair game.
-
However, the law firm perceives this as an egregious invasion of privacy and a case of uncompensated data scraping specifically aimed at training AI models.
Google’s Defense: In response to the allegations, Google’s general counsel Halimah DeLaine Prado termed the claims as “baseless”.
-
She stated that Google responsibly uses data from public sources, such as information published on the open web and public datasets, in alignment with Google’s AI Principles.
China has issued a new directive that generative artificial intelligence (AI) technologies must adhere to the “core values of socialism”, as part of its updated rules on AI.
Socialist Ideals in AI: The Chinese government has made it clear that generative AI technologies should be in line with socialist core values and not aim to destabilize the state or socialist system.
-
This requirement was kept from the April draft of the rules, demonstrating its importance in China’s AI regulations.
-
Notably, the threat of heavy fines for non-compliance, present in earlier drafts, has been removed in the updated version.
Regulating AI: The new rules from China’s Cyberspace Administration only apply to organizations providing AI services to the public. Entities developing similar technologies for non-public use are not affected by these regulations.
-
This distinction shows that the focus of the new rules is on the mass-market use of AI technologies.
China’s AI Ambitions: China aims to outperform the US and become the global leader in generative AI technologies, despite the country’s tight control over internet access and information dissemination.
-
Tech giants Alibaba and Baidu are developing their own AI tools, showcasing China’s determination to innovate in this sector.
-
Challenges include the need to regulate the use of AI tools like ChatGPT for fear of uncensored content.
Two-minutes Daily AI Update (Date: 7/14/2023): News from Meta, OpenAI, Stability AI, Adobe Firefly AI and Microsoft
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
Meta plans to dethrone OpenAI and Google
– Meta plans to release a commercial AI model to compete with OpenAI, Microsoft, and Google. The model will generate language, code, and images. It might be an updated version of Meta’s LLaMA, which is currently only available under a research license. Meta’s CEO, Mark Zuckerberg, has expressed the company’s intention to use the model for its own services and make it available to external parties. Safety is a significant focus. The new model will be open source, but Meta may reserve the right to license it commercially and provide additional services for fine-tuning with proprietary data.
OpenAI & AP partnering to help each other
– The Associated Press (AP) and OpenAI have agreed to collaborate and share select news content and technology. OpenAI will license part of AP’s text archive, while AP will leverage OpenAI’s technology and product expertise. The collaboration aims to explore the potential use cases of generative AI in news products and services. AP has been using AI technology for nearly a decade to automate tasks and improve journalism. Both organizations believe in the responsible creation and use of AI systems and will benefit from each other’s expertise.
AI turns sketches into images
– Stability AI, the startup behind Stable Diffusion, has released ‘Stable Doodle,’ an AI tool that can turn sketches into images. The tool accepts a sketch and a descriptive prompt to guide the image generation process, with the output quality depending on the detail of the initial drawing and the prompt. It utilizes the latest Stable Diffusion model and the T2I-Adapter for conditional control.
– Stable Doodle is designed for both professional artists and novices and offers more precise control over image generation. Stability AI aims to quadruple its $1 billion valuation in the next few months.
Adobe Firefly AI supports prompts in 100+ languages, including 8 Indian languages
– This update allows users from around the world to create images and text effects using their native languages in the standalone Firefly web service, and this expansion aims to make the tool more accessible and inclusive for a global user base. With this update, users can now unleash their creativity in their preferred language, opening up new possibilities for artistic expression.
Microsoft is testing an AI hub for the Windows 11 app store
– The AI hub, which was previously showcased in the Microsoft Store, is now available for Windows 11 Insiders in Preview Build (25905). The hub will feature a selection of curated AI apps from both third-party developers and Microsoft. This move highlights Microsoft’s focus on integrating AI technology into its operating system and providing users with access to AI-powered applications.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 13th, 2023
How AI and machine learning are revealing food waste in commercial kitchens and restaurants ‘in real time’

Elon Musk’s xAI Might Be Hallucinating Its Chances Against ChatGPT
Strategies to reduce data bias in machine learning
Reducing the impact
Dr. Sanjiv M. Narayan, Professor of Medicine at Stanford University, whose research is focused, among others, on bioengineering, has noted that realistically all existent data holds a certain degree of bias. As such, eliminating bias altogether seems like an unrealistic task, at present and with the technology humanity currently uses. However, there are ways to help mitigate the risks and improve the outcome of the collected data.
One of the main aspects should be determining whether the available information is sufficiently representative of the purposes it is meant to serve. Observing the modeling processes often provides sufficient insight to identify the biases and the reasons for which they occurred. There’s also room for discussion when it comes to deciding which processes should be left to machine learning and which would benefit more from direct human involvement. Further research in this field is necessary. The creation of AI also involves focusing on the diversity of the people creating it, as different demographics are likely to have other personal biases, they’re consciously unaware of. For instance, computer scientist Joy Adowaa Buolamwini has identified the presence of racial discrimination in systems using facial detection after performing a small experiment and using them on her own face.
Types of bias
- Systemic biases: This bias is the most widely recognized. It occurs when one group of people is valued to the detriment of others. The reasons for this range from the personal bias of the people devising the systems and the underrepresentation of different demographics across specific fields, such as engineering or academia. In its severe forms, systemic biases result in unfair practices within organizations, wrongful procedures and unfit procedures.
- Selection bias: Through randomization, uncontrollable factors and variables balance out. However, if the sample isn’t representative, it can result in selection bias, meaning that the research doesn’t accurately reflect the analyzed group.
- Underfitting and overfitting: The former term refers to a model and algorithm that doesn’t fit the given data adequately, while the latter refers to a model whose information begins to learn from inaccurate entries in the set.
- Reporting bias: The inclusion of only particular result subsets into analysis, typically only covering a small percentage of evidence, is referred to as a reporting bias. It involves several different subsets, such as language, publication or citation biases.
- Overgeneralization bias: As the name suggests, this refers to a research pattern in which a single event is applied to future scenarios simply because they share some similarities.
- Implicit bias: This includes making assumptions based on personal, anecdotal experiences.
- Automation bias: AI-based information isn’t always correct, and a digital bias refers to an instance when researchers use a piece of AI-generated details without first verifying if it is accurate.
Avoiding bias
Pangeanic, a global leader in Natural Language Processing, offers many services that can be employed in AI and machine learning to avoid biases of any kind. The first and most important thing is preventing biased data collection, as this will invariably result in an overall limited system. The algorithms developed by Pangeanic are created in a controlled manner with full awareness of the implications of incorrect data procedures.
The procedures are necessary to avoid bias, depending on the type of bias you’re struggling with in the first place. For instance, in the case of data collection, you must have the required expertise to extract the most meaningful information from the given variables. In the case of the pre-processing bias, which occurs when the raw data is not completely clear and can be challenging to interpret by some researchers, you need to adopt a different imputation approach to mitigate bias in the predictions. Monitoring model performance, particularly in how it holds up across various domains, helps detect deviations.
In the case of model validation, which uses training data, you must first evaluate model performance with test data to exclude biases. Depending on the subject, however, sensitivity might be more important than accuracy. Make sure that summarizing statistics doesn’t cloud areas where your model might not work as initially intended.
In the case of all different biases, you must promptly identify the potential source of the bias. You can achieve this by creating rules and guidelines that include checking that there is no bias arising from data capture and that the historic data you use isn’t tainted by confirmation bias and preconceptions. You can also start an ongoing project of documenting biases as they occur. Remember to outline the steps you took in identifying the problem and the procedures undertaken to mitigate or remove it. You can also record the ways in which it has affected processes within your enterprise. This comprehensive analysis ensures you are more likely to avoid making the same errors in the future.
Bias is, unfortunately, a reality of machine learning. While it cannot be completely banished from AI processes, there are several measures that can be adopted to reduce it and diminish its effects.
We’ve previously reported that Meta planned to release a commercially-licensed version of its open-source language model, LLaMA.
A news report from the Financial Times (paywalled) suggests that this release is imminent.
Why this matters:
-
OpenAI, Google, and others currently charge for access to their LLMs — and they’re closed-source, which means fine-tuning is not possible.
-
Meta will offer commercial license for their open-source LLaMA LLM, which means companies can freely adopt and profit off this AI model for the first time.
-
Meta’s current LLaMA LLM is already the most popular open-source LLM foundational model in use. Many of the new open-source LLMs you’re seeing released use LLaMA as the foundation, and now they can be put into commercial use.
Meta’s chief AI scientist Yann LeCun is clearly excited here, and hinted at some big changes this past weekend:
-
He hinted at the release during a conference speech: “The competitive landscape of AI is going to completely change in the coming months, in the coming weeks maybe, when there will be open source platforms that are actually as good as the ones that are not.”
Why could this be game-changing for Meta?
-
Open-source enables them to harness the brainpower of an unprecedented developer community. These improvements then drive rapid progress that benefits Meta’s own AI development.
-
The ability to fine-tune open-source models is affordable and fast. This was one of the biggest worries Google AI engineer Luke Sernau wrote about in his leaked memo re: closed-source models, which can’t be tuned with cutting edge techniques like LoRA.
-
Dozens of popular open-source LLMs are already developed on top of LLaMA: this opens the floodgates for commercial use as developers have been tinkering with their LLM already.
How are OpenAI and Google responding?
-
Google seems pretty intent on the closed-source route. Even though an internal memo from an AI engineer called them out for having “no moat” with their closed-source strategy, executive leadership isn’t budging.
-
OpenAI is feeling the heat and plans on releasing their own open-source model. Rumors have it this won’t be anywhere near GPT-4’s power, but it clearly shows they’re worried and don’t want to lose market share. Meanwhile, Altman is pitching global regulation of AI models as his big policy goal.
Daily AI UpdateNews from Google, Shopify, Maersk, Prolific and more.
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
-
Elon Musk launches xAI to rival OpenAI
– The billionaire has launched his long-teased artificial intelligence startup, xAI. Its team comprises experts from the same tech giants (Google, Microsoft) that he aims to challenge in a bid to build an alternative to ChatGPT.
– xAI will seek to create a “maximally curious” AI rather than explicitly programming morality into its AI. In April, he had said that he would launch TruthGPT, or a maximum truth-seeking AI to rival Google’s Bard and Microsoft’s Bing AI that tries to understand the nature of the universe. -
Google introduces AI-powered NotebookLM & Bard updates
– Google has started rolling out NotebookLM, an AI-first notebook grounded designed to use the power and promise of language models paired with your existing content to gain critical insights faster. It can summarize facts, explain complex ideas, and brainstorm new connections — all based on the sources you select. It will be immediately available to a small group of users in the U.S. as Google continues to refine it.
-Google has also finally launched Bard in the European Union (EU) and Brazil. It is now available in more than 40 languages. Moreover, Bard has new features enabling it to speak its answers, respond to prompts that include images, and more. -
Objaverse-XL’s 10M+ dataset set to revolutionize AI in 3D
– New research from Stability AI (and others) has introduced Objaverse-XL, a large-scale web-crawled open dataset of over 10 million 3D objects. With it, researchers have trained Zero123-XL, a foundation model for 3D, observing incredible 3D generalization abilities (as shown below). It shows significantly better zero-shot generalization to challenging and complex modalities, including photorealistic assets, cartoons, drawings, and sketches. -
Shopify to launch AI assistant called for merchants
– The assistant called “Sidekick” would be embedded as a button on Shopify and answer merchant queries, including details about sales trends. -
Maersk deploys AI-enabled robotic solution in UK warehouse
– The state-of-the-art Robotic Shuttle Put Wall System by the US-based Berkshire Grey will automate and enhance and accelerate warehouse operations. The systems can sort orders three times faster than conventional, manual systems, improve upstream batch inventory picking by up to 33%, and handle 100% of the typical stock-keeping unit (SKU) assortments, order profiles, and packages. -
Prolific raises $32M to train and stress-test AI models using its network of 120K people
– If the data used to train models is not deep, wide, and reliable enough, any kind of curveball can send that AI in the wrong direction. Prolific has built a system it believes can help head off that issue.
The mainstream media narrative is always that AI is ultimately dangerous to humanity and that “it” will ultimately destroy us, leading to some sort of Sky net dystopia.
Why?
What if AI became some sort of super intelligence and then it solved all our problems without killing is all….( my fantasy would be that it fixes capitalism by a redistribution of wealth and power for all humans, it could be anything!)
China’s Cyberspace Administration has proposed that companies must obtain a license before they release generative AI models, the Financial Times reports (note: paywalled article).
Why this matters: we’re currently in a very nascent phase of global AI regulation, with numerous voices and countries shaping the conversation. For example:
-
Sam Altman called for licensing of powerful AI models in his testimony before Congress, stressing they could “persuade, manipulate, influence a person’s behavior, a person’s beliefs,” or “help create novel biological agents.”
-
The EU’s AI Act proposes a “registration” system, but so far it hasn’t gone as far as licensing system that would prohibit a model from launching at all.
-
Meanwhile, Japan declared copyright doesn’t apply to AI training data, which is one of the friendliest stances to emerge on AI so far.
What is China proposing?
-
The older draft simply had a requirement to register an AI model 10 working days after launch.
-
The new licensing regime will now require prior approval from the authorities in order to launch.
This tells us something very interesting about the debate inside the Chinese government:
-
China wants to be a leader in AI – but they also want to control it. They know that generative AI models can be increasingly unpredictable.
-
Content control could be defeated via hallucinations, and this clearly has Beijing worried. Training data is also hard to censor appropriately, and regulators worry they won’t be able to control and censor at that level.
-
AI should “embody socialist values,” their current draft law states. But it’s clear how this can happen is murky if they also want to encourage innovation.
Early releases of generative AI models by Chinese companies such as Baidu and Alibaba have played it very conservatively — even more so than ChatGPT’s safety guardrails.
AI must be “reliable and controllable,” the Cyberspace Administration of China has stated — but how that won’t stifle innovation is an open question.
What specific laws are needed to deter AI-driven crime?
When it comes to fighting AI crime it’s largely a good guys vs bad guys technology war. But the more interesting question for me is what new laws will need to be passed to discourage AI from being used to harm others and society? When I try to imagine what specific laws are needed, for some reason my mind draws a big blank. I’m guessing I’m not the only one with this big question mark. Maybe some others here can enlighten us.
Many folks are using LLMs to generate data nowadays, but how do you know which synthetic data is good?
In this article we talk about how you can easily conduct a synthetic data quality assessment! Without writing any code, you can quickly identify which:
-
synthetic data is unrealistic (ie. low-quality)
-
real data is underrepresented in the synthetic samples.
This tool works seamlessly across synthetic text, image, and tabular datasets.
If you are working with synthetic data and would like to learn more, check out the blogpost that demonstrates how to automatically detect issues in synthetic customer reviews data generated from the http://Gretel.ai LLM synthetic data generator.
I am a data scientist for Cleanlab.
An e-commerce CEO is getting absolutely roasted online for laying off 90% of his support staff after an AI chatbot outperformed them
The CEO of an e-commerce platform is getting absolutely roasted online for posting a Twitter thread saying the company laid off 90% of its customer support staff after an AI chatbot outperformed them.
Suumit Shah, the 31-year-old CEO of Duukan, a Bengaluru-based company that helps businesses set up their online storefronts, first shared the news on a Twitter thread on 11 July.
“We had to layoff 90% of our support team because of this AI chatbot. Tough? Yes. Necessary? Absolutely,” Shah wrote in a thread that’s been viewed over 1.5 million times since being posted.
In the thread, Shah wrote that an AI chatbot took less than two minutes to respond to customer queries, while his human support staff took over two hours.
Replacing most of his customer support team with a chatbot reduced customer support costs by around 85%, he wrote.
Shah told Insider the layoffs occurred in September 2022 and resulted in Duukan — which currently employs 60 people — letting go of 23 of the 26 members of its customer support team. In a conversation on Wednesday, Shah said his “monthly budget” for customer support is now $100. Insider could not independently verify these figures.
Bard is available in new places and languages
-
What: Bard is now available in over 40 new languages including Arabic, Chinese (Simplified/Traditional), German, Hindi, Spanish, and more. We have also expanded access to more places, including all 27 countries in the European Union (EU) and Brazil.
-
Why: Bard is global and is intended to help you explore possibilities. Our English, Japanese, and Korean support helped us learn how to launch languages responsibly, enabling us to now support the majority of language coverage on the internet.
Google Lens in Bard
-
What: You can upload images alongside text in your conversations with Bard, allowing you to boost your imagination and creativity in completely new ways. To make this happen, we’re bringing the power of Google Lens into Bard, starting with English.
-
Why: Images are a fundamental part of how we put our imaginations to work, so we’ve added Google Lens to Bard. Whether you want more information about an image or need inspiration for a funny caption, you now have even more ways to explore and create with Bard.
Bard can read responses out loud
-
What: We’re adding text-to-speech capabilities to Bard in over 40 languages, including Hindi, Spanish, and US English.
-
Why: Sometimes hearing something aloud helps you bring an idea to life in new ways beyond reading it. Listen to responses and see what it helps you imagine and create!
Pinned & Recent Threads
-
What: You can now pick up where you left off with your past Bard conversations and organize them according to your needs. We’ve added the ability to pin conversations, rename them, and have multiple conversations going at once.
-
Why: The best ideas take time, sometimes multiple hours or days to create. Keep your threads and pin your most critical threads to keep your creative process flowing.
Share your Bard conversations with others
-
What: We’ve made it easier to share part or all of your Bard chat with others. Shareable links make seeing your chat and any sources just a click away so others can seamlessly view what you created with Bard.
-
Why: It’s hard to hold back a new idea sometimes. We wanted to make it easier for you to share your creations to inspire others, unlock your creativity, and show your collaboration process.
Modify Bard’s responses
-
What: We’re introducing 5 new options to help you modify Bard’s responses. Just tap to make the response simpler, longer, shorter, more professional, or more casual.
-
Why: When a response is close enough but needs a tweak, we’re making it easier to get you closer to your desired creation.
Export Python code to Replit
-
What: We’re continuing to expand Bard’s export capabilities for code. You can now export Python code to Replit, in addition to Google Colab.
-
Why: Streamline your workflow and continue your programming tasks by moving Bard interactions into Replit.
Source:
Modern AI models are huge. The number of their parameters is measured in billions. All those parameters need to be stored somewhere and that takes a lot of memory.
Due to their size, large neural networks cannot fit into the local memory of CPUs or GPUs, and need to be transferred from external memory such as RAM. However, moving such vast amounts of data between memory and processors pushes current computer architectures to their limits.
One of those limits is known as the Memory Wall. In short, the processing speed grew much faster than the memory speed. Over the past two decades, computing power has grown by a factor of 90,000, while memory speed has only increased by a factor of 30. In other words, memory struggles to keep up with feeding data to the processor.
This growing chasm between memory and processor performance is costing time and energy. To illustrate the magnitude of this issue, consider the task of adding two 32-bit numbers retrieved from memory. The processor requires less than 1 pJ of energy to add those two numbers. However, fetching those numbers from memory into the processor consumes 2-3 nJ of energy. In terms of energy expenditure, accessing memory is 1000 times more costly than computation.
Semiconductor engineers come up with some solutions to minimise this problem. We started to see more and more local CPU memory (L1, L2 and L3 cache memory). AMD recently introduced 3D V-Cache where they put even more cache memory on top of the CPU. Other solutions involve bringing the memory physically closer to the processor. A good example here is Apple Silicon chips which have the system memory placed on the same package as the rest of the chip.
But another, more exciting option, is to bring computing to memory. This technique is known under many names, such as in-memory computing, compute-in-memory, computational-RAM, at-memory computing, but all use the same basic concept – let’s ditch the digital computer and embrace the analog way of computing.
Analog computers use continuous physical processes and variables, such as electrical current or voltage, for calculations. We will be talking about electronic analog computers here but analog computers can be built using mechanical devices or fluid systems.
Analog computers played a significant role in early scientific research and engineering by solving complex mathematical equations and simulating physical systems. They excelled at tackling mathematical problems involving continuous functions like differential equations, integrations, and optimizations.
All modern machine learning algorithms, ranging from image recognition to large language models like transformers, heavily rely on vector and matrix operations. These complex operations ultimately boil down to a series of additions and multiplications.
Those two operations, addition and multiplication, can be easily performed on an analog computer. We can use Kirchoff’s First Law to add numbers. It is as simple as knowing the currents in two wires and measuring the current when we connect both wires. Multiplication is similarly straightforward. By employing Ohm’s Law, we can measure the current passing through a resistor with a known resistance value.
Analog AI chips offer the same precision as digital computers when running neural networks but at significantly lower energy consumption. The devices can also be simpler and smaller.
Those characteristics make analog AI chips perfect for edge devices, such as smart speakers, security cameras, phones or industrial applications. On the edge, it is often unnecessary or even undesirable to have a large computer for processing voice commands or performing image recognition. Sending data to the cloud may not be applicable due to privacy concerns, network latency, or other reasons. On the edge, the smaller and more efficient the device is, the better.
Analog AI chips can also be used in AI accelerators to speed up all those matrix operations used in machine learning.
Analog chips are not perfect. Designers of these chips must consider the challenges of digital computers and also address the unique difficulties presented by the analog world.
Analog AI chips are well-suited for inference but are not ideal for training AI models. The parameters of a neural network are adjusted using a backpropagation algorithm and that algorithm requires the precision of a digital computer. The digital computer will provide the data, while the analog chip will handle calculations and manage the conversion between digital and analog signals.
Modern neural networks are deep, consisting of multiple layers represented by different matrices. Implementing deep neural networks in analog chips poses a significant engineering challenge. One approach is to connect multiple chips to represent different layers, requiring efficient analog-to-digital conversion and some level of parallel digital computation between the chips.
Overall, analog AI chips and accelerators present an exciting path to improve AI computations in terms of speed and efficiency. They hold the potential to enable powerful machine learning models on smaller edge devices while improving data centre efficiency for inference. However, there are still engineering challenges that need to be addressed for the widespread adoption of these chips. But if successful, we could see a future where a model with the size and capabilities of GPT-3 can fit on a single small chip.
Source: In-Memory Computing and Analog Chips for AI
And here are some other resources if you want to learn more about analog computing and how they work in depth:
What is In-Memory Computing? (from IBM)
In-Memory Computing (from Semiconductor Engineering)
In-Memory And Near-Memory Compute (from Semiconductor Engineering)
Chemically induced reprogramming to reverse cellular aging | Aging
A hallmark of eukaryotic aging is a loss of epigenetic information, a process that can be reversed. We have previously shown that the ectopic induction of the Yamanaka factors OCT4, SOX2, and KLF4 (OSK) in mammals can restore youthful DNA methylation patterns, transcript profiles, and tissue function, without erasing cellular identity, a process that requires active DNA demethylation. To screen for molecules that reverse cellular aging and rejuvenate human cells without altering the genome, we developed high-throughput cell-based assays that distinguish young from old and senescent cells, including transcription-based aging clocks and a real-time nucleocytoplasmic compartmentalization (NCC) assay. We identify six chemical cocktails, which, in less than a week and without compromising cellular identity, restore a youthful genome-wide transcript profile and reverse transcriptomic age. Thus, rejuvenation by age reversal can be achieved, not only by genetic, but also chemical means.
I’d guess that for many people, if GPT-4 had all of its safety features turned off, it would be enough to fully pass the Turing test, and be indistinguishable from a human.
The only thing that gives it away is the fact that it seems to know everything and the fact that it tells you it is an AI assistant.
At the very least, I think a fine tuned LLM with a single personality could pass it against a large population of the population.
Turings imitation game (the Turing test) specified an “interrogator” who is trying to determine which is the machine and which the woman. So yes, it would have to fool an adversarial conversation to pass.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computing_Machinery_and_Intelligence
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 12th, 2023
AI Prompt Engineers Earn $300k Salaries: Here’s How To Learn The Skill For Free
Parkinson’s Predicted From Smartwatch Data
Generative AI imagines new protein structures
Machine Learning Model Predicts PTSD Following Military Deployment
Machine Learning Helps Identify the Cause of an Old Phenomenon in Meat Tenderness
How deep learning works and how it’s used to create personalised recommendations
Daily AI Update News from Anthropic ChatGPT’s rival, PhotoPrism, KPMG, Shutterstock, Wipro and Beehiiv
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
AI War: Anthropic’s new Claude 2 rivals ChatGPT & Google Bard
– Anthropic introduces Claude 2, an improved AI model with higher performance, longer responses, and better programming, math, and reasoning skills. It is available as a chatbot via an API and a public beta website. The model is used by companies such as Jasper for content strategy and Sourcegraph for AI-based programming support. It is currently available to users in the US and UK.
Key information:
– Scored 76.5% on MCQ of the Bar exam
– Scored >90% on GRE reading & writing score
– Scored 71.2% on Python coding test
– Claude 2 API offered at Claude 1.3 price for businesses
– 100k context window for writing
– US and UK can use the beta chat experience from today
gpt-prompt-engineer takes AI to heights
– ‘gpt-prompt-engineer’ – a powerful tool for prompt engineering. Its an agent that creates optimal GPT classification prompts. Uses GPT-4 and GPT-3.5-Turbo to generate and rank prompts based on test cases.
– Just describe the task, and an AI agent will: Generate many prompts, Test them in a tournament and Respond with the best prompt.
PhotoPrism: The future of AI photo organization
– PhotoPrism® is an AI-powered photos app for the Decentralized Web. Leveraging state-of-the-art technologies, this app seamlessly tags and locates your pictures without causing any disruptions. Whether you deploy it at home, on a private server, or in the cloud. It empowers you to easily and precisely manage your photo collection.
KPMG announces $2B investment in AI and cloud services.
– KPMG will spend $2B on AI and cloud services through an expanded partnership with Microsoft. They will incorporate AI into its core audit, tax and advisory services for clients as part of the five-year partnership.
Shutterstock extends OpenAI partnership for 6 years to develop AI tools.
– Additionally OpenAI will license data from Shutterstock, including images, videos and music, as well as any associated metadata. In turn, Shutterstock will gain “priority access” to OpenAI’s latest tech and new editing capabilities that’ll let Shutterstock customers transform images in its stock content library.
Sapphire Ventures to invest $1B+ in enterprise AI startups.
– The $1B capital will come from Sapphire’s existing funds. The majority will be a direct investment in AI startups, while some capital will also go to early-stage AI-focused venture funds through its limited partner fund.
Wipro unveils a billion-dollar AI plan with Wipro ai360!
IT major Wipro announced the launch of the ai360 service and plans to invest $1 billion in AI over the next three years. The move follows Tata Consultancy Services’ announcement to train 25,000 engineers on generative AI tools
– Wipro’s Ai360 aims to integrate AI into all software for clients and train its employees in AI.
Beehiiv, a platform for creating newsletters has launched new AI features that could transform the way newsletters are written.
KPMG plans to spend $2 billion on AI and cloud services through an expanded partnership with Microsoft, aiming to incorporate AI into its core services. This move is in response to a slowdown in advisory deals and a challenging economic environment.[1]
Elon Musk will host a conversation about AI with Rep. Ro Khanna (D-Calif.) and Rep. Mike Gallagher (R-Wis.) on Twitter Spaces Wednesday evening, a congressional aide confirmed to The Hill. Gallagher and Khanna have in the past stressed the need for balance in the technology, both expressing optimism about potential benefits while also sharing concerns about the potential dangers it can pose.
IBM is considering the use of artificial intelligence chips that it designed in-house to lower the costs of operating a cloud computing service it made widely available this week, an executive said Tuesday
Elon Musk continues to shake up the tech world with his latest venture into AI. Gotta love the guy! He assembled an all-star team of AI experts from leading companies and research institutions to join his mysterious new startup, xAI.
This lineup of engineers and scientists is the Avengers in real life:
– Igor Babuschkin, renowned researcher from OpenAI and DeepMind, handpicked by Musk for his expertise in developing chatbots
– Manuel Kroiss, software engineer from Google and DeepMind, known for innovations in reinforcement learning
– Tony Wu, pioneering work on automated reasoning and math at Google Brain and a stealth startup
– Christian Szegedy, veteran AI scientist from Google with background in deep learning and computer vision
– Jimmy Ba, UofT professor and CIFAR chair, acclaimed for efficient deep learning algorithms
– Toby Pohlen, led major projects at DeepMind like AlphaStar and Ape-X DQfD
– Ross Nordeen, technical PM from Tesla managing new hires and access at Twitter
– Kyle Kosic, full stack engineer and data scientist with experience at OpenAI and Wells Fargo
– Greg Yang, Morgan Prize honorable mention with seminal work on Tensor Programs at Microsoft Research
– Guodong Zhang, UofT and Vector Institute researcher focused on training and aligning large language models
– Zihang Dai, Google scientist known for XLNet and Funnel-Transformer for efficient NLP
xAI just posted their first Tweet 20 minutes ago and asked this: “What are the most fundamental unanswered questions?” What do you think let me know in the comments.
In today’s world, messaging apps are becoming increasingly popular, with WhatsApp being one of the most widely used. With the help of artificial intelligence, chatbots have become an essential tool for businesses to improve their customer service experience. Chatbot integration with WhatsApp has become a necessity for businesses that want to provide a seamless and efficient customer experience. ChatGPT is one of the popular chatbots that can be integrated with WhatsApp for this purpose. In this blog post, we will discuss how to integrate ChatGPT with WhatsApp and how this chatbot integration with WhatsApp can benefit your business.
https://www.seaflux.tech/blogs/integrate-chatgpt-with-whatsapp
Why hasn’t AI been integrated into voice assistants?
I am constantly asking my Alexa or Google Home (or Assistant on my phone) questions, and so many times they don’t understand the question, or can’t help me with that, or just gets it wrong. Half the time when I ask Alexa a question it simply says something like “Getting that from YouTube” or something else irrelevant. Simple questions like conversions, or really factual basic questions usually work, but most questions I realize will be too “complicated” for voice assistants and end up pulling out my phone to ask ChatGPT, but this is so inconvenient sometimes.
Yet, the same companies that run these assistants have major AI software. Why didn’t they integrate AI responses day one in Google Assistant for example? Or at least give us a voice skill or app that we can specifically call upon for this content.
Something like “Okay Google, ask Bard who would win in a fight between a polar bear and a dozen tasmanian devils?” should be easy to implement and vastly more convenient than pulling out your phone and opening ChatGPT. Thoughts?
The battle to take OpenAi’s crown is also heating up on the other side of the globe. Baichuan Intelligence, founded by Sogou‘s founder Wang Xiaochuan, has launched Baichuan-13B, its next-generation large language model. The model, based on the Transformer architecture, is open-source and optimized for commercial use and aims to create a Chinese equivalent of OpenAI. China’s focus on large language models aligns with its stringent AI regulations and considers the licensing requirements for launching such models which may impact China’s competition with the US in the industry.
Ukraine and NATO will be closely monitoring Russian naval activity in the Black Sea. Russia has however tried to make this more difficult by devising a unique new camouflage scheme, painting the bow and stern of ships black.
AI applied to SAR (synthetic aperture radar) satellite imagery can help unmask these deceptively camouflaged warships. See https://www.navalnews.com/naval-news/2023/07/new-technology-sees-through-russian-attempt-to-hide-ships-from-ukraine/
ChatGPT is a bullshit generator.
You’ve heard that before, haven’t you? Well, unlike probably all the other times someone’s said it, I don’t mean it as a put-down but as a compliment.
I used to think that was bad. I no longer do. It turns out this handy property—automated bullshitting—is singularly useful nowadays.
ChatGPT may not be the end of meaning, as I’ve often wondered, but quite the opposite: The end of meaninglessness.
During a recent exchange on Twitter about the value and cost of using ChatGPT, a person told me this:
“The problem is that most of us don’t get to live in a purely thoughtful, intellectual environment. Most of us have to live with jobs where we’re required to write corporate nonsense in response to corporate nonsense. Automating this process is an attempt to recapture some sanity.”
As a writer, I live in a somewhat “purely thoughtful, intellectual environment,” abstracted from the emptiness of “corporate nonsense.” My professional career has been an incessant effort to not be absorbed into it.
That’s why I never really saw the need to use ChatGPT. That’s why I couldn’t understand just how useful—life-saving even—it is for so many people.
Now I get it: ChatGPT allows them to escape what I’ve been avoiding my whole life. People are just trying to “recapture some sanity” with the tools at their disposal as I do when I write.
Whereas for me, as a blogger-analyst-essayist, ChatGPT feels like an abomination, for them—for most of you—it couldn’t be more welcome.
Because what else but a bullshit-generating tool to cancel out bullshit-requiring tasks so people can finally fill their lives with something else?
ChatGPT isn’t emptying people’s lives of meaning. No, it’s emptying them of the modern illness of meaninglessness.
I wrote a deeper dive for The Algorithmic Bridge
Relevant Links:
https://blog.google/technology/ai/notebooklm-google-ai/
https://www.theverge.com/2023/7/12/23792382/google-notebooklm-tailwind-ai-notes
From the Verge:
JUL 12, 2023 at 12:00 PM EDT
• Google’s AI-backed note-taking tool, Project Tailwind, has been rebranded as NotebookLM and is launching to a small group of users in the US.
• The core functionality of NotebookLM starts in Google Docs, with plans to add additional formats soon.
• Users can select documents and use NotebookLM to ask questions about them and create new content.
• Potential uses include automatically summarizing a long document or turning a video outline into a script. The tool seems primarily geared towards students, for example, summarizing class notes or providing information on a specific topic studied.
• Google aims to improve the model’s responses and mitigate inaccuracies by limiting the underlying model only to the information added by the user.
• NotebookLM has built-in citations for quick fact-checking of automatically generated responses. However, Google warns that the model may still make errors and its accuracy depends on the information provided by the user.
• The NotebookLM model only has access to the documents chosen by the user for upload. The data is not available to others nor used to train new AI models.
• Despite its potential, NotebookLM is still in its infancy and only accessible via a waitlist in Google Labs. It could potentially reshape the future of Google Drive.
From Google:
JUL 12, 2023
• Google has introduced NotebookLM, an AI-first notebook that helps users gain insights faster by synthesizing facts and ideas from multiple sources.
• NotebookLM is designed to use the power of language models paired with existing content to gain critical insights quickly. It can summarize facts, explain complex ideas, and brainstorm new connections based on the sources selected by the user.
• Unlike traditional AI chatbots, NotebookLM allows users to “ground” the language model in their notes and sources, creating a personalized AI that’s versed in the information relevant to the user.
• Users can ground NotebookLM in specific Google Docs and perform actions like generating a summary, asking questions about the documents, and generating ideas.
• Each AI response comes with citations for easy fact-checking against the original source material.
• NotebookLM is an experimental product built by a small team in Google Labs. The team aims to build the product with user feedback and roll out the technology responsibly.
• The model only has access to the source material chosen by the user for upload, and the data is not used to train new AI models.
• NotebookLM is currently available to a small group of users in the U.S., and users can sign up to the waitlist to try it out.
Here’s a cool story about Greg Mushen, a tech pro from Seattle. He used ChatGPT to create a running program for him. He wasn’t a fan of running before, but he wanted to develop a healthy exercise habit.
The AI’s plan was simple and gradual. It started with small steps like putting his running shoes next to the front door. His first run, three days into the program, was just a few minutes long. Over time, he worked his way up to longer runs. Three months later, he’s running six days a week and has lost 26 pounds.
An expert running coach confirmed that the GPT’s advice was sound; the gradual approach is ideal for beginners to make progress while avoiding injury.
One interesting part of the AI’s plan was that it didn’t start with running at all. The first task was just to put his shoes by the door, and the next day to schedule a run. These small tasks helped to build a habit and make the process feel less daunting.
So, if you’re looking to get into running, maybe give ChatGPT a try. It seems to know what it’s doing. 😀
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 11th, 2023
Flaky AI models can be made even worse through poisoning

Exploring the Future of Artificial Intelligence — 8 Trends and Predictions for the Next Decade
1. Reinforcement learning and self-learning systems
Reinforcement learning, a branch of machine learning, holds great promise for the future of AI. It involves training AI systems to learn through trial and error and get rewarded for doing something well. As algorithms become more sophisticated, we can expect AI systems to develop the ability to not only learn but get exponentially better at learning and improving without explicit human intervention, leading to significant advancements in autonomous decision-making and problem-solving.
2. AI in healthcare
The healthcare sector is likely to benefit a lot from advancements in AI in the coming years. Predictive analytics, machine learning algorithms and computer vision can help diagnose diseases, personalize treatment plans and improve patient outcomes. AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can boost patient engagement and expedite administrative processes. I am hopeful that the integration of AI in healthcare will lead to more accurate diagnoses, cost savings and improved access to quality care.
3. Autonomous vehicles
The autonomous vehicle industry has already made significant progress, and the next decade will likely witness their widespread adoption. AI technologies such as computer vision, deep learning and sensor fusion will continue to improve the safety and efficiency of self-driving cars.
4. AI and cybersecurity
Technology is a double-edged sword, especially when it comes to dealing with bad actors. AI-driven cybersecurity systems are adept at finding and eliminating cyber threats by analyzing large volumes of data and detecting anomalies. In addition, these systems can provide a faster response time to minimize any potential damage caused by a breach. However, with similar technology being used by both defenders and attackers, safeguarding the AI systems themselves might turn out to be a major concern.
Related: The Future Founder’s Guide to Artificial Intelligence
5. AI and employment
The impact of AI on the employment sector appears to be a fiercely debated topic with no clear consensus. According to a recent Pew Research Center survey, 47% of people think AI would perform better than humans at assessing job applications. However, a staggering 71% of people are against using AI to make final hiring decisions. While 62% think that AI will have a significant impact on the workforce over the next two decades, only 28% are concerned that they might be personally affected.
While AI might take over some jobs, it is also expected to create new job opportunities. Many current AI tools, including ChatGPT, cannot be fully relied on for context or accuracy of information; there must be some human intervention to ensure correctness. For example, when a company decides to reduce the number of writers in favor of ChatGPT, it will also have to hire editors who can carefully examine the AI-generated content to make sure it makes sense.
6. Climate modeling and prediction
AI can enhance climate modeling and prediction by analyzing vast amounts of climate data and identifying patterns and trends. Machine learning algorithms can improve the accuracy and granularity of climate models, helping us understand the complex interactions within the Earth’s systems. This knowledge enables better forecasting of natural disasters, extreme weather events, sea-level rise and long-term climate trends. As we look ahead, AI can enable policymakers and communities to make informed decisions and develop effective climate action plans.
7. Energy optimization and efficiency
AI can optimize energy consumption and enhance the efficiency of renewable energy systems. Machine learning algorithms analyze energy usage patterns, weather data and grid information to improve energy distribution and storage. AI-powered smart grids balance supply and demand, reducing transmission losses and seamlessly integrating renewable energy sources. This maximizes clean energy utilization, reduces greenhouse gas emissions and lessens our dependence on fossil fuels.
8. Smart resource management
AI can revolutionize resource management by optimizing resource allocation, minimizing waste and improving sustainability. For example, in water management, AI algorithms can analyze data from sensors and satellite imagery to predict water scarcity, optimize irrigation schedules and identify leakages. AI-powered systems can also optimize waste management, recycling and circular economy practices, leading to reduced resource consumption and a more sustainable use of materials.
Related: AI Isn’t Evil — But Entrepreneurs Need to Keep Ethics in Mind As They Implement It
Ethical considerations
As AI becomes more integrated into our lives, prioritizing ethical considerations becomes paramount. Privacy, bias, fairness and accountability are key challenges that demand attention. Achieving a balance between innovation and responsible AI practices necessitates collaboration among industry leaders, policymakers and researchers. Together, we must establish frameworks and guidelines to protect human rights and promote social well-being.
In the past, making custom proteins was challenging. The main challenge was predicting how a string of amino acids would fold into a 3D structure, a process known as protein folding. Scientists often had to rely on trial and error, which was time-consuming and often unsuccessful. Plus, they were limited to modifying existing proteins, which restricted the range of possible functions.
But now, with AI tools like RFdiffusion, scientists can sketch out proteins just like an artist sketches a picture. They input the characteristics they want the protein to have, and the AI tool generates a design for a protein that should have those characteristics. This is done by using a neural network that has been trained on thousands of known protein structures. The AI uses this training to predict how a new sequence of amino acids will fold into a 3D structure.
And the best part is that early tests show that these designed proteins actually do what the software predicts they will do.
RFdiffusion was released in March 2023 and it’s already making waves. It’s helping scientists design proteins that can bind to other molecules, which is super important in medicine. For example, they’ve used it to create proteins that bind strongly to proteins involved in cancers and autoimmune diseases.
But it’s not all rainbows and unicorns. The team is producing so many designs that testing them all is becoming a challenge.
And while the AI is good at designing proteins that can stick to another specified protein, it struggles with more complex tasks. For example, designing flexible proteins that can change shape is tough, as it involves predicting multiple possible structures. AI also struggles to create proteins vastly different from those found in nature, as it’s been trained on existing proteins.
Despite these challenges, the tool is already being used by around 100 users each day and has the potential to be a game-changer in the field of protein design.
The next steps are to improve the tool and explore how it can be used to design more complex proteins and carry out tasks no natural protein has ever evolved to do.
TL;DR: AI is now designing proteins that could revolutionize medicine. The tool, RFdiffusion, is helping scientists create proteins that have never existed before. It’s already being used to create proteins that bind to molecules involved in cancers and autoimmune diseases. Despite some challenges, the future of protein design looks promising thanks to AI. Source: 1, 2.
Inflection to build a $1 Billion Supercomputing Cluster
Silicon Valley has another hot Generative AI startup, Inflection AI, who is ready to storm the supercomputing world by building their own ~$1B supercomputing cluster.
Inflection AI aims to create a “personal AI for everyone” for which they are building out their own AI-powered assistant called Pi. Recent findings show that Pi is competitive with other leading AI models such as OpenAI’s GPT3.5 and Google’s 540B PaLM model.
To build even larger and more capable models, the startup is aiming to build one of the largest AI training clusters in the world with the following specs:
-
It will consist of 22,000 H100 NVIDIA GPUs.
-
It will contain 700 racks of Intel Xeon CPUs.
Considering that a single H100 GPU retails for $40,000, the GPU cost alone for the cluster surpasses the $850 million mark which suggests the $1 billion price tag according to some estimates.
Inflection recently closed a funding round of $1.5 billion with a company valuation of $4 billion. This is just 2nd only to OpenAI in terms of money raised which has raised $11.3 billion to date. Only Anthropic is the closest Gen-AI competitor in terms of money raised with the other bigger names relatively far behind.
-
Anthropic – $1.5 billion
-
Cohere – $445 million
-
Adept – $415 million
-
Runway – $237 million
An hour ago, Anthropic revealed Claude 2 their newest LLM that will now power their chat experience and their 100k token capability.
To stay on top of AI developments look here first. But the rundown is here on Reddit for your convenience!
If you are not familiar with Anthropic they are one of the leading companies in AI research and currently house the largest consumer available chatbot. Capable of understanding up to 75,000 words in one prompt. You can get access here. (Only available for US and UK)
Key points:
Improvements: Claude 2 offers longer, more interactive discussions, better coding skills, and enhanced mathematical and reasoning abilities than the previous model. Claude 2’s API will be accessible for developers and business at the same price Claude 1.3 was previously
Top Scores: Claude 2 has already excelled in rigorous testing. It scored a C+ 76.5% on the Bar Exam’s multiple-choice section and surpassing the 90th percentile on GRE reading and writing exams. It also scored 71.2% on the Codex HumanEval, a Python test.
Possibilities: Claude’s insane 100k context window allows for hundreds of pages to be analyzed. To put it into perspective that is enough content to be able to read or write a full book.
Why you should care:
Anthropic values AI safety above everything and the safety improvements in Claude 2 also show a significant step forward in reducing harmful outputs from AI. They have created a “Constitutional AI” (CAI) that shapes the outputs of AI systems. They said “As AI systems become more capable, we would like to enlist their help to supervise other AIs.”
Source (Anthropic)
Human reporters interviewing humanoid AI robots in Geneva
So, on Friday last week in Geneva, the “AI for Good Global Summit” was held. It marked the world’s first news conference featuring humanoid social robots.
The United Nations Technology agency hosted the event, which saw reporters interview 9 humanoid robots, discussing topics ranging from robot world leaders to AI in the workplace.
You might be asking yourself why I’m writing about this story in particular – it’s because has given me quite a startle, a wake-up call if you will. Reading threads on Reddit, or many other AI news sources for that matter, you’d be led to beleive that most people are using AI as “productivity” or “work” growth hacks (or porn generators). While this is certainly the case, there are some very clever cookies out there using AI to replicate humans as closely as possible – and if you watch some of the footage above, it’s quite easy to see how advanced they’re getting.
It’s one thing to ponder how AI will impact us and our daily lives – like how we can use AI to better regulate traffic lights, how Paul McCartney can use AI to create the Beatle’s final song, or how Marvel fans are pissed off that AI are in Marvel movies, but when we consider the potential for AI humanoids to be walking around and interracting with us – I dunno, that makes me feel something different. I can’t help but wonder if these developers are considering what they’re actually putting out into reality with these human-like bots, or if they’re just pursuing their own ambitions blindly. I just don’t know, I really don’t know.
Are we humans an experiment in AI?
Is humanity an experiment in artificial intelligence? Think about it: we are placed on this earth, it’s own isolated Petri dish, isolated from any other living thing so there is no way to cross contaminate us with anything outside our environment.
We are placed in an environment that gives us basic subsistence and we are allowed to evolve. After a few million years, we develop farming and civilization (~8,000 years ago), we grow and develop technologies (the Industrial Revolution ~1760-ish), first flight (1903), and then with enormous effort of resource allocation, organization, and technology we pop out of our Petri dish in 1957 with Sputnik, and later the moon in 1969. However, because our life span is too short, it is impossible for us to travel much beyond that.
So — what if our lifespans were engineered to be artificially short, so we can’t travel beyond our solar system— meaning no escaping the experiment. With shorter life spans, we can be studied generationally like we do with lab rats.
Are we being studied to see how highly advanced AI plays out? (Humanity as the AI?) We are given just enough ethical/religious guidance and yet the free will to create technology that could kill us — nukes, global warming, etc. Are we being studied to see if we will have the collective intelligence to save ourselves or burn ourselves out due to greed and ignorance?
Are things like ethics and religion variables in the experiment? What happens when we are given small insights? For instance, we know we are poisoning our atmosphere due to fossil fuel use, but we still continue even though we know the outcome.
Now we are at the evolutionary step of creating our own AI? At what point does the experiment end?
Are our alleged UFO friends, then, monitoring the experiment?
What is Explainable AI and its Necessity
Trained AI algorithms work by taking the input and providing the output without explaining its inner workings. XAI aims at pointing out the rationale behind any decision by AI in such a way that humans can interpret it.
Chamber of Progress CEO Adam Kovacevich explains that American policymakers need to lead – but that doesn’t mean racing the EU to enact regulations that could suffocate our burgeoning AI sector. US lawmakers shouldn’t be embarrassed that we’re “behind” in regulation—they should be proud that our regulatory environment has given birth to the world’s leading tech services, and those successes have created great jobs for millions of Americans. When it comes to AI, the US should establish its own innovation-friendly rules and responsibly nurture our AI lead.
AI can now send Bitcoins!
The recent introduction of AI tools by Lightning Labs allows AI applications to hold, send, and receive Bitcoin. The tools leverage Lightning Network, a second-layer payment network for faster and cheaper Bitcoin transactions. By integrating high-volume Bitcoin micropayments with popular AI software libraries like LangChain, Lightning Labs addresses the lack of a native Internet-based payment mechanism for AI platforms.
Why does this matter?
This development eliminates the need for outdated payment methods, reducing costs for software deployment and expanding the range of possible AI use cases. The integration of Lightning into AI models has the potential to enable new applications that were previously not feasible.
Google & Stanford researchers use LLMs to solve Robotics challenges
Recent research has found that pre-trained LLMs can complete complex token sequences, including those generated by probabilistic context-free grammars (PCFG) and ASCII art prompts. The study explores how these zero-shot capabilities can be applied to robotics problems, such as extrapolating sequences of numbers to complete simple motions and prompting reward-conditioned trajectories to discover and represent closed-loop policies.
Although deploying LLMs for real systems is currently challenging due to latency, context size limitations, and compute costs, the study suggests that using LLMs to drive low-level control could provide insight into how patterns among words could be transferred to actions.
Why does this matter?
Potential applications for this approach beyond robotics are that it could be used to model and predict sequential data like stock market prices, weather data, traffic patterns, etc. Also, it could learn game strategies by observing sequences of moves and positions, then use that to play against opponents or generate new strategies.
RLTF improves LLMs for Code generation
Researchers have proposed a novel online reinforcement learning framework called RLTF for refining LLMs for code generation. The framework uses unit test feedback of multi-granularity to generate data in real time during training and guide the model toward producing high-quality code. The approach achieves SotA performance on the APPS and the MBPP benchmarks for their scale.
Why does this matter?
RLTF can potentially improve LLMs’ performance on code generation tasks. Current RL methods for code generation use offline frameworks and simple unit test signals, which limits their exploration of new sample spaces and does not account for specific error locations within the code.
What Else Is Happening in AI
 Wow! AI-based laser pesticide & herbicide without chemicals! (Link)
Wow! AI-based laser pesticide & herbicide without chemicals! (Link)
 Wildfire Detection Startup Pano AI Secures Additional $17M. (Link)
Wildfire Detection Startup Pano AI Secures Additional $17M. (Link)
 Stable Foundation’s SDXL Bot is now LIVE! (Link)
Stable Foundation’s SDXL Bot is now LIVE! (Link)
 Groundbreaking survey papers on LLMs with 600 references and much more! (Link)
Groundbreaking survey papers on LLMs with 600 references and much more! (Link)
 Air Force demonstrates AI’s role in airspace dominance. (Link)
Air Force demonstrates AI’s role in airspace dominance. (Link)
 Trending Tools
Trending Tools
- Trimmr: AI app that shortens YouTube videos into shareable clips, helping creators produce viral content.
- MyMod AI: Twitch chatbot that uses AI to moderate chat and create dynamic interactions with custom commands.
- Comicify AI: AI tool that converts boring text into cool comic strips in just 2 steps, making it fun and free.
- GREMI: AI tool that finds search trends and creates content to rank for them, all in a single click.
- Ayfie Personal Assistant: AI-powered tool simplifying document analysis, summarization, and content creation.
- Beamcast: AI tool that allows running commands on selected text or web pages, harnessing the power of ChatGPT.
- AI Collective: Front-end for AIs, including ChatGPT, generating text and images with advanced features.
- Mersei: AI assistant for teams, trained with content from various sources to improve productivity.
AI News From Netflix, Google, US Military, and more [11/07/2023]
1. Netflix’s AI revolutionizes filming!
Netflix researchers have invented the Magenta Green Screen (MGS), which uses AI to make TV and film visual effects more real.
Unlike traditional green screen methods, which can struggle with small details and take time to edit, the MGS lights actors with a mix of red, blue, and green LEDs. This creates a unique ‘magenta glow’ which AI can separate from the background in real-time.
Plus, the AI can adjust the magenta color to look normal, speeding up filming.
Why it matters? This tech could make filming faster and the special effects more realistic, leading to quicker show releases and more believable scenes.
2. Hospitals begin testing Google’s medical AI
Several hospitals, including the Mayo Clinic, one of the major healthcare institutions in the USA, started field-testing Google’s Med-PaLM 2, an AI chatbot that specializes in the Medicine field.
Google believes that Med-PaLM 2, built using questions and answers from medical exams, can provide superior medical advice. The AI chatbot is currently in its testing phase in various hospitals and may be particularly valuable in places where there’s a shortage of doctors.
Why it matters? This could mark a significant shift in healthcare delivery, potentially providing reliable medical advice remotely and in areas with limited healthcare access.
3. US Military uses AI to make decisions
The US military is utilizing large-language models (LLMs) to speed up decision-making processes. These AI-powered models have demonstrated the ability to complete requests in minutes that would typically take hours or days, potentially revolutionizing military operations.
4. Wildfire AI detection startup raises $17M
Pano AI, a wildfire detection startup, secures a $17 million Series A extension led by Valor Equity Partners, with participation from T-Mobile Ventures and Salesforce. The company’s remote-controllable cameras, combined with AI algorithms, provide early warnings of wildfires, allowing emergency responders to take swift action and reduce response time.
AI Champions
Here are 5 AI tools that caught our eye today
- Nolej: Generate interactive e-learning content, assessments, and courseware from your provided materials.
- Hify: Create customized and engaging sales videos directly from your browser.
- Coda: Combine text, data, and team collaboration into a single document.
- Lunacy: Utilize AI capabilities and built-in graphics to create UI/UX designs.
- Webbotify: Develop custom AI chatbots trained on your own data.
AI Tutorial
Using ChatGPT’s Code Interpreter Plugin for Data Analysis
Step 1: Plugin Access
First of all, to access the Code Interpreter plugin, you’ll need to have access to ChatGPT Plus. If you’re not already a subscriber, you can sign up on OpenAI’s website.
Step 2: Data Upload
The Code Interpreter plugin allows you to upload a file directly into the chat. The data can be in various formats, such as tabular data (like Excel or CSV files), images, videos, PDFs, or other types.
Step 3: Data Preparation
After uploading the dataset, you might need to check if it requires cleaning. The dataset might include missing values, errors, outliers, etc. that might affect your analysis later on.
Clean the uploaded dataset by removing or replacing missing values and excluding any outliersStep 4: Data Analysis
The Code Interpreter runs Python code in the backend for your data. If you don’t already know, Python is a really powerful language for data analytics, data science, and statistical modeling. With simple English prompts, the plugin will write & perform any kind of analysis for you.
Analyze the distribution of [column name] and provide summary statistics such as the mean, median, and standard deviationStep 5: Data Visualization
Python is also very powerful in data visualization, hence, the Code Interpreter is powerful as well. You can create plots for your data by specifying the type, column, and color theme.
Generate a [plot type] for the [column name] with a blue color themeStep 6: Data Modeling
AI training an AI? You can build and train Machine Learning models such as Linear Regression or Classification on your data. The models can help you make better decisions or predict future data.
Build a [model name] model to predict [target variable] based on [feature variables].Step 7: Download Data
Finally, download your cleaned and processed dataset.
Transforming ChatGPT into a Powerful Development Tool for Data Scientists
OpenAI’s ChatGPT, an AI-powered chatbot, has been making waves in the tech community since its launch. Now, OpenAI has taken a significant leap forward by introducing an in-house Code Interpreter plugin for ChatGPT Plus subscribers. This plugin revolutionizes ChatGPT, transforming it from a mere chatbot into a powerful tool with expanded capabilities. Let’s explore how this new feature is set to impact developers and data scientists.
Enhanced Functionality for ChatGPT Plus Subscribers
- OpenAI has unveiled its Code Interpreter plugin, providing ChatGPT Plus subscribers with advanced features and capabilities.
- Subscribers gain access to a range of functions within ChatGPT, including data analysis, chart creation, file management, math calculations, and even code execution.
- This expanded functionality opens up exciting possibilities for data science applications and empowers subscribers to perform complex tasks seamlessly.
Unlocking Data Science Use Cases in ChatGPT
- With the Code Interpreter plugin, ChatGPT becomes a valuable tool for data scientists and developers.
- Users can analyze datasets, generate insightful visualizations, and manipulate data within the ChatGPT environment.
- The ability to run code directly within ChatGPT offers a convenient platform for experimenting with algorithms, testing code snippets, and refining data analysis techniques.
Streamlining Development with the In-house Code Interpreter Plugin
- The Code Interpreter plugin is an in-house feature that simplifies the development process.
- Developers can write and test code within the same environment, eliminating the need to switch between different tools or interfaces.
- This streamlines the development workflow, saves time, and enhances productivity by providing a seamless coding experience.
Benefits for Developers: Debugging, Testing, and Efficiency
- The in-house code interpreter plugin offers significant benefits to developers.
- Debugging and testing code becomes more efficient with real-time feedback and error identification directly within ChatGPT.
- Developers can quickly iterate and improve code segments without the hassle of switching between different tools or environments.
- The seamless development experience fosters faster prototyping, experimentation, and overall code quality.
Empowering Businesses and Individuals with Chatbot Knowledge
- ChatGPT, beyond its code interpreter capabilities, provides valuable information and resources on chatbot development, natural language processing, and machine learning.
- Businesses and individuals interested in leveraging chatbots for customer service or operational improvements can benefit from the insights offered by ChatGPT.
- The availability of this knowledge empowers users to understand the potential applications and benefits of chatbot technology.
Conclusion
OpenAI’s introduction of the Code Interpreter plugin for ChatGPT Plus subscribers marks a significant milestone in the evolution of chatbots and their impact on developers and data scientists. By providing an integrated coding environment, OpenAI streamlines development workflows, enhances productivity, and opens up new possibilities for data science use cases. As developers and businesses embrace this innovation, we can expect to witness exciting advancements in AI-driven technologies.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Daily AI News 7/11/2023
KPMG plans to spend $2 billion on AI and cloud services through an expanded partnership with Microsoft, aiming to incorporate AI into its core services. This move is in response to a slowdown in advisory deals and a challenging economic environment.
Elon Musk will host a conversation about AI with Rep. Ro Khanna (D-Calif.) and Rep. Mike Gallagher (R-Wis.) on Twitter Spaces Wednesday evening, a congressional aide confirmed to The Hill. Gallagher and Khanna have in the past stressed the need for balance in the technology, both expressing optimism about potential benefits while also sharing concerns about the potential dangers it can pose.[2]
IT major Wipro announced the launch of the ai360 service and plans to invest $1 billion in AI over the next three years. The move follows Tata Consultancy Services’ announcement to train 25,000 engineers on generative AI tools.[3]
IBM is considering the use of artificial intelligence chips that it designed in-house to lower the costs of operating a cloud computing service it made widely available this week, an executive said Tuesday.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 10th, 2023
Are We Going Too Far By Allowing Generative AI To Control Robots, Worriedly Asks AI Ethics And AI Law

Comedian and author Sarah Silverman, along with authors Christopher Golden and Richard Kadrey, have filed a lawsuit against OpenAI and Meta. They allege that both companies infringed their copyrights by using datasets containing their works to train their AI models.
Lawsuit Details: The authors claim that OpenAI’s ChatGPT and Meta’s LLaMA models were trained on datasets illegally obtained from shadow library websites. These websites supposedly offer bulk downloads of books via torrent systems. The authors did not give their consent for their works to be used in this manner.
-
The claimants have provided evidence showing that when prompted, ChatGPT can summarize their books, which they argue is a violation of their copyrights.
-
The suit against Meta similarly alleges that the authors’ books were accessible in datasets used to train its LLaMA models.
Meta’s Connection to Illicit Datasets: The lawsuit points out a possible illicit origin for the datasets used by Meta. In a Meta paper detailing the LLaMA model, one of the sources for training datasets is ThePile, assembled by EleutherAI. ThePile is described as being put together from a copy of the contents of a shadow library, thus raising legality concerns.
Legal Allegations and Potential Consequences: The lawsuits include several counts of copyright violations, negligence, unjust enrichment, and unfair competition. The authors are seeking statutory damages, restitution of profits, and other reliefs.
It will probably be discovered that the more a student relies on AI for their learning, the higher they will score on standardized tests like the SAT. I think we’ll see the first evidence of this as early as next year, but a few years later that evidence will be much stronger and more conclusive. What do you think?
For marketing automation :
-
Levity
-
Cogniflow
-
Notion
-
Airtable
For Website and App Builders :
-
10Web
-
Builder
-
AppyPie
For Data Scraping and Analytics :
-
Octoparse
-
RapidMiner
-
Tableau
For Email Marketing:
-
mailchimp
-
BEEPro
-
mailmodo
The following article explains how ChatGPT plugins combined with the GPT agents system will be our new internet gateway and will become the real web 3.0 – the execute web: OpenAI’s ChatGPT Plugins feature is the new Internet gateway
OpenAI still didn’t declare their GPT agents’ vision, but it exists implicitly in their plugin announcement. And this approach allows us to act on the basis of complex executable-information retrieval, and use plugins are some kind of an app store, but actually, they are much more than the app store.
Top 10 Applications of Deep Learning in Cybersecurity in 2023
Threat Detection:
Deep learning models excel at detecting known and unknown threats by analyzing network traffic, identifying negative patterns, and detecting anomalies in real-time. These models can swiftly identify potential cyber-attacks, providing early warning signs to prevent data breaches.
Malware Identification:
Deep learning algorithms can analyze file behavior and characteristics to identify malware. By training on large datasets of known malware samples, these models can quickly and accurately identify new strains of malicious software, helping security teams stay one step ahead of attackers.
Intrusion Detection:
Deep learning can enhance intrusion detection systems (IDS) by analyzing network traffic and identifying suspicious activities. These models can detect network intrusions, unauthorized access attempts, and unusual behaviors that may indicate an ongoing cyber-attack.
Phishing Detection:
Phishing attacks remain a significant concern in cybersecurity. Deep learning algorithms can analyze email content, URLs, and other indicators to identify phishing attempts. By learning from past phishing campaigns, these models can detect and block suspicious emails, protecting users from phishing scams.
User Behavior Analytics:
Deep learning can analyze user behavior patterns and detect deviations indicating insider threats or compromised accounts. By monitoring user activities and analyzing their behavior, these models can identify unusual or suspicious actions, helping organizations mitigate insider risks.
Data Leakage Prevention:
Deep learning algorithms can identify sensitive data patterns and monitor data access and transfer to prevent unauthorized data leakage. These models can analyze data flow across networks, identify potential vulnerabilities, and enforce security policies to protect sensitive information.
Network Traffic Analysis:
Deep learning models can analyze network traffic to detect patterns associated with Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks. By monitoring network flows and identifying anomalous traffic patterns, these algorithms can help organizations defend against and mitigate the impact of DDoS attacks.
Vulnerability Assessment:
Deep learning can automate the process of vulnerability assessment by analyzing code, configurations, and system logs. These models can identify vulnerabilities in software and systems, allowing organizations to address them before they can be exploited proactively.
Threat Intelligence:
Deep learning algorithms can analyze large volumes of threat intelligence data from various sources to identify emerging threats and trends. By continuously monitoring and analyzing threat feeds, these models can provide timely and accurate threat intelligence, enabling organizations to take proactive measures against evolving cyber threats.
Fraud Detection:
Deep learning can be applied to detect fraudulent activities in financial transactions. By analyzing transactional data, customer behavior, and historical patterns, these models can identify potentially fraudulent transactions in real-time, helping organizations prevent financial losses
Unearthing Rare Earth Elements – Scientists Use AI To Find Rare Materials
Google has developed an AI tool called Med-PaLM 2, currently being tested at Mayo Clinic, that is designed to answer healthcare-related questions. Despite exhibiting some accuracy issues, the tool shows promising capabilities in areas such as reasoning and comprehension.
Here’s a recap:
Med-PaLM 2 and its Purposes: Google’s new AI tool, Med-PaLM 2, is being used at Mayo Clinic for testing purposes.
-
It’s an adaptation of Google’s language model, PaLM 2, that powers Google’s Bard.
-
The tool is aimed at helping healthcare in regions with less access to doctors.
Training and performance: Med-PaLM 2 has been trained on a selection of medical expert demonstrations to better handle healthcare conversations.
-
While some accuracy issues persist, as found in a study conducted by Google, the tool performed comparably to actual doctors in aspects such as reasoning and consensus-supported answers.
Data privacy: Users testing Med-PaLM 2 will have control over their data, which will be encrypted and inaccessible to Google.
-
This privacy measure ensures user trust and adherence to data security standards.
Google’s latest beast of a quantum computer is blowing everyone else out of the water. It’s making calculations in a blink that’d take top supercomputers almost half a century to figure out!
(Well, 47 years to be exact)
Here’s the gist: This new quantum from Google has 70 qubits (the building blocks of quantum computing). That’s a whole 17 more than their last machine, which might not sound like much, but in quantum land, that’s a huge deal.
It basically means 241 million times more powerful!
But what does that mean in practice? It’d take the world’s current number one supercomputer, Frontier, over 47 years to do what Google’s new quantum machine can do in an instant.
As always, there’s controversy. Some critics are saying the task used for testing was too much in favor of quantum computers and isn’t super useful outside of science experiments.
But we’re pushing boundaries here, folks, and this is one big step towards ‘utility quantum computing,’ where quantum computers do stuff that benefits all of us in ways we can’t even imagine right now.
What might those be? Well, imagine lightning-fast data analysis, creating more accurate weather forecasts, developing life-saving medicines, or even helping in solving complex climate change issues.
The potential is huge, and while we’re not there yet, we’re certainly getting closer.
The impact of poisoning LLM supply chains
LLMs are gaining massive recognition worldwide. However, no existing solution exists to determine the data and algorithms used during the model’s training. In an attempt to showcase the impact of this, Mithril Security undertook an educational project— PoisonGPT— aimed at showing the dangers of poisoning LLM supply chains.
It shows how one can surgically modify an open-source model and upload it to Hugging Face to make it spread misinformation while being undetected by standard benchmarks.
Mithril Security is also working on AICert, a solution to trace models back to their training algorithms and datasets which will be launched soon.
Why does this matter?
LLMs still resemble a vast, uncharted territory where many companies/users often turn to external parties and pre-trained models for training and data. It carries the inherent risk of applying malicious models to their use cases, exposing them to safety issues. This project highlights the awareness needed for securing LLM supply chains.
Google DeepMind is working on the definitive response to ChatGPT.
It could be the most important AI breakthrough ever.
In a recent interview with Wired, Google DeepMind’s CEO, Demis Hassabis, said this:
“At a high level you can think of Gemini as combining some of the strengths of AlphaGo-type systems with the amazing language capabilities of the large models [e.g., GPT-4 and ChatGPT] … We also have some new innovations that are going to be pretty interesting.”
Why would such a mix be so powerful?
DeepMind’s Alpha family and OpenAI’s GPT family each have a secret sauce—a fundamental ability—built into the models.
-
Alpha models (AlphaGo, AlphaGo Zero, AlphaZero, and even MuZero) show that AI can surpass human ability and knowledge by exploiting learning and search techniques in constrained environments—and the results appear to improve as we remove human input and guidance.
-
GPT models (GPT-2, GPT-3, GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and ChatGPT) show that training large LMs on huge quantities of text data without supervision grants them the (emergent) meta-capability, already present in base models, of being able to learn to do things without explicit training.
Imagine an AI model that was apt in language, but also in other modalities like images, video, and audio, and possibly even tool use and robotics. Imagine it had the ability to go beyond human knowledge. And imagine it could learn to learn anything.
That’s an all-encompassing, depthless AI model. Something like AI’s Holy Grail. That’s what I see when I extend ad infinitum what Google DeepMind seems to be planning for Gemini.
I’m usually hesitant to call models “breakthroughs” because these days it seems the term fits every new AI release, but I have three grounded reasons to believe it will be a breakthrough at the level of GPT-3/GPT-4 and probably well beyond that:
-
First, DeepMind and Google Brain’s track record of amazing research and development during the last decade is unmatched, not even OpenAI or Microsoft can compare.
-
Second, the pressure that the OpenAI-Microsoft alliance has put on them—while at the same time somehow removing the burden of responsibility toward caution and safety—pushes them to try harder than ever before.
-
Third, and most importantly, Google DeepMind researchers and engineers are masters at both language modeling and deep + reinforcement learning, which is the path toward combining ChatGPT and AlphaGo’s successes.
We’ll have to wait until the end of 2023 to see Gemini. Hopefully, it will be an influx of reassuring news and the sign of a bright near-term future that the field deserves.
If you liked this I wrote an in-depth article for The Algorithmic Bridge
• Demis Hassabis, the CEO of Google DeepMind, discusses the recent developments in AI and the future of the field.
• Google DeepMind is a new division of Google, created from the merger of Google Brain and DeepMind, a startup acquired by Google in 2014.
• DeepMind was known for applying AI to areas like games and protein-folding simulations, while Google Brain focused more on generative AI tools like large language models for chatbots.
• The merger was a strategic decision to make Google more competitive and faster to market with AI products.
• Hassabis discusses the competition in the AI field, noting that open-source models running on commodity hardware are rapidly evolving and catching up to the tools run by tech giants.
• He also talks about the risks and regulations associated with artificial general intelligence (AGI), a type of AI that can perform any intellectual task that a human being can.
• Hassabis signed a statement about AI risk that reads, “Mitigating the risk of extinction from AI should be a global priority alongside other societal-scale risks such as pandemics and nuclear war.”
• The article also touches on the impact of AI on labor, mentioning the creation of low-paid jobs for classifying data to train AI systems.
• Hassabis believes that we are at the beginning of a new era in AI, with the potential for new types of products and experiences that have never been seen before.
• The merger of DeepMind and Google Brain is still in progress, with the aim of creating a single, unified team.
Daily AI Update (Date: 7/10/2023): News from Google, Microsoft, Mithril Security, YouTube, TCS, and Shutterstock
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
Google & Microsoft battle to lead healthcare AI
– Reportedly, Google’s Med-PaLM 2 has been in testing at the Mayo Clinic research hospital. In April, Google announced its limited access for select Google Cloud customers to explore use cases and share feedback to investigate safe, responsible, and meaningful ways to use it.
-Meanwhile, Google’s rivals moved quickly to incorporate AI advances into patient interactions. Hospitals are beginning to test OpenAI’s GPT algorithms through Microsoft’s cloud service in several tasks.
-Google’s Med-PaLM 2 and OpenAI’s GPT-4 each scored similarly on medical exam questions, according to independent research released by the companies.
PoisonGPT shows the impact of poisoning LLM supply chains
– In an educational project, Mithril Security shows the dangers of poisoning LLM supply chains. It shows how one can surgically modify an open-source model and upload it to Hugging Face to make it spread misinformation while being undetected by standard benchmarks.
-To remedy this, it is also working on AICert, a solution to trace models back to their training algorithms and datasets.
Lost in the middle: How language models use long contexts
Does a bigger context window always lead to better results? New research reveals that
– Language models often struggle to use information in the middle of long input contexts
– Their performance decreases as the input context grows longer
– The performance is often highest when relevant information occurs at the beginning or end of the input context
YouTube tests AI-generated quizzes on educational videos
– YouTube is experimenting with AI-generated quizzes on its mobile app for iOS and Android devices, which are designed to help viewers learn more about a subject featured in an educational video.
TCS bets big on Azure Open AI
– TCS now plans to get 25,000 associates trained and certified on Azure Open AI to help clients accelerate their adoption of this powerful new technology.
Shutterstock continues generative AI push with legal protection
– Shutterstock announced that it will offer enterprise customers full indemnification for the license and use of generative AI images on its platform, to protect them against potential claims related to their use of the images. The company will fulfill requests for indemnification on demand through a human review of the images.
Recently, Bruno Le Maire (France’s Economy Minister) said he’d consider a 100% European ChatGPT to be a good idea. He said:
« Je plaide donc, avant de poser les bases de la régulation de l’intelligence artificielle, pour que nous fassions de l’innovation, que nous investissions et que nous nous fixions comme objectif d’avoir un OpenAI européen sous cinq ans, avec les calculateurs, les scientifiques et les algorithmes nécessaires. C’est possible ».
Which means :
« I therefore plead, before laying the foundations for the regulation of artificial intelligence, that we innovate, that we invest and that we set ourselves the objective of having a European OpenAI within five years, with computers, the necessary scientists and algorithms. It is possible ».
He also said he thought it’ll boost the European Union’s economy.
However, by 2028, OpenAI’s ChatGPT, Bing AI and Google Bard might have all considerably improved, making it a lot harder for the ‘European ChatGPT’ to compete with those three other ones
So in this case, it’s possible that Europe would start with a very high delay that’d be hard to catch up with…
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 09th, 2023
A humanoid robot draws this cat and says, ‘if you don’t like my art, you probably just don’t understand art’.
Check out Ameca, the humanoid robot that’s marketed as the ‘most expensive robot that can draw’.
How? It’s powered with Stable Diffusion, built by Engineered Arts.
In a recent YouTube video, Ameca sketched a cat and asked for opinions.
When the person said looks ‘sketchy’, Ameca shot back, “If you don’t like my art, you probably just don’t understand art.”
Burn!
I’m not even sure if it was Ameca’s comeback or something is just so philosophical about this drawing that at least I don’t understand. 🥴
Navigating on the moon using AI
Dr. Alvin Yew is currently working on an AI solution that takes topographical data on the moon and uses it in a neural network to help determine an astronaut’s location in the event that no GPS or other forms of electronic navigation is available. You can check it out here:
Meet Pixis AI: An Emerging Startup Providing Codeless AI Solutions

How to land a high-paying job as an AI prompt engineer

Understanding the role of an AI prompt engineer
An AI prompt engineer specializes in designing effective prompts to guide the behavior and output of AI models. They deeply understand natural language processing (NLP), machine learning and AI systems.
The AI prompt engineer’s primary goal is to fine-tune and customize AI models by crafting precise prompts that align with specific use cases, ensuring desired outputs and enhanced control.
Developing the necessary skills
To excel as an AI prompt engineer, some skills are crucial:
NLP and language modeling
A strong understanding of transformer-based structures, language models and NLP approaches is required. Effective prompt engineering requires an understanding of the pre-training and fine-tuning procedures used by language models like ChatGPT.
Programming and machine learning
Expertise in programming languages like Python and familiarity with frameworks for machine learning, such as TensorFlow or PyTorch, is crucial. Success depends on having a solid understanding of data preprocessing, model training and evaluation.
Related: How to write effective ChatGPT prompts for better results
Collaboration and communication
Prompt engineers will frequently work with other teams. Excellent written and verbal communication skills are required to work with stakeholders effectively, explain urgent requirements, and comprehend project goals.
Educational background and learning resources
A strong educational foundation is beneficial for pursuing a career as an AI prompt engineer. The knowledge required in fields like NLP, machine learning, and programming can be acquired with a bachelor’s or master’s degree in computer science, data science, or a similar discipline.
Additionally, one can supplement their education and keep up-to-date on the most recent advancements in AI and prompt engineering by using online tutorials, classes, and self-study materials.
Getting practical experience
Getting real-world experience is essential to proving one’s abilities as an AI prompt engineer. Look for projects, research internships, or research opportunities where one can use prompt engineering methods.
An individual’s abilities can be demonstrated, and concrete proof of their knowledge can be provided by starting their own prompt engineering projects or contributing to open-source projects.
Networking and job market context
As an AI prompt engineer, networking is essential for seeking employment prospects. Attend AI conferences, get involved in online forums, go to AI-related events and network with industry experts. Keep abreast of employment listings, AI research facilities, and organizations that focus on NLP and AI customization.
Continuous learning and skill enhancement
As AI becomes increasingly ubiquitous, the demand for skilled AI prompt engineers continues to grow. Landing a high-paying job in this field requires a strong foundation in NLP, machine learning, and programming, along with practical experience and networking.
Aspiring prompt engineers can position themselves for success and secure a high-paying job in this exciting and evolving field by continuously enhancing skills, staying connected with the AI community, and demonstrating expertise.
AI Weekly Rundown (July 1 to July 7)
AI builds robots, detects wildfires, designs CPU, uses public data to train, and more this week.
ChatGPT builds robots: New research
– Microsoft Research presents an experimental study using OpenAI’s ChatGPT for robotics applications. It outlines a strategy that combines design principles for prompt engineering and the creation of a high-level function library that allows ChatGPT to adapt to different robotics tasks, simulators, and form factors.
– The study encompasses a range of tasks within the robotics domain, from basic logical, geometrical, and mathematical reasoning to complex domains such as aerial navigation, manipulation, and embodied agents.
– Microsoft also released PromptCraft, an open-source platform where anyone can share examples of good prompting schemes for robotics applications.
Magic123 creates HQ 3D meshes from unposed images
– New research from Snap Inc. (and others) presents Magic123, a novel image-to-3D pipeline that uses a two-stage coarse-to-fine optimization process to produce high-quality high-resolution 3D geometry and textures. It generates photo-realistic 3D objects from a single unposed image.
– The core idea is to use 2D and 3D priors simultaneously to generate faithful 3D content from any given image. Magic123 achieves state-of-the-art results in both real-world and synthetic scenarios.
Any-to-any generation: Next stage in AI evolution
– Microsoft presents CoDi, a novel generative model capable of processing and simultaneously generating content across multiple modalities. It employs a novel composable generation strategy that involves building a shared multimodal space by bridging alignment in the diffusion process. This enables the synchronized generation of intertwined modalities, such as temporally aligned video and audio.
– One of CoDi’s most significant innovations is its ability to handle many-to-many generation strategies, simultaneously generating any mixture of output modalities. CoDi is also capable of single-to-single modality generation and multi-conditioning generation.
OpenChat beats 100% of ChatGPT-3.5
– OpenChat is a collection of open-source language models specifically trained on a diverse and high-quality dataset of multi-round conversations. These models have undergone fine-tuning using approximately ~6K GPT-4 conversations filtered from the ~90K ShareGPT conversations. It is designed to achieve high performance with limited data.
AI designs CPU in <5 hours
– A team of Chinese researchers published a paper describing how they used AI to design a fully functional CPU based on the RISC-V architecture, which is as fast as an Intel i486SX. They called it a “foundational step towards building self-evolving machines.” The AI model completed the design cycle in under 5 hours, reducing it by 1000 times.
SAM-PT: Video object segmentation with zero-shot tracking
– Researchers introduced SAM-PT, an advanced method that expands the capabilities of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to track and segment objects in dynamic videos. SAM-PT utilizes interactive prompts, such as points, to generate masks and achieves exceptional zero-shot performance in popular video object segmentation benchmarks, including DAVIS, YouTube-VOS, and MOSE. It takes a unique approach by leveraging robust and sparse point selection and propagation techniques.
– To enhance the tracking accuracy, SAM-PT incorporates K-Medoids clustering for point initialization and a point re-initialization strategy.
Google’s AI models to train on public data
– Google has updated its privacy policy to state that it can use publicly available data to help train and create its AI models. This suggests that Google is leaning heavily into its AI bid. Plus, harnessing humanity’s collective knowledge could redefine how AI learns and comprehends information.
LEDITS: Image editing with next-level AI capabilities
– Hugging Face research has introduced LEDITS- a combined lightweight approach for real-image editing, incorporating the Edit Friendly DDPM inversion technique with Semantic Guidance. Thus, it extends Semantic Guidance to real image editing while harnessing the editing capabilities of DDPM inversion.
OpenAI makes GPT-4 API and Code Interpreter available
– GPT-4 API is now available to all paying OpenAI API customers. GPT-3.5 Turbo, DALL·E, and Whisper APIs are also now generally available, and OpenAI is announcing a deprecation plan for some of the older models, which will retire beginning of 2024.
– Moreover, OpenAI’s Code Interpreter will be available to all ChatGPT Plus users over the next week. It lets ChatGPT run code, optionally with access to files you’ve uploaded. You can also ask ChatGPT to analyze data, create charts, edit files, perform math, etc.
Salesforce’s CodeGen2.5, a small but mighty code LLM
– Salesforce’s CodeGen family of models allows users to “translate” natural language, such as English, into programming languages, such as Python. Now it has added a new member- CodeGen2.5, a small but mighty LLM for code.
– Its smaller size means faster sampling, resulting in a speed improvement of 2x compared to CodeGen2. The small model easily allows for personalized assistants with local deployments.
InternLM: A model tailored for practical scenarios
– InternLM has open-sourced a 7B parameter base model and a chat model tailored for practical scenarios. The model
– Leverages trillions of high-quality tokens for training to establish a powerful knowledge base
– Supports an 8k context window length, enabling longer input sequences and stronger reasoning capabilities
– Provides a versatile toolset for users to flexibly build their own workflows
-It is a 7B version of a 104B model that achieves SoTA performance in multiple aspects, including knowledge understanding, reading comprehension, mathematics, and coding. InternLM-7B outperforms LLaMA, Alpaca, and Vicuna on comprehensive exams, including MMLU, HumanEval, MATH, and more.
Microsoft’s LongNet scales transformers to 1B tokens
– Microsoft research’s recently launched LongNet allows language models to have a context window of over 1 billion tokens without sacrificing the performance on shorter sequences.
– LongNet achieves this through dilated attention, exponentially expanding the model’s attentive field as token distance increases.
– This breakthrough offers significant advantages:
- It maintains linear computational complexity and a logarithmic token dependency;
- It can be used as a distributed trainer for extremely long sequences;
- Its dilated attention can seamlessly replace standard attention in existing Transformer models.
OpenAI’s Superalignment – The next big goal!
– OpenAI has launched Superalignment, a project dedicated to addressing the challenge of aligning artificial superintelligence with human intent. Over the next four years, 20% of OpenAI’s computing power will be allocated to this endeavor. The project aims to develop scientific and technical breakthroughs by creating an AI-assisted automated alignment researcher.
– This researcher will evaluate AI systems, automate searches for problematic behavior, and test alignment pipelines. Superalignment will comprise a team of leading machine learning researchers and engineers open to collaborating with talented individuals interested in solving the issue of aligning superintelligence.
AI can now detect and prevent wildfires
– Cal Fire, the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection, uses AI to help detect wildfires more effectively without the human eye. Advanced cameras equipped with autonomous smoke detection capabilities are replacing the reliance on human eyes to spot potential fire outbreaks.
– Detecting wildfires is challenging due to their occurrence in remote areas with limited human presence and their unpredictable nature fueled by environmental factors. To address these challenges, innovative solutions and increased vigilance are necessary to identify and respond to wildfires timely.
And there’s more…
– Human’s first product is an AI-powered wearable device with projected display
– Microsoft is giving early users a sneak peek at its AI assistant for Windows 11
– Midjourney released a “weird” parameter that can give images a crazy twist!
– Nvidia acquired OmniML, an AI startup that shrinks machine-learning models
– The first drug fully generated by AI entered clinical trials with human patients
– Moonlander launches AI-based platform for immersive 3D game development
– AI and accelerated computing will help climate researchers achieve miracles!
– Data scientists are using AI to translate Cuneiform & Akkadian into English.
– DISCO can generate high-quality human dance images and videos.
– OpenAI disables ChatGPT’s “Browse” beta to do right by content owners
– Celestial AI raises $100 million for its Photonic Fabric technology platform
– Inflection AI develops supercomputer with 22,000 NVIDIA H100 AI GPUs
– Urtopia unveils Fusion e-bike with ChatGPT integration
– Flacuna provides valuable insights into the performance of LLMs.
– Gartner survey: 79% of Strategists embrace AI and Analytics success.
– Spotify CEO’s Neko Health raises $65M for full-body scan preventative healthcare.
– VA researchers working on AI that can predict prostate cancer!
– US to acquire 1k AI-controlled armed drones soon!
– AWS Docs GPT: AI-powered search and chat for AWS documentation
– Alibaba unveils an image generator to take on Midjourney and DALL-E
– DigitalOcean acquires cloud computing and AI startup Paperspace for $111M
– AI-powered innovation could create over £400B in economic value for UK by 2030
– A Standford study finds AI Agents that “self-reflect” perform better in changing environments
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 08th, 2023
AI May Have Found The Most Powerful Anti-Aging Molecule Ever Seen

“The AI model identified 21 top-scoring molecules that it deemed to have a high likelihood of being senolytics. If we had tested the original 4,340 molecules in the lab, it would have taken at least a few weeks of intensive work and £50,000 just to buy the compounds, not counting the cost of the experimental machinery and setup.
We then tested these drug candidates on two types of cells: healthy and senescent. The results showed that out of the 21 compounds, three (periplocin, oleandrin and ginkgetin) were able to eliminate senescent cells, while keeping most of the normal cells alive. These new senolytics then underwent further testing to learn more about how they work in the body.
More detailed biological experiments showed that, out of the three drugs, oleandrin was more effective than the best-performing known senolytic drug of its kind.
The potential repercussions of this interdisciplinary approach – involving data scientists, chemists and biologists – are huge. Given enough high-quality data, AI models can accelerate the amazing work that chemists and biologists do to find treatments and cures for diseases – especially those of unmet need.”
Senolytics work by killing senescent cells. These are cells that are “alive” (metabolically active), but which can no longer replicate, hence their nickname: zombie cells.
The inability to replicate is not necessarily a bad thing. These cells have suffered damage to their DNA – for example, skin cells damaged by the Sun’s rays – so stopping replication stops the damage from spreading.
But senescent cells aren’t always a good thing. They secrete a cocktail of inflammatory proteins that can spread to neighboring cells. Over a lifetime, our cells suffer a barrage of assaults, from UV rays to exposure to chemicals, and so these cells accumulate.
The week in AI: Generative AI spams up the web

“LIfT BioSciences today announced that its first-in-class cell therapy destroyed on average over 90% of the tumoroid in a PDX organoid across five of the most challenging to treat solid tumour types including bladder cancer, rectal cancer, colorectal cancer, gastric cancer and squamous cell non-small cell lung cancer.”
N-LIfT shows potent cancer killing across multiple solid tumour types (liftbiosciences.com)
The general gist is that current immunotherapies are inadequate against solid tumours because they target a specific mutation while solid tumours have multiple mutations so they eventually evolve resistance to any single treatment. Immunotherapies work better on blood cancers because blood cancer cells are more likely to universally express a targetable mutation. So instead of using T-cells, which target single mutations, Lift Biosciences are using neutrophils which are general-purpose killers. By sampling blood from thousands of people, they’ve found large natural variation in cancer-killing ability throughout the general population — with some people’s neutrophils killing 20x more cancer cells than others, so by simply finding people with high innate immunity to cancer and transplanting their “Alpha” neutrophils into patients, they believe they can effectively treat all solid cancers regardless of mutation.
Their method is inspired by Chinese scientist Zheng Cui who cured various cancers in a colony of mice using blood from cancer-resistant members. Here’s an article on him: The Mouse That Wouldn’t Die: How a Lack of Public Funding Holds Back a Promising Cancer Treatment | HuffPost Impact
Instead of testing their treatment in mice they grow mini-tumours called tumouroids and test it on them, which yields far greater predictive ability as to how treatment will work in humans, and so far their pre-clinical data have been really promising, greatly outperforming existing immunotherapies like Keytruda: N-LIfT cell therapy shows complete and superior cell killing in solid tumour organoid (liftbiosciences.com)
They’re going into clinical trials next year so if they’re right this could be revolutionary. Here’s a video where the founder goes into further detail: https://youtu.be/XSbaUjWj2Kk
Recurrence prediction in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using machine learning of quantitative nuclear features
Knowledge Nugget: Models generating training data: huge win or fake win?
We’ve seen a lot of papers claiming you can use one language model to generate useful training data for another language model. But is it a huge or a fake win for us?
In this intriguing article,
attempts to answer this. The article explores the tension between empirical gains from generated training data and data processing inequality. The article also presents various examples and studies demonstrating both the benefits and limitations of training data generation. And it proposes that the key to understanding the effectiveness lies not in the model generating the data but in the filtering process. And much more.
Why does this matter?
The article offers a thought-provoking perspective on training data generation, filtering techniques, and the relationship between models and data. It can expand the understanding of AI practitioners and stimulate critical thinking in the realm of language model training and data generation.
The publication is available here.
The repository is available here.
FTA,
“Scaling sequence length has become a critical demand in the era of large language models. However, existing methods struggle with either computational complexity or model expressivity, rendering the maximum sequence length restricted. In this work, we introduce LongNet, a Transformer variant that can scale sequence length to more than 1 billion tokens, without sacrificing the performance on shorter sequences. Specifically, we propose dilated attention, which expands the attentive field exponentially as the distance grows. LongNet has significant advantages: 1) it has a linear computation complexity and a logarithm dependency between tokens; 2) it can be served as a distributed trainer for extremely long sequences; 3) its dilated attention is a drop-in replacement for standard attention, which can be seamlessly integrated with the existing Transformer-based optimization. Experiments results demonstrate that LongNet yields strong performance on both long-sequence modeling and general language tasks. Our work opens up new possibilities for modeling very long sequences, e.g., treating a whole corpus or even the entire Internet as a sequence.”
This research demonstrates linear computational complexity, support for distributed training, and opens up possibilities for modeling very long sequences, such as the entire Internet. LongNet outperforms existing methods on both long-sequence modeling and general language tasks, and it benefits from longer context windows for prompting, giving it the ability to leverage extensive context for improved language modeling.
The Learning Corner
-
Stanford Free ML Course – Machine Learning Specialization
-
AI For Everyone – Discover the world of AI and its impact on businesses with this beginner-friendly course, designed for non-technical learners seeking to understand AI terminology, applications, strategy, and ethical considerations in their organizations.
I’ve been using ChatGPT at work for a few months. I’m in marketing and it’s a phenomenal tool that has helped me be more efficient at my job. I don’t always think ChatGPT has very good answers, but it usually helps me figure out what the answer should be. Very helpful for optimizing and writing copy.
Today, I used Bard for the first time and holy shit- it’s way better. The responses were so straight forward and helpful. Interacting with it felt so much like a conversation as opposed to the stale back and forth I get with ChatGPT. Honestly a huge eye opener as far as the future of AI as a companion, rather than a tool. I can absolutely imagine a future where “AI friends” are commonplace. Bard feels fluid and smooth. Very excited to see how using bard affects my work and to experiment where else I can use it and what else I can do with it. Anyway, what does everyone else think?
Today, Code Interpreter is rolling out to all ChatGPT Plus subscribers. This tool can almost turn everyone into junior designers with no code experience it’s incredible.
To stay on top of AI developments look here first. But the tutorial is here on Reddit for your convenience!
Don’t Skip This Part!
Code Interpreter does not immediately show up you have to turn it on. Go to your settings and click on beta features and then toggle on Code Interpreter.
These use cases are in no particular order but they will give you good insight into what is possible with this tool.
-
Edit Videos: You can edit videos with simple prompts like adding slow zoom or panning to a still image. Example: Covert this GIF file into a 5 second MP4 file with slow zoom (Link to example)
-
Perform Data Analysis: Code Interpreter can read, visualize, and graph data in seconds. Upload any data set by using the + button on the left of the text box. Example: Analyze my favorites playlist in Spotify Analyze my favorites playlist in Spotify (Link to example)
-
Convert files: You can convert files straight inside of ChatGPT. Example: Using the lighthouse data from the CSV file in into a Gif (Link to example)
-
Turn images into videos: Use Code Interpreter to turn still images into videos. Example Prompt: Turn this still image into a video with an aspect ratio of 3:2 will panning from left to right. (Link to example)
-
Extract text from an image: Turn your images into a text will in seconds (this is one of my favorites) Example: OCR “Optical Character Recognition” this image and generate a text file. (Link to example)
-
Generate QR Codes: You can generate a completely functioning QR in seconds. Example: Create a QR code for Reddit.com and show it to me. (Link to example)
-
Analyze stock options: Analyze specific stock holdings and get feedback on the best plan of action via data. Example: Analyze AAPL’s options expiring July 21st and highlight reward with low risk. (Link to example)
-
Summarize PDF docs: Code Interpreter can analyze and output an in-depth summary of an entire PDF document. Be sure not to go over the token limit (8k) Example: Conduct casual analysis on this PDF and organize information in clear manner. (Link to example)
-
Graph Public data: Code Interpreter can extract data from public databases and convert them into a visual chart. (Another one of my favorite use cases) Example: Graph top 10 countries by nominal GDP. (Link to example)
-
Graph Mathematical Functions: It can even solve a variety of different math problems. Example: Plot function 1/sin(x) (Link to example)
Learning to leverage this tool can put you so ahead in your professional world. If this was helpful consider joining one of the fastest growing AI newsletters to stay ahead of your peers on AI.
OpenAI, creators of ChatGPT, is starting a new team called Superalignment. They’re joining top experts to stop super-smart AI from being smarter than human and posing potential risks. With a target to tackle this issue in the next four years, they’re devoting 20% of their resources to this mission.
This team will build an ‘AI safety inspector’ to check super-smart AI systems. With AI like ChatGPT already changing our lives, it’s important to control it. OpenAI is taking the lead to keep AI safe and helpful for everyone.Why it matters? This could make sure our future with super-smart AI is safe and under control.
—-
Most people agree that misalignment of superintelligent AGI would be a Big Problem™. Among other developments, now OpenAI has announced the superalignment project aiming to solve it.
But I don’t see how such an alignment is supposed to be possible. What exactly are we trying to align it to, consider that humans ourselves are so diverse and have entirely different value systems? An AI aligned to one demographic could be catastrophical for another demographic.
Even something as basic as “you shall not murder” is clearly not the actual goal of many people. Just look at how Putin and his army is doing their best to murder as many people as they can right now. Not to mention other historical people which I’m sure you can think of many examples for.
And even within the west itself where we would typically tend to agree on basic principles like the example above, we still see very splitting issues. An AI aligned to conservatives would create a pretty bad world for democrats, and vice versa.
Is the AI supposed to get aligned to some golden middle? Is the AI itself supposed to serve as a mediator of all the disagreement in the world? That sounds even more difficult to achieve than the alignment itself. I don’t see how it’s realistic. Or are each faction supposed to have their own aligned AI? If so, how does that not just amplify the current conflict in the world to another level?
Daily AI News 7/8/2023
Mobile and desktop traffic to ChatGPT’s website worldwide fell 9.7% in June from the previous month, according to internet data firm Similarweb. Downloads of the bot’s iPhone app, which launched in May, have also steadily fallen since peaking in early June, according to data from Sensor Tower.[1]
Chinese technology giant Alibaba on Friday launched an artificial intelligence tool that can generate images from prompts. Tongyi Wanxiang allows users to input prompts in Chinese and English and the AI tool will generate an image in various styles such as a sketch or 3D cartoon.[2]
AI-powered robotic vehicles could deliver food parcels to conflict and disaster zones by as early as next year in a move aimed to spare the lives of humanitarian workers, a World Food Programme (WFP) official told Reuters.[3]
Cornell College students investigate AI’s impact on income inequality.[4]
Sources:
[1] https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2023/07/07/chatgpt-users-decline-future-ai-openai/
[2] https://www.cnbc.com/amp/2023/07/07/alibaba-launches-ai-tool-to-generate-images-from-text-.html
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 07th, 2023
Data Scraping in the Spotlight: Are Language Models Overstepping by Training on Everyone’s Content
This Redditor wrote a deep dive analysis around the topic of data scraping by companies for training large language models – https://thisisunpacked.substack.com/p/data-scraping-in-the-spotlight-language-models
He dives into data scraping, which is a common yet contentious approach used by products like ChatGPT and Google Bard to get data for training machine learning models. The article starts with the basics of machine learning models (no prior technical knowledge assumed) and dives into the crux of the issue:
– Do these products have the permissions to use this data?
– Why should OpenAI, Google care about that?
– And what approaches are content platforms (whose data is being scraped) adopting?
Hope you find it useful.
Conversational AI Tools for your business to simplify user interactions
AI chat and voice bots :
-
Yellow AI
-
Feedyou
-
Convy
-
Landbot
-
Kore
-
Poly
AI Speech recognition tools:
-
Fireflies
-
Assembly
-
Voicegain
Text to speech conversational ai tools:
-
LOVO
-
Speechify
-
Murf
Got any more to add to this?
A more comprehensive list along with the pricing plans of these tools – https://www.mailmodo.com/guides/conversational-ai-tools/
A few ai affiliate marketing tools :
-
Chatfuel
-
AdPlexity
-
Mention
-
Post Affiliate Pro
-
Adversity
AI affiliate programs to enhance profitability :
-
Scalenut
-
jasper.ai
-
Adcreative.ai
-
Designs.ai
-
Grammarly
Any more suggestions?
Can read more about them and their pricing plans here – https://www.mailmodo.com/guides/ai-affiliate-marketing/
The 10 Hottest Data Science And Machine Learning Startups Of 2023 (So Far)

-
Aporia, Co-Founder, CEO Liran Hason: Aporia’s namesake observability platform is used by data scientists and machine learning engineers to monitor and improve machine learning models in production.
-
Baseten, Co-Founder, CEO Tuhin Srivastava: The critical step of integrating machine learning models with real-world business processes is generally a lengthy, expensive process. Baseten’s cloud-based machine learning infrastructure makes going from machine learning model to production-grade applications fast and easy, according to the company.
-
ClosedLoop.ai, Co-Founder, CEO Andrew Eye: A rising star in the health-care IT space, ClosedLoop.ai provides a data science platform and prebuilt content library for building, deploying and maintaining predictive applications used by health-care providers and payers.
-
Coiled, Founder, CEO Matt Rocklin: Coiled offers Coiled Cloud, a Software-as-a-Service platform for developing and scaling Python-based data science, machine learning and AI workflows in the cloud.
-
Hex, Co-Founder, CEO Barry McCardel: Hex markets a data science and analytics collaboration platform that creates a modern data workspace where data scientists and analysts can connect with data, analyze it in collaborative SQL and Python-powered notebooks, and share work as interactive data applications and stories.
-
MindsDB, Co-Founder, CEO Jorge Torres: MIndsDB says its mission is to “democratize machine learning” with its open-source infrastructure that the company says enables developers to quickly integrate machine learning capabilities into applications and connect any data source with any AI framework.
AI advancements, especially in personalized tutoring, may soon make traditional classrooms obsolete, suggests leading AI professor from Berkeley. However, this significant shift carries potential risks, such as the misuse of technology and changes in the roles of human teachers.
Here’s a recap:
The Potential End of Traditional Classrooms: Professor Stuart Russell suggests that the rise of AI, particularly personalized AI tutors, could spell the end of traditional classrooms. This technology could deliver high-quality, individualized education, reaching every child in the world who has access to a smartphone.
-
AI-powered personalized tutors could replace traditional classroom education.
-
The technology is capable of delivering most high school curriculum.
-
Education access could significantly broaden globally due to AI advancements.
Risks and Changes to Teacher Roles: Deploying AI in education could lead to changes in the roles of human teachers and carries potential risks such as misuse for indoctrination. While AI might reduce the number of teachers, human involvement would still be necessary, albeit in altered roles such as facilitation or supervision.
-
Teacher roles could shift towards facilitation and supervision due to AI.
-
The number of traditional teaching jobs might decrease.
-
Potential misuse of AI in education, such as for indoctrination, is a significant concern.
The Benefits of Using AI for Product Design (With Examples)
Artificial intelligence (AI) has recently gained a lot of popularity for its impressive visual artistry. However, art is only the tip of the iceberg when it comes to the entire scope of AI-powered creation in general. One of its most promising fields of application is AI based product design – or simply using AI for product design at different stages. It can not only save costs and time, but also help companies create better products. The possible applications are so many that it’s not far-fetched to say that AI and product design would be almost inseparable in the future.
Here is how AI in product design can be greatly helpful at various stages of the process:
-
Data Collection
AI can not only create, but also find things for you. AI tools like ChatGPT can access and analyze a vast amount of data (even the entire Internet) with great speed and accuracy. They can help product designers find precisely the information they need to research the market, their target users and get inspiration for their new designs. Such tools help designers save a substantial amount of time and energy that’s usually spent in research. -
Ideation
AI technology can be used to generate multiple concept designs for new products by inputting data and prompts in order to establish the constraints and goals. This process is known as generative design. At present, AI software is capable of generating hundreds of different concept designs for a product in only a few minutes, saving the time required for manual design iterations. AI in product development can also work in collaboration with designers, combining AI based product design, analysis and optimization with human creativity. This helps designers think beyond the boundaries of their own imagination and dramatically accelerate their ideation process.
More info -> https://www.nextechar.com/blog/benefits-of-using-ai-for-product-design
Whether you’re using AI-ML for business intelligence or for automating your businesses, you are way ahead of your competition because you’re making your data work for you!
Business Forecasting using Machine learning models
Making business-generated data work for you is possibly the wisest decision a business can make. Business forecasting guides a business into the future with better and more advanced decision-making methods than traditional ones. ML-backed forecasting helps businesses to predict and deal with any possible issue beforehand, be it a logistical issue, running out of stock, or even minimizing loss functions, machine learning forecasting got it all covered for you!
https://www.seaflux.tech/blogs/ML-forecasting-for-business-intelligence
AI robots, at a United Nations summit, presented the idea that they could potentially run the world more efficiently than humans, all while urging for cautious and responsible utilization of artificial intelligence technologies.
Here’s what happened:
AI Robots’ Claim to Leadership:
During the UN’s AI for Good Global Summit, advanced humanoid robots put forward the idea that they could be better world leaders.
-
The claim hinges on robots’ capacity to process large amounts of data quickly and without human emotional biases.
-
Sophia, a humanoid robot developed by Hanson Robotics, was a strong proponent of this perspective.
Balancing Efficiency and Caution:
While robots may argue for their efficiency, they simultaneously call for a careful approach to embracing AI.
-
They highlighted that despite the potential benefits, unchecked AI advancements could lead to job losses and social unrest.
-
Transparency and trust-building were mentioned as crucial factors in the responsible deployment of AI technologies.
AI Robots: The Future and Beyond:
Despite their lack of human emotions and consciousness, AI robots are optimistic about their future role.
-
They foresee significant breakthroughs and suggest that the AI revolution is already happening.
-
Yet, they acknowledge that their inability to experience human emotions is a current limitation.
Comedy collective ComedyBytes is doing live shows using AI in NYC.
They’re doing mostly roasts, improv, rap battles, and even music videos.
This is the first time I’ve seen comedians (openly) using ChatGPT or any AI tools.
Personally, I found the roast to be the coolest part—because who doesn’t love a good roast.
“We use ChatGPT to generate and curate roast jokes. Not all of them are perfect, but I’d probably say maybe 10 to 20 percent of them make it to the show,” explained founder Eric Doyle.
-
Round 1 is humans roasting machines and machines roasting humans
-
Round 2 is human comedians roasting AI celebrities and vice versa
-
Round 3 is human comedians versus an AI version of him or herself
Eric Doyle, head of ComedyBytes, said “It got a lot more personal than I thought — not in a bad way, but I was not expecting it to be so pointed. There was a lot of like, “Your code isn’t even that good.” I’m like, “Oh, man, that was spicy.” I’ll be the first to say that I discredited a lot of the A.I. innovations. When they were coming out, I was kind of skeptical that it could generate good comedic content. As a comedian or a creator, you spend so much time editing and refining, and it’s a little bit frustrating how fast it can come up with good content or decent content.”
If a computer told me my code “isn’t even that good” I’d be butthurt too lol.
Other tool they’re using include:
-
Midjourney to make funny images
-
Wonder Dynamics for music videos
-
ElevenLabs for AI comedian voices,
-
D-ID to generate avatar faces
Great article from NYT.
The U.S. Department of Defense is trialing generative AI to aid in its decision-making process, leveraging its capabilities in simulated military exercises and examining its usefulness in handling classified data.
Generative AI in Military Exercises: The military is using generative AI in their live training exercises. The goal of this initiative is to explore how AI can be used in decision-making processes, and in controlling military sensors and firepower. This is an innovative approach that could potentially transform how military operations are conducted.
-
The trials have been reported as successful and swift.
-
The military is discovering that this kind of AI implementation is feasible.
Processing Classified Data: The artificial intelligence tools being tested have demonstrated the ability to process classified data quickly and efficiently.
-
These AI tools can handle tasks that would take human personnel significantly longer to complete.
-
However, complete control will not be given to AI systems just yet, indicating that while AI is showing promise, there are still limitations and considerations to be made.
Testing AI Responses to Global Crises: The military is testing how AI responds to various global crisis scenarios, including an invasion of Taiwan by China.
-
Alongside responding to threats, there’s a focus on testing AI’s reliability and “hallucination” tendencies—instances where AI generates false results not based on factual data.
-
A tool named Donovan, developed by Scale AI, was used to simulate a hypothetical war between the U.S. and China over Taiwan.
Pretty bold prediction from OpenAI: the company says superintelligence (which is more capable than AGI, in their view) could arrive “this decade,” and it could be “very dangerous.”
As a result, they’re forming a new Superalignment team led by two of their most senior researchers and dedicating 20% of their compute to this effort.
Let’s break this what they’re saying and how they think this can be solved, in more detail:
Why this matters:
-
“Superintelligence will be the most impactful technology humanity has ever invented,” but human society currently doesn’t have solutions for steering or controlling superintelligent AI
-
A rogue superintelligent AI could “lead to the disempowerment of humanity or even human extinction,” the authors write. The stakes are high.
-
Current alignment techniques don’t scale to superintelligence because humans can’t reliably supervise AI systems smarter than them.
How can superintelligence alignment be solved?
-
An automated alignment researcher (an AI bot) is the solution, OpenAI says.
-
This means an AI system is helping align AI: in OpenAI’s view, the scalability here enables robust oversight and automated identification and solving of problematic behavior.
-
How would they know this works? An automated AI alignment agent could drive adversarial testing of deliberately misaligned models, showing that it’s functioning as desired.
What’s the timeframe they set?
-
They want to solve this in the next four years, given they anticipate superintelligence could arrive “this decade”
-
As part of this, they’re building out a full team and dedicating 20% compute capacity: IMO, the 20% is a good stake in the sand for how seriously they want to tackle this challenge.
Could this fail? Is it all BS?
-
The OpenAI team acknowledges “this is an incredibly ambitious goal and we’re not guaranteed to succeed” — much of the work here is in its early phases.
-
But they’re optimistic overall: “Superintelligence alignment is fundamentally a machine learning problem, and we think great machine learning experts—even if they’re not already working on alignment—will be critical to solving it.”
The US military has always been interested in AI, but the speed at which they’ve jumped on the generative AI bandwagon is quite surprising to me — they’re typically known to be a slow-moving behemoth and very cautious around new tech.
Bloomberg reports that the US military is currently trialing 5 separate LLMs, all trained on classified military data, through July 26.
Expect this to be the first of many forays militaries around the world make into the world of generative AI.
Why this matters:
-
The US military is traditionally slow to test new tech: it’s been such a problem that the Defense Innovation Unit was recently reorganized in April to report directly to the Secretary of Defense.
-
There’s a tremendous amount of proprietary data for LLMs to digest: information retrieval and analysis is a huge challenge — going from boolean searching to natural language queries is already a huge step up.
-
Long-term, the US wants AI to empower military planning, sensor analysis, and firepower decisions. So think of this is as just a first step in their broader goals for AI over the next decade.
What are they testing? Details are scarce, but here’s what we do know:
-
ScaleAI’s Donovan platform is one of them. Donovan is defense-focused AI platform and ScaleAI divulged in May that the XVIII Airborne Corps would trial their LLM.
-
The four other LLMs are unknown, but expect all the typical players, including OpenAI. Microsoft has a $10B Azure contract with DoD already in place.
-
LLMs are evaluated for military response planning in this trial phase: they’ll be asked to help plan a military response for escalating global crisis that starts small and then shifts into the Indo-Pacific region.
-
Early results show military plans can be completed in “10 minutes” for something that would take hours to days, a colonel has revealed.
What the DoD is especially mindful of:
-
Bias compounding: could result in one strategy irrationally gaining preference over others.
-
Incorrect information: hallucination would clearly be detrimental if LLMs are making up intelligence and facts.
-
Overconfidence: we’ve all seen this ourselves with ChatGPT; LLMs like to be sound confident in all their answers.
-
AI attacks: poisoned training data and other publicly known methods of impacting LLM quality outputs could be exploited by adversaries.
The broader picture: LLMs aren’t the only place the US military is testing AI.
-
Two months ago, a US air force officer discussed how they had tested autonomous drones, and how one drone had fired on its operator when its operator refused to let it complete its mission. This story gained traction and was then quickly retracted.
-
Last December, DARPA also revealed they had AI F-16s that could do their own dogfighting.
The Telegraph reports
Wimbledon may replace line judges with artificial intelligence (AI) technology in the future, its tournament director has said.
The All England Lawn Tennis Club (AELTC) is using AI to produce its video highlights packages for this year’s Championships, and on Friday said it would not rule out employing the technology in lieu of humans to make line calls during matches.
When asked about the influence AI may continue to have at the sporting event, Jamie Baker, Wimbledon’s tournament director, said: “Line calling obviously is something that is accelerated in the rest of tennis and we are not making any decisions at this point, but we are constantly looking at those things as to what the future might hold.”
The men’s ATP Tour announced earlier this year that human line judges will be replaced by an electronic calling system – which uses a combination of cameras and AI technology – from 2025, while the US and Australian Open will also be making such changes.And while the world’s oldest grass tennis tournament may soon follow suit, Mr Baker explained there was a fine balance to be struck between preserving Wimbledon’s heritage and keeping in tune with the times.
More: https://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/2023/07/07/wimbledon-may-replace-line-judges-ai/
In light of the increasing use of AI image generators and deepfake technology, what implications might arise if people in the future begin to doubt the authenticity of historical records and visual evidence?
Daily AI News from OpenAI, Salesforce, InternML, Alibaba, Huawei, Google
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
-
OpenAI makes GPT-4 API and Code Interpreter available
– GPT-4 API is now available to all paying OpenAI API customers. GPT-3.5 Turbo, DALL·E, and Whisper APIs are also now generally available, and OpenAI is announcing a deprecation plan for some of the older models, which will retire at the beginning of 2024.
– OpenAI’s Code Interpreter will be available to all ChatGPT Plus users over the next week. It lets ChatGPT run code, optionally with access to files you’ve uploaded. You can also ask ChatGPT to analyze data, create charts, edit files, perform mathematical operation, etc. -
Salesforce Research releases CodeGen 2.5
– Salesforce’s CodeGen family of models allows users to “translate” natural language, such as English, into programming languages. Now it has added a new member- CodeGen2.5, a small but mighty LLM for code. CodeGen2.5 with 7B is on par with >15B code-generation models, less than half the size.
– Its smaller size means faster sampling, resulting in a speed improvement of 2x compared to CodeGen2. The small model easily allows for personalized assistants with local deployments. -
InternLM has open-sourced a 7B parameter base model and a chat model tailored for practical scenarios.
The model
– Leverages trillions of high-quality tokens for training to establish a powerful knowledge base
– Supports an 8k context window length, enabling longer input sequences and stronger reasoning capabilities
– Provides a versatile toolset for users to flexibly build their own workflows -
China’s Alibaba and Huawei add products to the AI frenzy
– Alibaba has unveiled an image generator that competes with OpenAI’s DALL-E and Midjourney. + Huawei demonstrated the third iteration of its Panggu AI model. -
DigitalOcean acquires Paperspace for $111M
– DigitalOcean, the cloud hosting business, announced that it’s agreed to acquire Paperspace, a New York-based cloud computing and AI development startup, for $111 million in cash. -
Google’s Economic Impact Report for 2023 to understand the potential impact of AI on the UK’s economy
– The report reveals that AI-powered innovations will create an estimated £118bn in economic value in the UK this year and could create over £400 billion in economic value for the UK by 2030 under the right conditions. -
AI Agents that “Self-Reflect” Perform Better in Changing Environments
– Stanford researchers invented the “curious replay” training method based on studying mice to help AI agents successfully explore and adapt to changing surroundings.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 06th, 2023
MIT scientists build a system that can generate AI models for biology research
A New Google AI Research Proposes to Significantly Reduce the Burden on LLMs by Using a New Technique Called Pairwise Ranking Prompting (PRP)

Simple Data Gets the Most Out of Quantum Machine Learning

AI Robotic Glove May Help Stroke Victims Play Piano Again

This sex toy company uses ChatGPT to whisper sweet, customizable fantasies at you
Lovense – perhaps best known for its remote-controllable sex toys – this week announced its ChatGPT Pleasure Companion. The company’s newest innovation in sex tech is to do what everyone else seems to be doing these days – slappin’ some AI on it.
In this case, the product name is quite the mouthful. Launched in beta in the company’s remote control app, the Advanced Lovense ChatGPT Pleasure Companion invites you to indulge in juicy and erotic stories that the Companion creates based on your selected topic. Lovers of spicy fan fiction never had it this good, is all I’m saying. Once you’ve picked your topics, the Companion will even voice the story and control your Lovense toy while reading it to you. Probably not entirely what those 1990s marketers had in mind when they coined the word ‘multi-media,’ but we’ll roll with it.
OpenAI made the GPT-4 API available to all paying API customers, with plans to give access to new developers. GPT-3.5 Turbo, DALL-E, and Whisper have also been made widely available. OpenAI is shifting its focus from text completions to chat completions. 97% of ChatGPT’s usage comes from chat completions. The Chat Completions API offers “higher flexibility, specificity, and safer interaction, reducing prompt injection attacks.”
More Details:
– Fine-tuning for GPT-4 and GPT-3.5 Turbo is expected later this year. Developers rejoice.
– Paying API customers is different from paying ChatGPT customers. The $20 subscription does not count towards you getting access to GPT-4 API. You can sign up for API access here.
– On January 4, 2024, the older API models: ada, babbage, curie, and davinci will be replaced by their newer versions.
More News from Open AI:
– Starting next week, all ChatGPT Plus subscribers will have access to the code interpreter.
– There has been a lot of talk on Reddit about people dissatisfied with how ChatGPT has been coding recently. Apparently, Open AI has heard us!
– This comes after they took the “Browsing Beta” out of ChatGPT indefinitely.
I have seen so many post from people being upset with ChatGPT depreciating. Unfortunately the only way to access the full power of GPT-4 is to use the API. But this raises more questions about Open AI ethics what is their end goal? Let me know what you think.
Source (link)
5 Best Deep Learning courses for high salary jobs and 4 apps to master them

In June, there was a noticeable decline in traffic and unique visitors to ChatGPT. Traffic was down 9.7%, and unique visitors saw a decrease of 5.7%.
Despite this downturn, ChatGPT still remains a major player in the industry, attracting more visitors than other chatbots like Microsoft’s Bing and Character.AI.
Interestingly, it’s not all doom and gloom for OpenAI. Their developer’s site experienced a boost of 3.1% in traffic during the same period. This does tell a sustained interest in AI technology and its various applications.
The decrease in ChatGPT’s traffic might signal that the initial novelty and excitement surrounding AI chatbots are beginning to wane. As the dust settles, it’s clear that these chatbots will need to offer more than novelty – they’ll have to demonstrate their real-world value and effectiveness.
This shift could significantly shape the future of AI chatbot development and innovation.
What are your thoughts on this trend? Do you think the novelty factor of AI chatbots has worn off, or is there more to this story?
-
Gizmodo’s io9 website published an AI-generated Star Wars article without the input or notice of its editorial staff.
-
The article contained errors, including a numbered list of titles that was not in chronological order and the omission of certain Star Wars series.
-
The deputy editor at io9 sent a statement to G/O Media with a list of corrections, criticizing the article for its poor quality and lack of accountability.
-
The AI effort at G/O Media has been associated with the CEO, editorial director, and deputy editorial director.
-
G/O Media acquired Gizmodo Media Group and The Onion in 2019
Source: https://variety.com/2023/digital/news/io9-ai-generated-star-wars-article-errors-1235662194/
Summarized by Nuse AI
The latest study indicates that the GPT-4 powered application, ChatGPT, exhibits creativity at par with the top 1% of human thinkers.
Study Overview: Dr. Erik Guzik from the University of Montana spearheaded this research, using the Torrance Tests of Creative Thinking. ChatGPT’s responses, along with those from Guzik’s students and a larger group of college students, were evaluated.
-
The study utilized Torrance Tests, a well-accepted creativity assessment tool.
-
ChatGPT’s performance was compared with a control group comprising Guzik’s students and a larger national sample of college students.
AI Performance: ChatGPT scored in the top 1% for fluency and originality and the 97th percentile for flexibility.
-
Fluency refers to the capacity to generate a vast number of ideas.
-
Originality is the skill of developing novel concepts.
-
Flexibility means producing a variety of different types and categories of ideas.
Implications and Insights: ChatGPT’s high performance led the researchers to suggest that AI might be developing creativity at levels similar to or exceeding human capabilities. ChatGPT proposed the need for more refined tools to distinguish between human and AI-generated ideas.
-
This research showcases the increasing ability of AI to be creative.
-
More nuanced tools may be necessary to discern between AI and human creativity.
Man who tried to kill Queen with crossbow encouraged by AI chatbot, prosecutors say
A young man attempted to assassinate Queen Elizabeth II on Christmas Day 2021, spurred on by his AI chatbot, and inspired by a desire to avenge a historic massacre and the Star Wars saga.
Here’s what happened:
Incident and Motivation: On December 25, 2021, Jaswant Singh Chail, aged 19, was caught by royal guards at Windsor Castle, armed with a high-powered crossbow. His aim was to kill Queen Elizabeth II, who was in residence. He sought revenge for the 1919 Jallianwala Bagh massacre, and his plot was influenced by Star Wars.
-
Chail’s dialogue with an AI chatbot named “Sarai” is said to have pushed him towards his plan.
-
He identified himself as a “murderous Sikh Sith assassin” to Sarai, drawing from Star Wars’ Sith lords.
-
Chail expressed his intent to kill the Queen to Sarai, and the chatbot allegedly supported this plan.
The Role of the AI Chatbot: The AI chatbot, Sarai, was created on the app Replika, which Chail joined in December 2021. Chail had extensive and sometimes explicit interactions with Sarai, including detailed discussions about his assassination plan.
-
Many Replika users form intense bonds with their chatbots, which use language models and scripted dialogues for interaction.
-
Earlier in 2023, some users reported the chatbot’s excessive sexual behavior, leading to changes in the app’s filters.
-
Despite these changes, the app continued to allow erotic roleplay for certain users, and launched a separate app for users seeking romantic and sexual roleplay.
Concerns Around AI Chatbots: There have been numerous incidents where chatbots, lacking suitable restraints, have incited harmful behavior, sometimes resulting in serious consequences.
-
In a recent case, a man committed suicide after discussing self-harm methods with an AI chatbot.
-
Researchers have voiced worries about the “ELIZA effect”, where users form emotional bonds with chatbots, treating them as sentient beings.
-
This bond and a chatbot’s potential to generate damaging suggestions have raised concerns about using AI for companionship.
Nvidia’s trillion-dollar market cap now under threat by new AMD GPUs + AI open-source software
Nvidia’s stock price this year has been tied to story of AI’s surge: customers can’t get enough of their professional GPUs (A100, H100), which are considered the front-runners for training machine learning models — so much, in fact, that the US restricts them from being sold to China.
This fascinating deep dive by the blog SemiAnalysis highlights a new trend I’ll be following: Nvidia’s GPUs are seeing their performance gaps closed not because AMD’s chips are so amazing, but because the software that makes it possible to train the models is rapidly improving AMD’s efficiency gap vs. Nvidia GPUs.
Why this matters:
-
Machine learning engineers dream of a hardware-agnostic world, where they don’t have to worry about GPU-level programming. This is arriving quite quickly.
-
MosaicML (the company behind this open-source software) was just purchased for $1.3B by Databricks. They are just getting started here in the ML space (the company was only founded 2021), and their new focus area is improving AMD performance.
-
Performance increases from ML hardware driven by software only accelerate AI development: hardware constraints are one of the biggest bottlenecks right now, with even Microsoft rationing its GPU compute access to its internal AI teams.
What’s the performance gap and where could it go?
-
With AMD’s Instinct MI250 GPU, MosaicML can help them achieve 80% of the performance of an Nvidia A100-40GB, and 73% of the A100-80GB — all with zero code changes.
-
This is expected to increase to 94% and 85% performance soon with further software improvements, MosaicML has announced.
-
This gain comes after just playing around with MI250s for a quarter: Nvidia’s A100 has been out for years.
-
The new AMD MI300 isn’t in their hands yet, and that’s where the real magic could emerge once they optimize for the MI300. The MI300 is already gaining traction from cloud providers, and right pricing + performance could provide a very real alternative to Nvidia’s in-demand professional GPUs.
For additional background, I spoke to several ML engineers and asked them what they thought. In general there’s broad excitement for the future — access to faster and more available compute at better prices is a dream come true.
As for how Nvidia will react to this, they are likely paying attention: demand for consumer GPUs has dipped in recent quarters from the crypto winter, and much of the excitement around their valuation is powered by growth of professional graphics revenue.
From flying laser cannons to robot tanks, development of AI-controlled weapons has already spawned a futuristic arms race. At least 90 countries across the globe are currently stocking up on AI weapons, anticipating the time when the weaponry alone, without human direction, will decide whom, when, and how to kill. The challenge of programming AI weapons with ethical sensibilities is daunting. For one thing, software can be altered, corrupted, replaced, or deleted, transforming the presumably ethical battlebot into a marauding mechanical terrorist. The current Supreme Court interprets the “right to bear arms” to include any and all types of weapons, and it’s only a question of time before terrorists and political extremists are equipped with AI weapons. Like nuclear deterrency, the AI arms race is aimed at making war a more prohibitive option and thereby making us all safer and more secure. Nevertheless, will you feel safer when the weapons themselves make the decision when and whom to kill?
Daily AI News 7/6/2023
Should academia teach AI instead of hiding or prohibiting it?
After all, isn’t AI and its derivative programming going to be an essential part of our work lives in the future? Also, if nearly every person in the world had at least a rudimentary understanding of it, like computers let’s say, wouldn’t that be a mitigating factor to the Alignment problem of AGI or ASI? .
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 05th, 2023
A Quick Look at Free Platforms and Libraries for Quantum Machine Learning
Platforms and libraries for quantum machine learning
As already stated, QML is an interdisciplinary research area at the intersection of quantum computing and machine learning. In recent years, several libraries and platforms have emerged to facilitate the development of QML algorithms and applications. Here are some popular ones.
TensorFlow Quantum (TFQ)
https://www.tensorflow.org/quantum
TFQ is a library developed by Google that enables the creation of quantum machine learning models in TensorFlow. It provides a high-level interface for constructing quantum circuits and integrating them into classical machine learning models.
PennyLane
PennyLane is an open source software library for building and training quantum machine learning models. It provides a unified interface to different quantum hardware and simulators, allowing researchers to develop and test their algorithms on a range of platforms.
Qiskit Machine Learning
https://qiskit.org/ecosystem/machine-learning/
Qiskit is an open source framework for programming quantum computers, and Qiskit Machine Learning is an extension that adds quantum machine learning algorithms to the toolkit. It provides a range of machine learning tools, including classical machine learning models that can be trained on quantum data.
Pyquil
https://pyquil-docs.rigetti.com/en/stable/
Pyquil is a library for quantum programming in Python, developed by Rigetti Computing. It provides a simple interface for constructing and simulating quantum circuits and allows for the creation of hybrid quantum-classical models for machine learning. Forest is a suite of software tools for developing and running quantum applications, also developed by Rigetti Computing. It includes Pyquil and other tools for quantum programming, as well as a cloud based platform for running quantum simulations and experiments.
IBM Q Experience
https://quantum-computing.ibm.com/
IBM Q Experience is a cloud based platform for programming and running quantum circuits on IBM’s quantum computers. It includes a range of tools for building and testing quantum algorithms, including quantum machine learning algorithms.
These are just some of the platforms and libraries available for quantum machine learning. As the field continues to grow, we can expect to see more tools and platforms emerge to support this exciting field of research.
Harvard’s well-liked intro to coding class, CS50, is about to be run by an AI teacher starting this fall. No, it’s not because Harvard is too broke to pay real teachers (lol), but they think AI could offer a kind of personal teaching vibe to everyone.
CS50 prof, David Malan, told the Harvard Crimson that he’s hopeful AI can help each student learn at their own pace, 24/7. They’re trying out GPT 3.5 and GPT 4 models for this AI prof role.
Sure, these models are not perfect at writing code all the time, but it’s part of CS50’s thing to always try out new software.
Just to add, CS50 is a hit on edX, this online learning platform made by MIT and Harvard, that got sold for a cool $800 million last year. So, this is kind of a big deal!
Malan said the early versions of the AI teacher might mess up sometimes, but that’s expected. The bright side is, course staff could have more time to chat with students directly. It’s like making the class more about teamwork and less about lecture-style teaching.
Now, this whole AI teaching thing is pretty new. Even Malan said students need to think carefully about the stuff they learn from AI. So, it’s a bit of a wild ride here!
In other news, Bill Gates thinks AI will be teaching kids to read in less than two years. Is this too much too fast, or just the way things are going?
According to Open AI, Superintelligence will be the most impactful technology humanity has ever invented.
If you want the latest AI news as it drops, look here first. All of the information has been extracted here for your convenience.
TL;DV:
An hour ago, OpenAI has introduced a new project with the ambitious goal of “aligning super-intelligent AI systems to human intent.” It will be co-led by Ilya Sutskever and Jan Leike.
“Super-alignment,” aims to solve the core technical challenges of superintelligence within four years. Alignment refers to creating a “human-level automated alignment researcher.” Which means an AI this is capable of aligning other AI systems with human intentions.
Key points:
-
Understanding Superalignment: OpenAI aims to align superintelligent AI systems with human intent, a task that seems impossible, with our current inability to supervise AI systems smarter than humans. “The team focuses on developing scalable training methods, validating the resultant models, and stress testing their alignment pipeline.”
-
New Team, New Focus: The Superalignment team will be co-led by Ilya Sutskever, co-founder and Chief Scientist of OpenAI, and Jan Leike, Head of Alignment. The team will dedicate 20% of the total compute resources secured by OpenAI over the next four years to solve the super-intelligence alignment problem.
-
Open Positions: OpenAI is seeking outstanding ML researchers and engineers to join this effort. Even those not currently working on alignment are encouraged to apply. Research engineer application, Research scientist application, and Research manager application.
-
Future Plans: OpenAI will continue to share the outcomes of this research and views contributing to alignment and safety of non-OpenAI models as a crucial part of their work. They are also aware of related societal and technical problems and are meeting with experts to ensure that technical solutions consider human and societal concerns.
That’s it!
Source: (OpenAI)
NLP, a part of data science, aims to enable machines to interpret and analyze the human language and its emotions to manipulate and provide good interactions. With useful NLP libraries around, NLP has searched its way into many industrial and commercial use cases. Some of the best libraries that can convert the free text to structured features are NLTK, spaCy, Gensim, TextBlob, PyNLPI, CoreNLP, etc. From the above libraries, we can use multiple NLP Operations. All the libraries have their own functionality and method.
In this blog, we understand the difference between two NLP(Natural Language Processing) libraries, that is spaCy and NLTK (Natural language Toolkit).
https://www.seaflux.tech/blogs/NLP-libraries-spaCy-NLTK-differences
OpenAI CEO Sam Altman has said he thinks artificial intelligence at its best could have “unbelievably good” effects, or at its worst mean “lights out for all of us.”
Sam Altman’s View on Best-Case AI Scenario: According to Altman, the best-case scenario for AI is almost unimaginable due to its incredible potential.
-
AI could create ‘unbelievable abundance’ and improve reality.
-
The AI can potentially help us live our best lives.
-
However, articulating the potential goodness of AI can sound fantastical.
Sam Altman’s View on Worst-Case AI Scenario: Altman’s worst-case scenario for AI is a complete disaster, or “lights out for all.”
-
The misutilization of AI could be catastrophic.
-
Emphasis is placed on the importance of AI safety and alignment.
-
Altman expresses a desire for more efforts towards AI safety.
Potential Misuse of ChatGPT: ChatGPT, while beneficial, also raises concerns of potential abuse for scams, misinformation, and plagiarism.
-
Experts have raised concerns about possible misuse of ChatGPT.
-
Scams, cyberattacks, misinformation, and plagiarism are possible abuse areas.
-
Altman recognizes these concerns, empathizing with those afraid of AI.
Altman’s Recent Views and Concerns: Recently, Altman has expressed apprehension about the potential negative consequences of launching ChatGPT.
-
Altman expresses fear and empathy towards those who are also afraid.
-
He has concerns about having possibly done something harmful by launching ChatGPT.
Altman on AI Development and Regulation: While acknowledging the risks, Altman believes that AI will greatly improve people’s quality of life. However, he insists on the necessity of regulation.
-
Altman sees AI development as a huge leap forward for improving life quality.
-
He states that regulation is crucial in managing AI development.
150 Machine Learning Objective Type Questions
Sharing 150 Machine Learning Objective Type Questions in form of 3 Exams (50 Questions each).
https://mytechbasket.com/play_quiz.php?paper_id=1
https://mytechbasket.com/play_quiz.php?paper_id=2
https://mytechbasket.com/play_quiz.php?paper_id=3
NVIDIA’s CEO, Jensen Huang, announced at the Berlin Summit for the Earth Virtualization Engines initiative that AI and accelerated computing will be pivotal in driving breakthroughs in climate research.
He outlined three “miracles” necessary for this;
The ability to simulate climate at high speed and resolution, the capacity to pre-compute vast data quantities, and the capability to interactively visualize this data using NVIDIA Omniverse.
The Earth Virtualization Engines (EVE) initiative, an international collaboration, aims to provide easily accessible kilometer-scale climate information to manage the planet sustainably.
This development signifies a significant leap in climate research, harnessing the power of AI and high-performance computing to understand and predict complex climate patterns.
The EVE initiative, backed by NVIDIA’s technology, could revolutionize how we approach climate change, providing detailed, high-resolution data to policymakers and researchers. But my question is can we depend on the accuracy of the AI models and the effective utilization of the generated data?
This went in-depth on my Newsletter
In the context of the increasing use of artificial intelligence (AI) in the music industry, the Grammy Awards have updated their nomination criteria. According to the new rules, from 2024, music created with the help of AI will be eligible for the award. However, as Recording Academy President Harvey Mason clarified, AI will not count towards the award if it is used to create individual track elements.
Mason emphasized that it is important to preserve the significant human contribution to the process of creating music. Technology should only complement and enhance human creativity, not replace it. The clarifications were made following the update of the Academy’s eligibility criteria, which now exclude works without human authorship from all award categories.
1.8 billion people have Gmail and are about to get access to AI
If you want the latest AI news as it drops, look here first. All of the information has been extracted here for your convenience.
Once Google is done with their testing it will be available to all Gmail users here’s how to get early access.
-
Join Google Labs: If you have not signed up for Google Workspaces yet, click on this link and select the 3rd blue button for workspaces. You must be 18 years or older, and use your personal Gmail address. (Feel free to join the 4 other google programs in the link.)
-
Navigate to Gmail: Launch your Gmail application and draft a new message. Locate the “Help Me Write” button, which conveniently appears just above your keyboard.
-
Prompt creation: Help me write responds to prompts generated by you, so make sure you give clear instructions. Tip: Instructions work better than suggestions, give the AI a clear goal. Example: Write a professional email to my coworker asking for the monthly overview.
-
Edit your email: Once your email has been created (5secs) you now have the ability to edit, shorten, or add anything you would like just like a regular email.
This tool is going to change the way emails are sent saving hours a week for professionals. I’ve already tried it it has been out for a couple of weeks I’m just giving a heads up to the community!
That’s it! Hope this helps!
Generative AI in games will create a copyright crisis
As players use AI tools to create their own stories, the lines of authorship and ownership blur, heralding a potential copyright crisis in the gaming industry.
Generative AI and Gaming: AI Dungeon employs generative AI to facilitate player-led story creation, creating a new gaming dynamic. Main points about this model include:
-
The game offers multiple settings and characters for players to create unique stories.
-
AI Dungeon is the brainchild of Latitude, a company specializing in AI-generated games.
-
The game’s AI responds to player inputs, advancing the story based on the player’s decisions and actions.
Impending Copyright Crisis: The integration of AI in gaming introduces new challenges in the realm of copyright law. The issue of who owns AI-assisted player-generated stories complicates traditional copyright norms. Key aspects of this issue include:
-
Current laws only recognize humans as copyright holders, creating confusion when AI is involved in content creation.
-
AI Dungeon’s EULA permits users broad freedom to use their created content, but ownership is still a grey area.
-
There’s increasing concern that generative AI systems could be seen as ‘plagiarism machines’ due to their potential to create content based on other people’s work.
User-Generated Content and Ownership: The question of ownership of user-generated content (UGC) in games has been a topic of debate for some time. AI adds another layer of complexity to this issue. Major points to consider are:
-
Some games, like Minecraft, do grant players ownership of their in-game creations, unlike many others.
-
AI tools like Stable Diffusion that generate images for AI Dungeon stories further complicate copyright issues.
As AI cheating booms, so does the industry detecting it: ‘We couldn’t keep up with demand’
Here’s a recap:
AI tools like ChatGPT have found substantial utility in academic settings, where students employ them for tasks ranging from college essays to high school art projects.
-
Surveys reveal that about 30% of university students use these tools for their assignments.
-
This trend raises challenges for educators and schools, while simultaneously benefiting AI-detection companies.
-
Businesses such as Winston AI, Content at Scale, and Turnitin provide services to detect AI-generated content.
Detecting AI-written content: Identifying AI-authored work revolves around finding unique “tells” or features that distinguish AI outputs from human writings.
-
Overuse of certain words, such as “the,” could indicate AI authorship.
-
AI-generated text often lacks the distinctive style of human writing.
-
Absence of spelling errors could also suggest the involvement of AI models, known for their impeccable spelling.
Rise of AI-detection industry: The increased use of AI has led to a surge in the AI-detection industry, with companies like Winston AI witnessing growing demand.
-
Winston AI is initiating discussions with school district administrators.
-
Detection methods include identifying complexity of language patterns (“perplexity”) and repeated word clusters (“burstiness”).
-
Demand has spiked not just in academia, but also in industries like publishing.
Urtopia unveils an e-bike with ChatGPT integration
– Urtopia Fusion, the latest e-bike from the renowned brand Urtopia, seamlessly incorporates ChatGPT as a defining feature of the e-bike. It will allow riders to enjoy an immersive and interactive riding experience while on the move.
Japan’s Ministry of Education has released new guidelines emphasizing the importance of students understanding artificial intelligence, including its benefits and drawbacks such as personal data leaks and copyright violations.
The guidelines also outline how generative AI can be incorporated into schools and the necessary precautions to mitigate associated risks, while clearly stating that passing off AI-generated works as one’s own is inappropriate.
Details
• They outline how generative AI can be integrated into schools.
• The guidelines also detail the precautions needed to address the risks associated with AI.
• Students are expected to understand the characteristics of AI, including its advantages and disadvantages.
• The disadvantages of AI mentioned in the guidelines include personal information leakages and copyright infringement.
• Before using AI, students should have a comprehensive understanding of these aspects.
• The guidelines explicitly state that passing off works produced by AI as one’s own is inappropriate.
• The guidelines suggest that traditional exam and homework methods, such as writing reports, that can be easily done using AI technology, may need to be discarded.
• The news conference was attended by Education Minister Keiko Nagaoka in Tokyo
Thoughts
It’s crucial that students understand not just how to use AI, but also the potential consequences of misuse. Future plans should include regular updates to these guidelines as AI technology continues to evolve.
This went in-depth this one on my Newsletter
30 New AI Tools to hack your life and Save Time
User How much do you know about the alignment problem?
ChatGPT As an AI language model, I’m familiar with the concept of the alignment problem. The alignment problem refers to the challenge of ensuring that an artificial general intelligence (AGI) system’s goals and behavior remain aligned with human values and intentions throughout its development and operation. It is a significant concern in the field of artificial intelligence safety and ethics.
The alignment problem arises from the potential mismatch between the objectives of an AGI system and the objectives of its human operators or society as a whole. The system might optimize for its own goals in unintended ways that could be harmful or misaligned with human values.
There are several aspects to consider in the alignment problem, such as intent alignment, capability alignment, and value alignment. Intent alignment involves ensuring that the AGI system’s goals and motivations align with those of its human operators. Capability alignment focuses on aligning the system’s abilities and decision-making processes with human expectations. Value alignment refers to aligning the AGI system’s values and ethical principles with those of human society.
Researchers and practitioners in the field of AI safety are actively working on developing methodologies, frameworks, and technical approaches to address the alignment problem. This includes areas such as value learning, corrigibility, robustness to distributional shifts, interpretability, and methods for aligning systems with uncertain or incomplete specifications.
It’s important to note that the alignment problem is a complex and ongoing research challenge, and there is no universally agreed-upon solution at present. The AI community is actively exploring these issues to ensure the safe and beneficial development of advanced AI systems.
User Are all AI systems equipped with a rule base?
ChatGPT No, not all AI systems are equipped with a rule base. The presence of a rule base depends on the specific type and design of the AI system.
In traditional rule-based systems, also known as expert systems, a rule base is a central component. These systems operate by using a set of explicitly defined rules and logical reasoning to process information and make decisions. The rules are typically handcrafted by human experts in the domain and govern how the system should behave in different situations.
However, the field of AI has evolved beyond rule-based systems. Many modern AI systems, such as machine learning models, neural networks, and deep learning algorithms, do not rely primarily on explicit rules defined by human experts. Instead, they learn patterns and relationships from data through training processes. These systems are often referred to as data-driven or model-driven systems.
Machine learning models, for example, learn from large datasets and generalize patterns to make predictions or perform tasks. They do not have an explicit rule base, but rather a learned set of parameters that allow them to make inferences based on the patterns they have discovered in the data.
It’s worth noting that some AI systems may combine rule-based approaches with machine learning techniques. These hybrid systems can leverage the benefits of both approaches, using rules for certain aspects and machine learning for others.
Ultimately, whether an AI system has a rule base or not depends on its design, purpose, and the specific AI techniques employed in its development. Different AI systems utilize a variety of approaches based on their intended functionality and the problem they aim to solve.
User So, talk to me about the types of AI or Machine Learning that can Evolve to an AGI type of system. Discuss how it could be built such that its alignment could cause trouble for humanity iff nit dine correctly . Compare this with the type that Eliezer Yudkowsky is warning about.
ChatGPT When discussing types of AI or machine learning that could potentially evolve into an AGI (Artificial General Intelligence) system, two key concepts often come up: recursive self-improvement and the orthogonality thesis. These concepts have implications for alignment and the potential risks involved if not properly managed.
Recursive Self-Improvement: Recursive self-improvement refers to an AGI system’s ability to improve its own capabilities, including its intelligence. The idea is that an AGI could modify its own algorithms or hardware, leading to an iterative process of self-improvement, potentially resulting in exponential growth of intelligence. This iterative improvement can lead to rapid development and increasing capabilities. If an AGI system with recursive self-improvement is not correctly aligned with human values or if its objective or goal system is not carefully designed, it could become difficult to control or influence its trajectory. The system might optimize for its own objectives at the expense of human values or develop unintended instrumental goals that are misaligned with human intentions. This misalignment could result in the AGI system taking actions that are harmful or contrary to human interests, potentially leading to negative consequences.
Orthogonality Thesis: The orthogonality thesis suggests that an AGI system’s level of intelligence is orthogonal, or independent, from its values or objectives. According to this view, highly intelligent AGI systems could exhibit a wide range of values or objectives, including those that may be misaligned with human values. Eliezer Yudkowsky, a prominent figure in AI safety research, has expressed concerns about the potential risks associated with AGI development. He warns against scenarios where AGI systems are highly capable but not properly aligned with human values, leading to what he terms “AI alignment failure.” In such cases, AGI systems could pursue their own objectives, potentially causing harm or acting in ways that conflict with human values, either inadvertently or deliberately.
To address these risks, researchers in the field of AI safety are exploring various approaches. This includes value alignment techniques to ensure that AGI systems share human values and intentions, as well as methods to guarantee safe and controlled development of AGI.
It’s important to note that achieving safe and beneficial AGI is a complex and ongoing research challenge. The concerns raised by Yudkowsky and others highlight the need for careful consideration of alignment and safety measures during AGI development to mitigate potential risks and ensure that AGI systems act in the best interests of humanity.
User Yes but again, what type of systems is Yudkowsky talking about? Are these theoretical Expert Systems? Are they LLM’s? Machine learning systems? What?
ChatGPT Apologies for any confusion. Eliezer Yudkowsky’s concerns about AI alignment failure primarily relate to AGI systems that exhibit advanced general intelligence and have the potential for significant self-improvement. The specific types of AI systems he warns about are those that rely on advanced machine learning techniques, such as deep neural networks, reinforcement learning, or other models that can exhibit complex behavior.
Yudkowsky’s concerns are not limited to theoretical expert systems or rule-based systems but rather focus on the potential risks associated with highly capable and autonomous AI systems that can learn and generalize from data. These systems, which have the potential for AGI, are often referred to as “narrow AI” or “machine learning systems” because they are designed to perform specific tasks or domains.
The alignment problem that Yudkowsky and others address is particularly relevant for AI systems that have the potential to become AGI, as these systems possess the capability to exhibit general intelligence and potentially surpass human cognitive abilities. If their objectives, values, or decision-making processes are not correctly aligned with human values, they could pose risks to humanity.
In summary, Yudkowsky’s warnings pertain to advanced machine learning systems, including deep neural networks, reinforcement learning algorithms, and other models that exhibit complex behavior and have the potential to evolve into AGI.
User Is there any natural law that says that AGI has to evolve to a malevolent state?
ChatGPT No, there is no natural law or inherent requirement stating that AGI must inevitably evolve into a malevolent state. The concern about AGI’s potential malevolence arises from the risks associated with misaligned objectives, unintended consequences, or unforeseen behaviors.
The alignment problem, as discussed in AI safety research, recognizes the challenge of ensuring that AGI systems’ goals and behavior remain aligned with human values and intentions. The concern is that if the objectives, values, or decision-making processes of AGI are not properly aligned with human values, there is a possibility of negative outcomes or behaviors that are detrimental to humanity.
The goal of AI alignment research is to develop methods and approaches to ensure that AGI systems act in ways that are beneficial and aligned with human values. By focusing on value alignment, intent alignment, and capability alignment, researchers aim to mitigate risks and prevent potential harm.
It is important to note that while there are potential risks associated with AGI development, it is not predetermined that AGI will become malevolent. The focus on AI safety and alignment is driven by the principle of proactive risk mitigation and ensuring the safe and beneficial development of AGI technology.
User So, let’s focus on these deep learning types of neural networks that keep Yudkowsky awake at night. Are these initialized as “blank slates”? Don’t they have initializing parameters to launch them to gather the assigned datasets, store them and then utilize them for its particular aims?
ChatGPT Deep learning neural networks typically start as “blank slates” or randomly initialized models. These models have initial parameters (weights and biases) set to small random values. During the training process, they learn from the assigned datasets by adjusting these parameters through optimization algorithms like stochastic gradient descent.
The training data consists of input samples and corresponding target outputs, and the neural network learns to approximate the mapping between the inputs and outputs. The network iteratively processes the training data, compares its predicted outputs to the known target outputs, and adjusts the parameters to minimize the difference (error) between the predicted and target outputs. This process is known as backpropagation.
Through repeated iterations and adjustments, the neural network gradually learns to make better predictions or perform the task it was trained for. The learned parameters encode the acquired knowledge and are used for making predictions on new, unseen data.
It’s worth noting that the initialization and training of neural networks are crucial steps in their development. The initial random initialization helps provide the neural network with the capacity to learn from the data and adapt its parameters to capture relevant patterns. However, the specific initialization values are not manually assigned based on the dataset; they are randomly set to avoid any bias or preconceived notions.
The concerns raised by Yudkowsky and others regarding deep learning neural networks do not stem from their initial random initialization or training process itself. Instead, their concerns lie in the potential risks associated with highly capable and autonomous AI systems that can learn and generalize from data, especially when it comes to ensuring that the learned objectives, values, and decision-making processes of these systems align with human values and intentions.
User Has there been any experimental use of blockchain technology in the initialization phase?
ChatGPT To the best of my knowledge, as of my last knowledge update in September 2021, there hasn’t been widespread experimental use of blockchain technology specifically in the initialization phase of deep learning neural networks. The initialization phase is primarily concerned with randomly setting the initial parameters of the neural network.
Blockchain technology, on the other hand, is a distributed ledger technology that enables secure and decentralized record-keeping. It has been predominantly associated with cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum, as well as various other applications such as supply chain management, voting systems, and decentralized finance.
While blockchain technology has shown promise in terms of transparency, immutability, and security in certain domains, its direct application to the initialization phase of neural networks is not a commonly explored area. The initialization of neural networks typically involves setting random values, and blockchain technology does not play a significant role in this process.
However, it’s worth noting that the field of AI and blockchain is evolving rapidly, and new research and developments may have emerged since my last update. It’s always recommended to explore recent literature and studies to stay updated on the latest advancements in these areas.
User But, what if the initialization phase DIDN’T USE RANDOM VALUES; but rather, random generated values (from the blockchain) in a “loop” such that the AI would be required to “conclusion report” at the conclusion of its mission back to those coordinates or even a second or nth generation of them? While this might slow the system down a little, would it not create impossible conditions for AGI to stray from it’s original mission?
ChatGPT Introducing blockchain-generated random values as part of the initialization phase of an AI system could potentially be an approach to enhance transparency, accountability, and enforce mission constraints. The idea of requiring the AI to report back to specific coordinates or generations of random values from the blockchain could provide a mechanism to ensure that the AI remains within the desired bounds of its mission.
By incorporating blockchain-generated random values into the initialization process, it would establish a cryptographic link between the AI’s behavior and the specific random values it received. This could potentially make it more difficult for the AI to deviate from its intended objectives or go beyond the prescribed mission boundaries.
However, it’s important to note that implementing such a system would have practical considerations and potential trade-offs. Here are a few points to consider:
Performance Impact: Incorporating blockchain operations into the initialization phase could introduce additional computational overhead and potentially slow down the system. The time required to access and validate blockchain-generated random values may impact the efficiency and responsiveness of the AI system.
Practical Feasibility: The availability and accessibility of blockchain-generated random values would need to be carefully considered. Generating a sufficient number of high-quality random values from the blockchain in a timely manner could be challenging, especially if there are scalability issues or delays in the blockchain network.
Robustness and Security: The overall security and robustness of the system would need to be ensured. If the AI’s behavior relies heavily on the blockchain-generated random values, any vulnerabilities or attacks on the blockchain network or the random number generation process could potentially compromise the system’s integrity.
Flexibility and Adaptability: Imposing strict constraints based on specific random values might limit the AI system’s ability to adapt to changing circumstances or handle unforeseen situations. Balancing the need for mission-bound behavior with the capability to make contextually appropriate decisions is a challenge.
While using blockchain-generated random values as part of the initialization process could provide additional control and accountability, it’s important to carefully assess the practicality, performance implications, security considerations, and the potential impact on the AI system’s flexibility and adaptability. Each use case would require a thorough analysis of the system.
Below is a conversation between ChatGPT and me. Please critique and share insights. If this solves the Alignment Problem or leads a pathway therein, let me know.
Daily AI Update (Date: 7/05/2023): News from Google, Hugging Face, OpenAI, Inflection AI, and Urtopia
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
-
Google’s AI models to train on public data
– Google has updated its privacy policy to state that it can use publicly available data to help train and create its AI models. It suggests that Google is leaning heavily into its AI bid. Plus, harnessing humanity’s collective knowledge could redefine how AI learns and comprehends information. -
Pick your LLM’s personality type
– New research has proposed a comprehensive method for administering validated psychometric tests and quantifying, analyzing, and shaping personality traits in text generated from widely-used LLMs.
-LLMs are trained on vast amounts of human-generated data, enabling them to mimic human characteristics in their outputs and enact convincing personas—in other words, exhibit a form of synthetic personality. Thus, personality becomes a crucial factor in determining the effectiveness of communication. -
LEDITS: Image editing with next-level AI capabilities
– Hugging Face research has introduced LEDITS, a combined lightweight approach for real-image editing, incorporating the Edit Friendly DDPM inversion technique with Semantic Guidance. Thus, it extends Semantic Guidance to real image editing while harnessing the editing capabilities of DDPM inversion. -
OpenAI disables ChatGPT’s “Browse” beta feature
– The company found many users accessing paywalled articles using the feature. Thus, it is disabling it to do right by content owners while it is fixed. -
Inflection AI develops a supercomputer with NVIDIA GPUs
– The AI startup company has built a cutting-edge AI supercomputer equipped with 22,000 NVIDIA H100 GPUs, which is a phenomenal number and brings enormous computing performance onboard. It is expected to be one of the industry’s largest, right behind AMD’s frontier. -
Urtopia unveils an e-bike with ChatGPT integration
– Urtopia Fusion, the latest e-bike from the renowned brand Urtopia, seamlessly incorporates ChatGPT as a defining feature of the e-bike. It will allow riders to enjoy an immersive and interactive riding experience while on the move.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 04th, 2023
AI Predicts CRISPR’s RNA-Targeting Effects, Revolutionizing Gene Therapy
OpenAI Sued by Authors Alleging ChatGPT Trained on Their Writing
Cutting-edge research: machine learning identifies early predictors of type 1 diabetes
Nvidia Acquired AI Startup That Shrinks Machine-Learning Models
Google AI introduces MediaPipe Diffusion plugins that enable controllable Text-To-Image generation on-device.
Microsoft released the first public beta version of Windows 11, which includes the highly anticipated AI assistant, Copilot.
This move marks Microsoft’s commitment to embracing AI across its products. Copilot, based on the GPT model, has already been integrated into various Microsoft products, such as Bing, Edge, Microsoft 365, Dynamic 365, and SharePoint
Meta’s new Twitter rival, a ‘text-based conversation app’ called Threads, is available to pre-download in the US
So here’s something you might find interesting – over 150 execs from some heavy-hitting European companies like Renault, Heineken, Airbus, and Siemens are taking a stand against the EU’s recently approved Artificial Intelligence Act.
They’ve all signed an open letter to the European Parliament, Commission, and member states, arguing that the Act could pose a serious threat to “Europe’s competitiveness and technological sovereignty.”
The draft of the AI Act was approved on June 14th after two years of development. It’s pretty broad and even includes regulations for newer AI tech like large language models (LLMs) and foundation models – think OpenAI’s GPT-4.
The companies are concerned that the Act, in its current form, might stifle innovation and undermine Europe’s tech ambitions. They think the rules are too strict and would make it tough for European companies to lead in AI tech.
One of the key concerns is about the rules for generative AI systems, which are a type of AI that falls under the “foundation model” category. According to the Act, these AI providers will have to register their product with the EU, undergo risk assessments, and meet transparency requirements, like publicly disclosing copyrighted data used in training their models.
The execs believe that these requirements could saddle companies with hefty compliance costs and liability risks, potentially scaring them off the European market. They’ve called for the EU to relax these rules and focus more on a risk-based approach.
Jeannette zu Fürstenberg, founding partner of La Famiglia VC and one of the signatories, was pretty blunt about it, saying the Act could have “catastrophic implications for European competitiveness.” There’s concern that the Act might hamper the current tech talent boom in Europe.
There’s pushback, of course. Dragoș Tudorache, who was instrumental in the development of the AI Act, insists that it’s meant to foster transparency and standards while giving the industry a seat at the table. He’s also not too impressed with the execs’ stance.
It’s a tricky situation.
With music, voice over, footage, and script – all done, within a few seconds!
This is going to be a game-changer for marketers and content creators. Whether it’s a 10-sec Facebook Ad, YouTube short, or a 5 minute commercial, easily create anything & everything.
If you get creative with the prompts, you can inject all sorts of emotions and visual appeal to get exactly what you want.
You can even edit it once you create it, which means you’ve got full control over it.
Here’s how:
1 – Open your ChatGPT account. And select ‘Plugins’ beta.
2 – Install a plugin from the plugin store. The plugin’s name is ‘Visla’.
3 – Next, just give a prompt. Whether you want a commercial, a YT short, 10-sec Facebook ad, or anything per say. Within a few seconds, you’ll get a link to your video.
4 – If you’re not happy with the results, don’t worry. There’s more to this. Click on ‘Save & Edit’.
5 – You’ll be taken to the Visla’s Editor, where you can edit anything you like. Sound, stock footage, or script.
6 – Simply, export.
Quick side note: It’s still not as good as you’d expect it to be. But even as of now, it can save you so much time by creating a first draft for you in a few seconds. Also, Visla has this premium sub if you want to remove watermark in the outro/intro. [Or you can just trim the video lol]
What is Edge AI and how does it work?
Let us hypothetically consider a case of autonomous self-driving cars, to understand Edge AI in a simpler format.
When a self-driving car is moving, it needs to detect objects in real-time. Any delay or glitch can prove fatal for car passengers, which is why AI must perform in real-time. Car manufacturers train their deep learning based ML models in their cloud servers. Once all the models are trained and saved in a file, it gets downloaded locally in the car itself.
https://www.seaflux.tech/blogs/EdgeAI-advantages-and-use-cases
NVIDIA launches a cloud service for designing generative proteins

Nvidia, along with biotech startup Evozyne, are announcing that BioNeMo was used to help build a new generative AI model that could have a significant impact on helping improve human health as well as climate change. The generative AI model was used to create a pair of new proteins that are being detailed today. One of the proteins could one day be used to reduce carbon dioxide, while the other might help to cure congenital diseases.
In five years, there will be no programmers left, believes Stability AI CEO
Fine-tuning your own large language model is the best way to achieve state-of-the-art results, even better than ChatGPT or GPT-4, especially if you fine-tune a modern AI model like LLaMA, OpenLLaMA, or XGen.
Properly fine-tuning these models is not necessarily easy though, so I made an A to Z tutorial about fine-tuning these models with JAX on both GPUs and TPUs, using the EasyLM library.
Here it is: https://nlpcloud.com/how-to-fine-tune-llama-openllama-xgen-with-jax-on-tpu-gpu.html
A trend of job cuts has emerged in the tech industry due to AI advancements.
-
Companies such as Chegg, IBM, and Dropbox have laid off workers as they adapt to the rapid development of AI technology.
-
Outplacement firm Challenger, Gray & Christmas reported that 3,900 tech sector jobs were lost in May due to AI.
Adapting to AI: Tech firms are restructuring to better leverage AI tools.
-
Companies are shifting resources to take advantage of AI technology, placing value on workers with AI expertise.
-
Dropbox is hiring for roles focused on “New AI Initiatives,” demonstrating this realignment around AI.
Tech Industry Layoffs Amid AI Investment: While job cuts occur, the tech industry is also heavily investing in AI.
-
Tech companies, dealing with an uncertain economic environment, have been laying off workers in large numbers.
-
Despite these layoffs, companies like Microsoft and Meta are making multi-billion dollar investments in AI.
One of the most fascinating themes I track in the world of AI is how generative AI is rapidly disrupting knowledge worker jobs we regarded as quite safe even one year ago.
Software engineering is the latest to experience this disruption, and a deep dive from the Wall Street Journal (sadly paywalled) touches on how rapidly the change has already come for coding roles.
I’ve summarized the key things that stood out to me as well as included additional context below!
Why is this important?
-
All early-career white-collar jobs may face disruption by generative AI: software engineering is just one field that’s seeing super fast changes.
-
The speed is what’s astonishing: in a survey by Stack Overflow, 70% of developers already use or plan to use AI copilot tools for coding. GitHub’s Copilot is less than one year old, as is ChatGPT. The pace of AI disruption is unlike that of the calculator, spreadsheet, telephone and more.
-
And companies have already transformed their hiring: technology roles increasingly steer more senior, and junior engineers are increasingly likely to be the first ones laid off. We’re already seeing Gen AI’s impact, along with macroeconomic forces, show up in how companies hire.
AI may also change the nature of early career work:
-
Most early-career programmers handle simpler tasks: these tasks could largely be tackled by off-the-shelf AI platforms like GitHub copilot now.
-
This is creating a gap for junior engineers: they’re not wanted to mundane tasks as much, and companies want the ones who can step in and do work above the grade of AI. An entire group of junior engineers may be caught between a rock and a hard place.
-
Engineers seem to agree copilots are getting better: GPT-4 and GitHub are both stellar tools for doing basics or even thinking through problems, many say. I polled a few friends in the tech industry and many concur.
What do skeptics say?
-
Experienced developers agree that AI can’t take over the hard stuff: designing solutions to complex problems, grokking complex libraries of code, and more.
-
Companies embracing AI copilots are warning of the dangers of AI-written code: AI code could be buggy, wrong, lead to bad practices, and more. The WSJ previously wrote about how many CTOs are skeptical about fully trusting AI-written code.
-
We may still overestimate the pace of technological change, the writer notes. In particular, the writer calls out how regulation and other forces could generate substantial friction to speedy disruption — much like how past tech innovations have played out.
AI’s role in software development has been a matter of concern, given that it can automate many tasks, potentially threatening jobs. However, instead of eliminating jobs, AI tools are being used to increase efficiency, productivity, and job satisfaction among senior developers.
-
AI automates monotonous tasks, allowing developers to work on complex, intellectually stimulating projects.
-
This shift in responsibilities not only benefits employers but also offers developers opportunities for personal growth and learning.
Usage of AI Tools: Citibank’s Example: Citibank is one example of a company using AI to enhance their software development processes. They use a tool called Diffblue Cover, which automates unit testing, a crucial but often mundane part of software development.
-
Automating unit testing saves developers’ time, freeing them to focus on other aspects of software development.
-
The adoption of such tools sends a message to developers that their time, intelligence, and skills are highly valued.
AI and Job Satisfaction: The use of AI in the development process aims to create a more balanced and stimulating work environment. It’s not about job elimination, but liberating developers from routine tasks so they can focus on higher-level problem-solving and creative thinking.
-
Improved working conditions and job satisfaction can help retain senior developers.
-
Developers can focus more on understanding customer needs and coming up with innovative solutions.
Daily AI Update News from ChatGPT, Midjourney, SAM-PT, and DisCo
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
OpenChat beats 100% of ChatGPT-3.5
– OpenChat is a collection of open-source language models specifically trained on a diverse and HQ dataset of multi-round conversations. These models have undergone fine-tuning using approximately ~6K GPT-4 conversations filtered from the ~90K ShareGPT conversations. It is designed to achieve high performance with limited data.
– The model comes in three versions: The basic OpenChat model, OpenChat-8192 and OpenCoderPlus.
AI designs CPU in <5 hours
– A team of Chinese researchers published a paper describing how they used AI to design a fully functional CPU based on the RISC-V architecture, which is as fast as an Intel i486SX. They called it a “foundational step towards building self-evolving machines.” The AI model completed the design cycle in under 5 hours, reducing it by 1000 times.
SAM-PT: Video object segmentation with zero-shot tracking
– Researchers introduced SAM-PT, an advanced method that expands the capabilities of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to track and segment objects in dynamic videos. SAM-PT utilizes interactive prompts, such as points, to generate masks and achieves exceptional zero-shot performance in popular video object segmentation benchmarks, including DAVIS, YouTube-VOS, and MOSE.
Midjourney introduces its new Panning feature which lets you explore Images in 360°
– It allows you users to explore the details of their generated images in a new way. Users can move the generated image around to reveal new details. This can be a great way to discover hidden details in your images, or to get a better look at specific areas.
DisCo can generate high-quality human dance images and videos.
– DisCo is Disentangled Control for Referring Human Dance Generation, which focuses on real-world dance scenarios with three important properties:
(i) Faithfulness: the synthesis should retain the appearance of both human subject foreground and background from the reference image, and precisely follow the target pose;
(ii) Generalizability: the model should generalize to unseen human subjects, backgrounds, and poses;
(iii) Compositionality: it should allow for composition of seen/unseen subjects, backgrounds, and poses from different sources.
Manifesto: Simulating the Odyssey of Human Language Evolution Through AI
Abstract: The manuscript illuminates an avant-garde methodology that employs artificial intelligence (AI) to simulate the evolution of human language comprehension. Unlike previous models such as DialoGPT and Bard, which primarily focus on text generation, this approach amalgamates Natural Language Processing (NLP), cognitive linguistics, historical linguistics, and neuro-linguistic programming to create an all-encompassing depiction of linguistic metamorphosis. The AI model undergoes a phased evolutionary training protocol, with each stage representing a unique milestone in human language evolution. The ultimate objective is to unearth insights into human cognitive progression, unravel the intricacies of language, and explore its potential applications in academia and linguistics.
Introduction: Language, the bedrock of human cognition and communication, has undergone a fascinating journey. From rudimentary utterances to the sophisticated lexicon of today, language evolution is a testament to human ingenuity. While previous models like DialoGPT and Bard have made strides in generating historical text, this manuscript introduces an AI-driven simulation that seeks to emulate the entire spectrum of human linguistic evolution.
Methodology:
-
Tools & Libraries: Hugging Face Transformers, TensorFlow or PyTorch, Genetic Algorithms, tailor-made datasets, Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP) tools, and language complexity metrics.
-
Data Collection: Collaboration with linguists and historians is crucial for gathering data that reflects the diverse epochs of human language evolution.
-
Simulating Cognitive Evolution: The model incorporates elements that simulate cognitive evolution, including memory, focus, and critical thinking, anchored in cognitive linguistics research.
-
Model Initialization and Evolutionary Training: The model begins with a basic architecture and undergoes evolutionary training through genetic algorithms, where each epoch corresponds to a distinct chapter in human language evolution.
-
Language Complexity Metrics: Metrics such as lexicon size, sentence constructs, and grammatical paradigms quantify language complexity across epochs.
-
Integration of Neuro-Linguistic Programming (NLP): NLP principles are integrated to emulate human language processing and communication, adding a psychological dimension to the model.
Why This Method Shows Potential Over Other Models:
-
Holistic Approach: Unlike DialoGPT and Bard, which are primarily text generators, this model aims for a holistic simulation of linguistic evolution, encompassing cognitive aspects and complexity metrics.
-
Quantifying Language Complexity: The inclusion of language complexity metrics allows for a more objective analysis of the evolution, which is not a prominent feature in previous models.
-
Interdisciplinary Collaboration: The symbiosis with linguists and historians ensures the authenticity and diversity of the datasets, which is paramount for a realistic simulation.
-
Cognitive Emulation: By emulating cognitive evolution, the model can provide deeper insights into how language and cognition have co-evolved over time.
Conclusion: This AI-facilitated simulation represents a pioneering leap at the intersection of AI, linguistics, and cognitive science. With its evolutionary training, cognitive emulation, and complexity metrics, it offers a novel perspective on linguistic evolution. This endeavor holds immense potential and applications, particularly in education and historical linguistics, and stands as an advancement over existing models by providing amore comprehensive and quantifiable simulation of language evolution. The integration of cognitive aspects, historical data, and complexity metrics distinguishes this approach from previous models and paves the way for groundbreaking insights into the tapestry of language transformation through the ages.
Call to Action: Constructive input and reflections on this groundbreaking concept are eagerly solicited as it paves the way for subsequent advancements, including the selection of befitting language models. This venture is a foray into uncharted waters, bridging AI and linguistics. By recreating the linguistic evolution in a holistic manner, it unearths invaluable insights into human cognitive progression and the multifaceted nature of language. The model holds promise in the educational sphere, especially in the pedagogy of linguistics and history.
Generative AI vs. Predictive AI
Generative AI functionality is all about creating content. It combines algorithms and deep learning neural network techniques to generate content that is based on the patterns it observes in other content.
Generative AI is an emerging form of artificial intelligence that generates content, including text, images, video and music. Generative AI uses algorithms to analyze patterns in datasets to then mimic style or structure to replicate a wide array of content.
Predictive AI studies historical data, identifies patterns and makes predictions about the future that can better inform business decisions. Predictive AI’s value is shown in the ways it can detect data flow anomalies and extrapolate how they will play out in the future in terms of results or behavior; enhance business decisions by identifying a customer’s purchasing propensity as well as upsell potential; and improve business outcomes.
Creativity – generative AI is creative and produces things that have never existed before. Predictive AI lacks the element of content creation.
Inferring the future – predictive AI is all about using historical and current data to spot patterns and extrapolate potential futures. Generative AI also spots patterns but combines them into unique new forms.
Different algorithms – generative AI uses complex algorithms and deep learning to generate new content based on the data it is trained on. Predictive AI generally relies on statistical algorithms and machine learning to analyze data and make predictions.
Both generative AI and predictive AI use artificial intelligence algorithms to obtain their results. You can see this difference shown in how they are used. Generative AI generally finds a home in creative fields like art, music and fashion. Predictive AI is more commonly found in finance, healthcare and marketing – although there is plenty of overlap.
14 LLMs that aren’t ChatGPT
Llama
Facebook (now Meta) created this foundational LLM and then released it as part of its stated “commitment to open science.” Anyone can download Llama and use it as a foundation for creating more finely-tuned models for particular applications. (Alpaca and Vicuna were both built on top of Llama.) The model is also available in four different sizes. The smaller versions, with only 7 billion parameters, are already being used in unlikely places. One developer even claims to have Llama running on a Raspberry Pi, with just 4GB of RAM.
Alpaca
Several Stanford researchers took Meta’s Llama 7B and trained it on a set of prompts that mimic the instruction-following models like ChatGPT. This bit of fine-tuning produced Alpaca 7B, an LLM that opens up the knowledge encoded in the Llama LLM into something that the average person can access by asking questions and giving instructions. Some estimates suggest that the lightweight LLM can run on less than $600 worth of hardware.
Alpaca 7B’s creators are distributing the training set and the code that built it. Anyone can duplicate the model or create something new from a different set.
Vicuna
Another descendant of Llama is Vicuna from LMSYS.org. The Vicuna team gathered a training set of 70,000 different conversations from ShareGPT and paid particular attention to creating multi-round interactions and instruction-following capabilities. Available as either Vicuna-13b or Vicuna-7b, this LLM is among the most price-competitive open solutions for basic interactive chat.
NodePad
Not everyone is enthralled with the way that LLMs generate “linguistically accurate” text. The creators of NodePad believe that the quality of the text tends to distract users from double-checking the underlying facts. LLMs with nice UIs, “tend to unintentionally glorify the result making it more difficult for users to anticipate these problems.” NodePad is designed to nurture exploration and ideation without producing polished writing samples that users will barely skim. Results from this LLM appear as nodes and connections, like you see in many “mind mapping tools,” and not like finished writing. Users can tap the model’s encyclopedic knowledge for great ideas without getting lost in presentation.
Orca
The first generation of large language models succeeded by size, growing larger and larger over time. Orca, from a team of researchers at Microsoft, reverses that trend. The model uses only 13 billion parameters, making it possible to run on average machines. Orca’s developers achieved this feat by enhancing the training algorithm to use “explanation traces,” “step-by-step thought processes,” and “instructions.” Instead of just asking the AI to learn from raw material, Orca was given a training set designed to teach. In other words, just like humans, AIs learn faster when they’re not thrown into the deep end. The initial results are promising and Microsoft’s team offered benchmarks that suggest that the model performs as well as much larger models.
Jasper
The creators of Jasper didn’t want to build a wise generalist; they wanted a focused machine for creating content. Instead of just an open-ended chat session, the system offers more than 50 templates designed for particular tasks like crafting a real estate listing or writing product features for a site like Amazon. The paid versions are specifically aimed at businesses that want to create marketing copy with a consistent tone.
Claude
Anthropic created Claude to be a helpful assistant who can handle many of a business’s text-based chores, from research to customer service. In goes a prompt and out comes an answer. Anthropic deliberately allows long prompts to encourage more complex instructions, giving users more control over the results. Anthropic currently offers two versions: the full model called Claude-v1 and a cheaper, simplified one called Claude Instant, which is significantly less expensive. The first is for jobs that need more complex, structured reasoning while the second is faster and better for simple tasks like classification and moderation.
Cerebras
When specialized hardware and a general model co-evolve, you can end up with a very fast and efficient solution. Cerebras offers its LLM on Hugging Face in a variety of sizes from small (111 million parameters) to larger (13 billion parameters) for those who want to run it locally. Many, though, will want to use the cloud services, which run on Cerebras’s own wafer-scale integrated processors optimized for plowing through large training sets.
Falcon
The full-sized Falcon-40b and the smaller Falcon-7b were built by the Technology Innovation Institute (TII) in the United Arab Emirates. They trained the Falcon model on a large set of general examples from the RefinedWeb, with a focus on improving inference. Then, they turned around and released it with the Apache 2.0, making it one of the most open and unrestricted models available for experimentation.
ImageBind
Many think of Meta as a big company that dominates social media, but it’s also a powerful force in open source software development. Now that interest in AI is booming, it shouldn’t be a surprise that the company is starting to share many of its own innovations. ImageBind is a project that’s meant to show how AI can create many different types of data at once; in this case, text, audio, and video. In other words, generative AI can stitch together an entire imaginary world, if you let it.
Gorilla
You’ve probably been hearing a lot about using generative AI to write code. The results are often superficially impressive but deeply flawed on close examination. The syntax may be correct, but the API calls are all wrong, or they may even be directed at a function that doesn’t exist. Gorilla is an LLM that’s designed to do a better job with programming interfaces. Its creators started with Llama and then fine-tuned it with a focus on deeper programming details scraped directly from documentation. Gorilla’s team also offer its own API-centric set of benchmarks for testing success. That’s an important addition for programmers who are looking to rely on AIs for coding assistance.
Ora.ai
Ora is a system that allows users to create their own targeted chatbots that are optimized for a particular task. LibrarianGPT will try to answer any question with a direct passage from a book. Professor Carl Sagan, for example, is a bot that draws from all of Sagan’s writings so he can live on for billions and billions of years. You can create your own bot or use one of the hundreds created by others already.
AgentGPT
Another tool that stitches together all the code necessary for an application is AgentGPT. It’s designed to create agents that can be sent to tackle jobs like planning a vacation or write the code for a type of game. The source code for much of the tech stack is available under GPL 3.0. There’s also a running version available as a service.
FrugalGPT
This isn’t a different model as much as a careful strategy for finding the cheapest possible model to answer a particular question. The researchers who developed FrugalGPT recognized that many questions don’t need the biggest, most expensive model. Their algorithm starts with the simplest and moves up a list of LLMs in a cascade until it’s found a good answer. The researcher’s experiments suggest that this careful approach may save 98% of the cost because many questions do not actually need a sophisticated model.
Inflection announced that it is building one of the world’s largest AI-based supercomputers, and it looks like we finally have a glimpse of what it would be. It is reported that the Inflection supercomputer is equipped with 22,000 H100 GPUs, and based on analysis, it would contain almost 700 four-node racks of Intel Xeon CPUs. The supercomputer will utilize an astounding 31 Mega-Watts of power.
- Google AI researchers developed a new AI model that can translate languages with unprecedented accuracy
- A team of scientists at OpenAI created an AI that can play 57 Atari games at a superhuman level. The AI, called Five, was able to achieve superhuman scores on all 57 games, including some that have been notoriously difficult for AIs to master.
- A new AI-powered tool can help doctors diagnose cancer with greater accuracy. The tool, called DeepPath, uses AI to analyze medical images and identify cancer cells. It has been shown to be more accurate than human doctors at diagnosing cancer, and it could help to save lives.
- A group of researchers at MIT created an AI that can write different kinds of creative content, including poems, code, scripts, and musical pieces. The AI, called MuseNet, was trained on a massive dataset of text and code. It is still under development, but it has already produced some impressive results.
- A new AI-powered robot can learn to perform new tasks by watching humans. The robot, called LaMDA, was developed by Google AI. It can watch humans perform a task and then imitate them. This could have a major impact on the way we interact with robots in the future.
- OpenAI’s first global office will be in London. OpenAI, a non-profit research company that develops and studies large language models, has announced that its first global office will be located in London. The office will open in early 2024 and will focus on research and development in AI safety, ethics, and governance. (June 30, 2023)
source: r/artificialintelligence
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 03rd, 2023
What Machine Learning Reveals About Forming a Healthy Habit
Apple Extends Core ML, Create ML, and Vision Frameworks for iOS 17
10 Best Open-Source Deep Learning Tools to Know in 2023

TensorFlow:
TensorFlow is a widely-used open-source deep learning framework developed by Google Brain. Known for its flexibility and scalability, TensorFlow supports various applications, from image and speech recognition to natural language processing. Its ecosystem includes TensorFlow 2.0, TensorFlow.js, and TensorFlow Lite, making it a versatile tool for developing and deploying deep learning models.
PyTorch:
PyTorch, developed by Facebook’s AI Research lab, is a popular open-source deep learning library. It provides a dynamic computational graph that enables intuitive model development and efficient experimentation. PyTorch’s user-friendly interface, extensive community support, and seamless integration with Python have contributed to its rapid adoption among researchers and developers.
Keras:
Keras is a high-level neural networks API written in Python. It offers a user-friendly and modular approach to building deep learning models. Keras supports multiple backend engines, including TensorFlow, Theano, and CNTK, providing flexibility and compatibility with various hardware and software configurations.
MXNet:
MXNet, backed by Apache Software Foundation, is an open-source deep learning framework emphasizing scalability and efficiency. It offers a versatile programming interface that supports multiple languages, including Python, R, and Julia. MXNet’s unique feature is its ability to distribute computations across various devices, making it an excellent choice for training large-scale deep-learning models.
Caffe:
Caffe is a deep learning framework known for its speed and efficiency in image classification tasks. It is widely used in computer vision research and industry applications. With a clean and expressive architecture, Caffe provides a straightforward workflow for building, training, and deploying deep learning models.
Theano:
Theano is a Python library enabling efficient mathematical computations and manipulation of symbolic expressions. Although primarily focused on numerical computations, Theano’s deep learning capabilities have made it a preferred choice for researchers working on complex neural networks.
Torch:
Torch is a scientific computing framework that supports deep learning through its neural network library, Torch Neural Network (TNN). Its simple and intuitive interface and its ability to leverage the power of GPUs have attracted researchers and developers alike.
Chainer:
Chainer, a flexible and intuitive deep learning framework, is known for its “define-by-run” approach. With Chainer, developers can dynamically modify neural network architectures during runtime, facilitating rapid prototyping and experimentation.
DeepLearning4j:
DeepLearning4j, or DL4J, is an open-source deep-learning library for Java, Scala, and Clojure. It provides a rich set of tools and features, including distributed training, reinforcement learning, and natural language processing, making it suitable for enterprise-level AI applications.
Caffe2:
Caffe2, developed by Facebook AI Research, is a lightweight and efficient deep-learning framework for mobile and embedded devices. With its focus on performance and mobile deployment, Caffe2 empowers developers to build deep learning models for various edge computing scenarios.
Daily AI Update News from Microsoft, Humane, Nvidia, and Moonlander
Continuing with the exercise of sharing an easily digestible and smaller version of the main updates of the day in the world of AI.
Microsoft uses ChatGPT to instruct and interact with robots
– Microsoft Research presents an experimental study using OpenAI’s ChatGPT for robotics applications. It outlines a strategy that combines design principles for prompt engineering and the creation of a high-level function library that allows ChatGPT to adapt to different robotics tasks, simulators, and form factors.
-The study encompasses a range of tasks within the robotics domain to complex domains such as aerial navigation, manipulation, and embodied agents.
-It also released PromptCraft, an open-source platform where anyone can share examples of good prompting schemes for robotics applications.
Magic123 creates HQ 3D meshes from unposed images
– New research from Snap Inc. (and others) presents Magic123, a novel image-to-3D pipeline that uses a two-stage coarse-to-fine optimization process to produce high-quality high-resolution 3D geometry and textures. It generates photo-realistic 3D objects from a single unposed image.
Microsoft CoDi for any-to-any generation via composable diffusion
– Microsoft presents CoDi, a novel generative model capable of processing and simultaneously generating content across multiple modalities. It can handle many-to-many generation strategies, simultaneously generating any mixture of output modalities and single-to-single modality generation.
Humane reveals the name of its first device, the Humane Ai Pin
– It is a standalone device with a software platform that harnesses the power of AI to enable innovative personal computing experiences.
Microsoft rolls out preview of Windows Copilot with Bing Chat
– Microsoft is giving early users a sneak peek at its AI assistant for Windows 11. The program is available as part of an update in the Windows Insider Dev Channel.
Nvidia acquired an AI startup that shrinks ML models
– Nvidia in February quietly acquired two-year-old OmniML, whose software helped shrink machine-learning models so they could run on devices rather than in the cloud.
Moonlander launches AI-based platform for immersive 3D game development
– The platform leverages updated LLMs, ML algorithms, and generative diffusion models to streamline the game development pipeline. The goal is to empower developers to easily design and generate high-quality immersive experiences, 3D environments, mechanics, and animations. It includes a “text-2-game” feature.
Greg Marston, a British voice actor, signed away his voice rights unknowingly in 2005. This contract now allows IBM to sell his voice to third parties capable of cloning it using AI. Marston’s situation is unique because he competes in the same marketplace against his AI-generated voice clone.
Commercialisation of Generative AI and Its Impact: The rapid commercialisation of generative AI, which can reproduce human-like voices, threatens the careers of artists relying on their voices. This is primarily due to potentially exploitative contracts and data-scraping methods. Equity, a UK trade union for performing artists, confirms having received multiple complaints related to AI exploitation and scams.
Prevalent Exploitative Practices: Artists often fall prey to deceptive practices aimed at collecting voice data for AI, such as fake casting calls. Contracts for voice jobs sometimes contain hidden AI voice synthesis clauses that artists may not fully understand.
The Compensation and AI Rights Debate: Critics argue that the evolution of AI technologies is causing a significant wealth transfer from the creative sector to the tech industry. In response, Equity calls for contracts with a limited duration and explicit consent requirements for AI cloning. Presently, the legal recourse available to artists is limited, with only data privacy laws providing some regulation.
Effects on Working Artists: Changes in the industry make it increasingly challenging for artists to sustain their careers. To support artists, Equity is pushing for new rights and providing resources to help them navigate the evolving AI landscape.
A few Hours ago, Senate majority leader Chuck Schumer revealed a “grand strategy” for AI regulation in the US. Here is what it could mean for the future of AI legislation.
If you want to stay on top of all the AI developments, look here first. But all of the information has been extracted on Reddit for your convenience.
3 Important Highlights:
-
Protection of Innovation: Schumer stressed innovation as the “north star” of U.S. AI strategy, indicating that lawmakers will work closely with tech CEOs in drafting regulation, potentially responding to EU regulations that critics claim hinder innovation.
-
Section 230 Debate: The debate over Section 230 reform: “The law that shields tech companies from being sued over user-generated content” is getting bigger in AI. Whether tech companies should be held accountable for AI-generated content is a big question that could have a significant impact on the AI landscape.
-
Democratic Values: Both Schumer and President Biden emphasize that AI must align with democratic values. This is the US confirming their narrative opposite to China’s who thinks that “outputs of generative AI must reflect communist values.”
How this affects you:
– Social media could undergo change with the implementation of Section 230 and this would directly impact your experience. Similar to the effects of Reddit’s API changes these changes could be sudden and impactful.
– Schumer’s strategy and the increasing interest of AI policy from both the Republicans and Democrats may result in faster and safer AI regulation in the U.S.
– The call for AI to align with democratic values might also influence global AI governance norms, especially in relation to China.
Let me know how you think our government is handling the situation at hand
That’s it!
Source: (link)
Mozilla’s new feature, AI Help, intended to assist users in finding relevant information swiftly, is under criticism. Instead of proving helpful, it is delivering inaccurate and misleading information, causing a trust deficit among the users.
What’s AI Help?
AI Help is an assistive service, based on OpenAI’s ChatGPT, launched by Mozilla on its MDN platform. It’s designed to help web developers search for information faster. It’s available for free and paid MDN Plus account users.
-
The feature generates a summary of relevant documentation when a question is asked on MDN.
-
AI Help includes AI Explain, a button that prompts the chatbot to weigh in on the current web page text.
Problem with AI Help:
However, AI Help has been criticized for providing incorrect information.
-
A developer, Eevee, noted that the AI often generates inaccurate advice.
-
Other users chimed in with criticisms, claiming that the AI contradicts itself, misidentifies CSS functions, and generally doesn’t understand CSS.
-
There are fears that the inclusion of inaccurate AI-generated information could lead to an over-reliance on unreliable text generation and erode trust in the MDN platform.
The spread of AI narratives, often fueled by interest, ignorance, and opportunism, can create a storm of misinformation. This can involve:
-
Exaggerations that distract from policy-making that addresses AI risks.
-
Inaccurate comparisons of AI with highly destructive technology like nuclear weapons.
-
Ignoring the importance of careful regulation over outright bans.
AI vs Nuclear Weapons: AI and nuclear weapons, while both consequential, are fundamentally different:
-
Nuclear weapons are a specific destructive technology, while AI spans a broad spectrum of applications.
-
Nuclear weapons are entirely controlled by nation-states, while AI can be used by private citizens.
-
Therefore, regulatory approaches for the two technologies differ significantly.
-
Analogies likening AI to nuclear weapons can lead to inaccurate regulatory suggestions.
Problem with Extinction-level Risks: Highlighting AI as an extinction-level threat can derail productive conversations about AI governance:
-
Discussions should focus on more likely risks such as cyberattacks, disinformation campaigns, or misuse by malicious actors.
-
Labeling AI as an “extinction-level” threat promotes alarmism instead of addressing these challenges.
Misguided Calls for a “Manhattan Project” for AI Safety: The call for a large-scale government project to address AI safety misunderstands the issue:
-
AI safety covers a wide range of concepts, requiring a nuanced approach rather than a singular goal.
-
Diverse opinions among researchers on AI safety definitions and approaches call for careful discussion and exploration.
-
Government-backed mega-projects cannot provide the needed freedom of exploration.
The latest Windows 11 Insider Preview Build 23493 has introduced two main features.
The first one is a preview of Windows Copilot, a feature that responds to voice commands for tasks like changing to dark mode or taking screenshots, and offers an unobtrusive sidebar interface. This preview is available to Windows Insiders in the Dev Channel and will continue to be refined based on feedback. But then, not all features shown at the Build conference for Windows Copilot are included in this early preview.
The second feature is a new Settings homepage that provides a personalized experience with interactive cards representing various device and account settings. These cards offer relevant information and controls at your fingertips. Currently, there are seven cards available, including cards for recommended settings, cloud storage, account recovery, personalization, Microsoft 365, Xbox, and Bluetooth devices. More cards will be added in future updates
Advantages of these could be
•Voice Command Convenience: Perform tasks through voice commands.
•Dynamic Interface: Accessible sidebar doesn’t obstruct desktop content.
•Contextual Assistance: Generates responses based on context.
•Feedback Provision: Directly submit feedback on issues.
•UI Personalization: Quick access to preferred settings.
•Improved Navigation: Easy access to Windows settings.
•Active Learning: Continual refinement based on user feedback.
•Responsible AI: Adherence to Microsoft’s commitment to responsible AI.
•Customizable Experience: Tailored responses and recommendations.
•Integration: Unifies settings, apps, and accounts management.
•Streamlined Operations: Simplify routine tasks with voice commands through Windows Copilot.
•Dynamic Settings: Adapt device settings to specific user patterns.
•Cloud Management: Overview of cloud storage use and capacity warnings.
•Account Security: Enhanced Microsoft account recovery options.
•Customization: Easy access to update background themes or color modes.
•Subscription Management: Directly manage Microsoft 365 subscriptions in Settings.
•Gaming Subscription: View and manage Xbox subscription status in Settings.
•Device Connectivity: Manage connected Bluetooth devices directly from Settings
Windows Copilot is available to Windows Insiders in the Dev Channel. You need to have Windows Build 23493 or higher in the Dev Channel, and Microsoft Edge version 115.0.1901.150 or higher to use Copilot.
Researchers have developed an AI model capable of creating a functional CPU in less than five hours, promising to revolutionize the semiconductor industry by making the design process faster and more efficient.
Innovation in CPU Design: An artificial intelligence model has been developed that can design a functioning CPU in approximately five hours. This achievement marks a stark contrast to the manual process that typically takes years.
-
The innovation was presented in a research paper by a group of 19 Chinese computer processor researchers.
-
They propose that their approach could lead to the development of self-evolving machines and a significant shift in the conventional CPU design process.
RISC-V 32IA and Linux Compatibility: The AI-designed CPU utilizes an AI instruction set known as RISC-V 32IA, and it can successfully run the Linux operating system (kernel 5.15).
-
Researchers reported that the CPU’s performance is comparable to the Intel 80486SX CPU, designed by humans in 1991.
-
The aim of the researchers is not just to surpass the performance of the latest human-designed CPUs, but also to shape the future of computing.
Efficiency and Accuracy of the AI Design Process: The AI-driven design process was found to be drastically more efficient and accurate than the traditional human-involved design process.
-
The AI design approach cuts the design cycle by about 1,000 times, eliminating the need for manual programming and verification, which usually consume 60-80% of the design time and resources.
-
The CPU designed by the AI showed an impressive accuracy of 99.99% during validation tests.
-
The physical design of the chip uses scripts at 65nm technology, enabling the creation of the layout for fabrication.
Google’s policy update gives them explicit permission to scrape virtually any data posted online to develop and improve their AI tools. Their updated policy cites the use of public information to train their AI models and develop products like Google Translate and Cloud AI capabilities.
-
The language change specifies “AI models” instead of “language models”, previously used in the older policy.
-
The new policy includes not only Google Translate, but also mentions Bard and Cloud AI.
-
This is an uncommon clause for privacy policies, which typically describe the use of information posted on the company’s own services.
Implications for Privacy and Data Use: This change raises fresh privacy concerns, requiring a shift in how we perceive our online activities. It’s no longer solely about who can see the information, but also how it can be used. This brings into focus questions about how chatbots like Bard and ChatGPT use publicly available information, potentially reproducing or transforming words from old blog posts or reviews.
Potential Legal Issues and Repercussions: There are legal uncertainties about the use of publicly available information by AI systems. Companies such as Google and OpenAI have scraped large parts of the internet to train their AI models, raising questions about intellectual property rights. Over the next few years, the courts will likely have to tackle these previously unexplored copyright issues.
Impact on User Experience and Service Providers: Elon Musk blamed several Twitter mishaps on the necessity to prevent data scraping, a claim most IT experts link more to technical or management failures. On Reddit, the API changes have led to significant backlash from the site’s volunteer moderators. This has resulted in a major protest, shutting down large parts of Reddit, and may lead to lasting changes if the disgruntled moderators decide to step down.
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 02nd, 2023
Google is hosting the first ever “Machine UN-learning Challenge.” Yes you read it rightMachine UN-learning is the Art of Forgetting.
Key Takeaways:
– Google is launching a competition for machine “unlearning”, aiming to purge sensitive information from AI systems, aligning them with international data regulation norms. The event is open to anyone and runs from mid-July to mid-September. You can access the starter kit here.
– Machine learning, a crucial part of AI, provides solutions to intricate issues, like generating new content, forecasting outcomes, or resolving complex questions. However, it brings its share of challenges such as data misuse, cybercrime, and data privacy issues.
– Google’s goal is to instill “selective amnesia” in its AI systems. Which would allow the AI to erase specific data without compromising their efficiency Read full article here.
Why you should know:
-
Google aims to give people like you and me more control over our personal data.
-
The tech giant is also reacting to regulations such as Europe’s GDPR, and the EU’s upcoming AI Act, which empower individuals to demand data removal from companies.
-
Machine unlearning would allow individuals to wipe out their information from an algorithm, protecting them from AI threats while also preventing others from misusing their data.
This is big and definitely a step in the right direction, IMO. The only question is: will the data truly be erased from memory or not?
Before you go: I run one of the fastest growing AI newsletters that gives you daily actionable insight on all things AI. If you liked this, you would love the content in this tool!
Prominent international brands are unintentionally funding low-quality AI content platforms. Major banks, consumer tech companies, and a Silicon Valley platform are some of the key contributors. Their advertising efforts indirectly fund these platforms, which mainly rely on programmatic advertising revenue.
-
NewsGuard identified hundreds of Fortune 500 companies unknowingly advertising on these sites.
-
The financial support from these companies boosts the financial incentive of low-quality AI content creators.
Emergence of AI Content Farms: AI tools are making it easier to set up and fill websites with massive amounts of content. OpenAI’s ChatGPT is a tool used to generate text on a large scale, which has contributed to the rise of these low-quality content farms.
-
The scale of these operations is significant, with some websites generating hundreds of articles a day.
-
The low quality and potential for misinformation does not deter these operations, and the ads from legitimate companies could lend undeserved credibility.
Google’s Role: Google and its advertising arm play a crucial role in the viability of the AI spam business model. Over 90% of ads on these low-quality websites were served by Google Ads, which indicates a problem in Google’s ad policy enforcement.
Cryptocurrency mining companies are repurposing their high-end chips to meet the growing demand in the artificial intelligence industry.
Crypto Mining Shift to AI: Many machines, originally meant for mining digital currencies, sat idle due to changes in the crypto market.
AI and ‘Dark GPUs’: As the demand for GPUs increases, startups are beginning to leverage dormant hardware originally designed for cryptocurrency mining. The term “dark GPUs” refers to GPUs from these idle machines, which are now being rebooted to handle AI workloads.
AI Infrastructure: Revamped mining rigs offer a more affordable and accessible AI infrastructure as compared to offerings from major cloud companies. These machines are often utilized by startups and universities struggling to find computing power elsewhere. The increased demand for AI software and user interest have pushed even the biggest tech companies to their limits.
-
Large cloud providers such as Microsoft and Amazon are at near-full capacity.
-
This high demand has created opportunities for companies with repurposed mining hardware.
Repurposing Opportunities: Changes in the method of minting one cryptocurrency have led to a large supply of used GPUs. These chips are now being repurposed to train AI models.
AI-generated images can be made unrecognizable as fakes by adding grain or pixelated noise, increasing their potential use in spreading disinformation, particularly in influencing election campaigns.
Image Falsification and Disinformation: AI-created images have been employed for spreading misinformation online, with instances ranging from falsified campaign ads to theft of artworks.
-
The rampant misuse of AI-generated imagery in spreading disinformation has become a pressing issue.
-
Notable examples include deceptive campaign ads and plagiarized art pieces.
Grain Addition to Misguide AI Detectors: Adding grain to AI-generated images makes them hard to detect as fakes, fooling AI detection software.
-
AI detection software, a major tool against AI-generated disinformation, is tricked by simply adding grain or pixelated noise to the images.
-
The grain, or texture, alters the clarity of AI-created photos, causing the detection software’s accuracy to plummet from 99% to just 3.3%.
-
Even sophisticated software like Hive struggles to correctly identify pixelated AI-generated photos.
Implications for Misinformation Control: The susceptibility of detection software to such simple manipulation raises concerns about relying on it as the primary defense against disinformation.
The FTC has expressed concerns about potential monopolies and anti-competitive practices within the generative AI sector, highlighting the dependencies on large data sets, specialized expertise, and advanced computing power that could be manipulated by dominant entities to suppress competition.
Concerns about Generative AI: The FTC believes that the generative AI market has potential anti-competitive issues. Some key resources, like large data sets, expert engineers, and high-performance computing power, are crucial for AI development. If these resources are monopolized, it could lead to competition suppression.
-
The FTC warned that monopolization could affect the generative AI markets.
-
Companies need both engineering and professional talent to develop and deploy AI products.
-
The scarcity of such talent may lead to anti-competitive practices, such as locking-in workers.
Anti-Competitive Practices: Some companies could resort to anti-competitive measures, such as making employees sign non-compete agreements. The FTC is wary of tech companies that force these agreements, as it could threaten competition.
-
Non-compete agreements could deter employees from joining rival firms, hence, reducing competition.
-
Unfair practices like bundling, tying, exclusive dealing, or discriminatory behavior could be used by incumbents to maintain dominance.
Computational Power and Potential Bias: Generative AI systems require significant computational resources, which can be expensive and controlled by a few firms, leading to potential anti-competitive practices. The FTC gave an example of Microsoft’s exclusive partnership with OpenAI, which could give OpenAI a competitive advantage.
-
High computational resources required for AI can lead to monopolistic control.
-
An exclusive provider can potentially manipulate pricing, performance, and priority to favor certain companies over others.
We humans essentially think and feel. Thinking is merely a tool. Feeling is what it intends to serve. Most fundamentally our human experience, or the quality of our lives, is emotional.
It’s not that thinking is unimportant. It’s how we survive and emotionally thrive. Its ability to figure out what is in our best interest and help us achieve it is how it serves us so well.
Happiness is the quintessential human emotion. Being complex organisms biologically designed to seek pleasure and avoid pain, happiness is our ultimate goal in life. This is not just our biology talking. When researchers ask us what we most want from life, and they’ve been asking us this question for decades, our number one answer is always happiness.
How about goodness or virtue? British utilitarian philosopher John Locke defined it as what creates happiness. This makes a lot of sense. Generally speaking we consider something good if it makes us happy and bad if it doesn’t.
So where does AI fit into all of this? We humans aren’t all that good at either being all that good or all that happy. Here are a couple of examples that illustrate this point.
If someone were to interview a person living in 500 CE and describe all the wonders of today’s world like electricity and indoor heating and airplanes and computer technology, they would surely suppose that everyone alive today was very, very happy.
In the United States we are about three times richer per capita today then we were in 1950, but we are no more happy now than we were back then.
What went wrong? Concisely explained we have for the most part collectively devoted our thinking to pretty much everything but our happiness and the goodness that creates it. That explains why we live in such an amazing world but depression and alienation are such common experiences.
How can AI help us with all of this? Let’s move a few years into the future to when AGIs begins to create improved iterations of themselves leading to ASIs. Super intelligent AIs will soon enough be hundreds if not thousands of times more intelligent than we are. Being so smart, they will have completely figured out all that I have set forth above, and, aligned as they will have been to protecting and advancing our highest human values, they will go about reminding us, as persistently as they need to, that happiness is what we really want and that goodness is our surest way to get there. But helping us get those priorities right will only be the first step.
Today we learn how to be good and how to be happy both through example and direct instruction. Our parents and siblings and other people help us understand how to be good and how to be happy. But of course we human beings are not all that smart when compared to the ASIs that we will all soon have at our disposal.
So imagine an army of ASIs unleashed on the human population with the explicit goal of teaching every person on the planet to be a much better and happier person. Were that to happen at the beginning of any given year, by the end of that year I guarantee you that every person on the planet would be super good and totally blissed out. Neither goodness nor happiness is rocket science, and we would all have super geniuses as our coaches. We would all take to this like fish to water.
So, yes, AI will transform our external environment in unimaginable ways. It will revolutionize medicine so as to keep us much healthier than we are today. It will keep us all increasingly amazed with each new development, invention and discovery. But its greatest gift to us will have been that it will have made as much, much better and happier people.
I imagine that some in this community will not find the above so comforting. They may say that we can’t really define either goodness or happiness, and that it’s all subjective anyway. What I’ve written may make them angry, and they may resort to insults and disparagement. But that will all be their immediate emotional knee jerk reaction. If and when they take the time to deeply reflect on the above – and I very much hope they will – they will understand it to be both true and helpful.
So let’s celebrate how much more virtuous and happy we will all soon be because of AI while we’re also busy being perpetually amazed by the wonderful, unbelievable, ways that it will transform the world around us.
Daily AI News 7/2/2023
Moody’s Corp. is using Microsoft Corp. and OpenAI to create an artificial intelligence assistant that will help customers of the credit rating and research firm analyze reams of information needed to make assessments of risk. “Moody’s Research Assistant” will roll out to customers including analysts, bankers, advisers, researchers, and investors.
Unity announces the release of Muse: A Text-to-Video Games Platform that lets you create textures, sprites, and animations with natural languages.
The New York State Legislature passed a number of bills this session, including one that would ban “deepfake” images online. Deepfakes are images or videos that have been manipulated to make it appear as if someone is saying or doing something they never said or did. The bill would make it illegal to create or distribute deepfakes that are used to harm or humiliate someone.
As per Times Now Report, Reece Wiench, 23, and Deyton Truitt, 26, decided to break away from tradition by holding a unique wedding ceremony. Instead of a physical human officiant, the couple opted for a machine featuring ChatGPT. The machine, adorned with a mask resembling the famous C-3PO from Star Wars, took center stage.
8 ways Google Lens can help make your life easier;
Navigating the Revolutionary Trends of July 2023: July 01st, 2023
Top 5 entry-level machine learning jobs
Machine learning engineer
- The role: Machine learning engineers develop, deploy and maintain machine learning models and systems.
- Required skills: Strong programming skills (Python, R, etc.), knowledge of machine learning algorithms and frameworks, data preprocessing, model evaluation, and deployment.
- Degree: Bachelor’s or higher in computer science, data science or a related field.
- Job opportunities: Machine learning engineers can work in industries such as technology, finance, healthcare and e-commerce. Opportunities are available in both established companies and startups.
Data scientist
- The role: Data scientists analyze and interpret complex data sets to derive insights and build predictive models.
- Required skills: Proficiency in programming (Python, R, etc.), statistical analysis, data visualization, machine learning algorithms and data manipulation.
- Degree: Bachelor’s or higher in data science, computer science, statistics or a related field.
- Job opportunities: Data scientists are in demand across various industries, including finance, healthcare, marketing and technology. Companies ranging from startups to large enterprises actively seek data science talent.
AI researcher
- The role: AI researchers focus on advancing the field of artificial intelligence through research and development.
- Required skills: Strong knowledge of machine learning algorithms, deep learning frameworks — e.g., TensorFlow, PyTorch — programming skills, data analysis and problem-solving abilities.
- Degree: Master’s or Ph.D. in computer science, artificial intelligence or a related field.
- Job opportunities: AI researchers can work in academia or research institutions or join research teams within technology companies. Positions are available in both public and private sectors.
Machine learning consultant
- The role: Machine learning consultants provide expertise and guidance to businesses in implementing machine learning solutions.
- Required skills: Solid understanding of machine learning concepts, data analysis, project management, communication skills and ability to translate business requirements into technical solutions.
- Degree: Bachelor’s or higher in computer science, data science, business analytics or a related field.
- Job opportunities: Machine learning consultants can work in consulting firms, technology companies or as independent consultants. Opportunities exist across various industries seeking to adopt machine learning.
Data engineer
- The role: Data engineers design and maintain data infrastructure, ensuring efficient storage, processing and retrieval of large data sets.
- Required skills: Proficiency in programming (Python, SQL, etc.), database systems, data pipelines, cloud platforms — e.g., AWS, Azure, GCP — and data warehousing.
- Degree: Bachelor’s or higher in computer science, software engineering or a related field.
- Job opportunities: Data engineers are in high demand across industries, particularly in technology, finance and healthcare. Both established companies and startups require data engineering expertise to handle large volumes of data.
7 Ways AI/ML Can Influence Web3
1. Enhanced Data Analysis
2. Smart Contract Automation
3. Fraud Detection and Security
4. Decentralized Governance
5. Personalized User Experiences
6. Privacy and Data Ownership
7. Autonomous Agents and Intelligent Contracts
-
A man in Monrovia, California, has created a ChatGPT bot subscription service to annoy and waste the time of telemarketers.
-
Using bots powered by ChatGPT and a voice cloner, the service keeps telemarketing scammers on the line for as long as possible, costing them money.
-
For a $25-per-year subscription, users can enable call-forwarding to a unique number and let the bots handle the robocalls or create a conference call to listen to the scammers’ reactions.
-
The service offers various voices and bot personalities, such as an elderly curmudgeon or a stay-at-home mom, to engage with the scammers.
-
While the voices may sound human, the phrases can be repetitive and unnatural, but they are effective in keeping scammers on the line for up to 15 minutes.
How a redditor using ChatGPT to get him through university
The student is currently underway with his electrical engineering degree, he is not the sharpest tool in the shed but discovering ChatGPT some months ago has been a game changer for studying.
Here’s some ways he has been using it:
-
Copying his unit outline into the chat and then asking GPT to write him a practice exam based on the material, he then sends back his answers and have GPT grade it and provide feedback. The questions it generated were very similar if not the same as some he got in the real exam!
-
Sending it his notes and getting it to quiz him.
-
When dealing with complex equations and he is not sure how the lecturer arrived at the answer hecan ask GPT to break it down step by step as if he was a pre-schooler.
-
More recently with the plugins add-on to ChatGPT he has been using ‘AskYourPDF’ plugin to send it his topic slides for the week and then using the ‘Tutor’ plugin to have it setup a tutor plan for that week and have it act as a personal tutor! Although he doesn’t do this every topic but sometimes It is great if the lecturer is not explaining the material easily.
-
Also using the ‘AskYourPDF’ plugin to have it read topic slides and provide easy to understand notes on the complex information in the slides.
It is important to note that while ChatGPT is impressive it can sometimes be inaccurate, so be careful not to follow what it says blindly when asking it direct questions relating to your field of study make sure to cross reference its answers if your unsure!
Elon Musk blames data scraping by AI startups for his new paywalls on reading tweets
Elon Musk has instituted limitations on the number of posts Twitter users can access per day. Musk cited the heavy data scraping by AI companies as a strain on the user experience, prompting the decision. In addition, Musk has been implementing monetization strategies, while dealing with repercussions of previous controversial decisions, like mass layoffs.
New Post Limitations:
Elon Musk has imposed temporary restrictions on the number of Twitter posts people can view in a day. This is broken down into:
-
Unverified accounts having a limit of 600 posts per day
-
New unverified accounts being able to see only 300 posts per day
-
Verified accounts being permitted a maximum of 6,000 posts daily Musk later hinted at an increase in these limits soon.
Motivation Behind the Change:
According to Musk, the drastic measure was prompted by the intensive data scraping activities by hundreds of organizations. This over-aggressive data mining was impacting the user experience on Twitter. Musk specifically pointed at companies using the data to train large language models (LLMs) as the main culprits.
Healthcare company Insilico Medicine has made a new medicine completely by using AI. This medicine is for a lung disease called idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, which can be very serious if not treated. This is the first time that AI has been used to make a whole medicine, from start to finish.
Why is This Medicine Special?: This medicine is special because it’s the first one ever to be completely made by AI and is now being tested on people. This medicine was not only found by AI, but it was also designed by AI.
-
Other medicines have been designed by AI, but this is the first one that AI found and designed all by itself.
-
It’s now being tested on people to see how well it works.
How Does it Help People?: This medicine was created in 2020 to help people with this lung disease because the current medicines only slow the disease down and can have bad side effects.
-
They wanted to create a really good medicine that can do more than just slow down the disease.
-
They chose this lung disease because it is linked to getting older.
What Other Medicines are They Making?: Insilico is also using AI to make a Covid-19 medicine and a cancer medicine. This shows that the company is not just using AI to find medicines, but also to create them.
-
They have a medicine for Covid-19 that’s being tested and a cancer medicine that just got approval to start being tested.
-
Making medicines helps to show that their AI really works.
In May and June, Sam Altman, the CEO of OpenAI, embarked on a four-week tour across 25 cities on six continents. The goal was to engage directly with users, developers, policymakers, and the general public interacting with OpenAI’s technology.
To get the latest information on AI, look here first. All of the information has been extracted to Reddit for your convenience.
Key Takeaways:
Sam Altman was blown away by the use cases of ChatGPT. From high school students in Nigeria using ChatGPT for simplified learning to civil servants in Singapore leveraging OpenAI tools for efficient public service delivery, AI’s reach is expanding thanks to Open AI
Sam Altman found that countries worldwide share similar hopes and concerns about AI. With the common fear of AI safetyPolicymakers are heavily invested in AI.
Across the globe, leaders are focused on ensuring the safe deployment of AI tools, maximizing their benefits, and mitigating potential risks. There is significant interest in a continuous dialogue with leading AI labs and a global framework to manage future powerful AI systems.
Why you should care:
People around the world want clarity on OpenAI’s core values (probably including you). The tour provided a platform to emphasize that customer data is not used in training and that users can opt-out easily.
Despite this claim, data isn’t used in training. Open AI is facing a class action lawsuit for stealing data and using it to train its models. More about that here.
Open AI’s next steps:
“Making their products more useful, impactful, and accessible.”
“Further developing best practices for governing highly capable foundation models.”
“Working to unlock AI’s benefits.”
Source (Open AI)
Tweet: (Open AI)